Unveiling the Mediterranean Climate: A Map of Sunshine and Diversity
Related Articles: Unveiling the Mediterranean Climate: A Map of Sunshine and Diversity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Mediterranean Climate: A Map of Sunshine and Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Mediterranean Climate: A Map of Sunshine and Diversity

The Mediterranean climate, a tapestry woven from warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters, graces a select band of regions across the globe. This unique climate, characterized by its distinct seasonal rhythm, has shaped the landscapes, ecosystems, and human cultures of these regions in profound ways. A Mediterranean climate map, a visual representation of this climatic phenomenon, serves as a key to understanding the distribution, characteristics, and implications of this fascinating climate zone.
Understanding the Mediterranean Climate Map
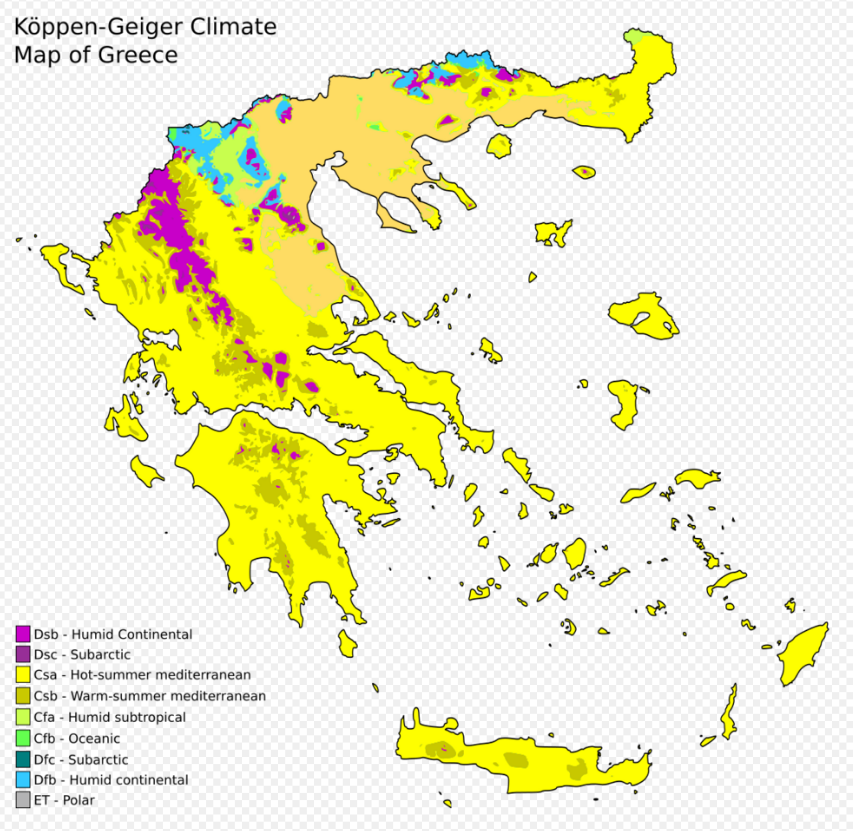
The Mediterranean climate map, often depicted on global climate maps, visually illustrates the distribution of this climate type across the world. It highlights the regions where summers are hot and dry, with average temperatures ranging from 20°C to 30°C, and winters are mild and wet, with temperatures rarely dipping below freezing. These regions typically receive most of their annual rainfall during the winter months, often associated with frontal systems originating from the north.
Key Features of the Mediterranean Climate
The Mediterranean climate is not merely defined by its temperature and rainfall patterns but also by a series of other distinctive features:
- Distinct Seasons: The clear division between the dry, hot summers and the wet, mild winters provides a strong seasonal rhythm that influences vegetation, agricultural practices, and even cultural traditions.
- Summer Drought: The extended dry period during summer is a defining characteristic, leading to drought-resistant vegetation and adaptation strategies among local flora and fauna.
- Mild Winters: The relatively mild winters, with temperatures rarely falling below freezing, allow for year-round agricultural activity in some regions and support a diverse range of plant and animal life.
- High Sunshine Hours: The Mediterranean climate is known for its abundant sunshine, often exceeding 2,500 hours per year. This abundant sunlight fuels the growth of Mediterranean vegetation and contributes to the region’s characteristic warm, sunny climate.
- Fire Risk: The combination of dry vegetation and hot, dry summers creates a heightened risk of wildfires, a natural phenomenon that plays a significant role in shaping Mediterranean ecosystems.
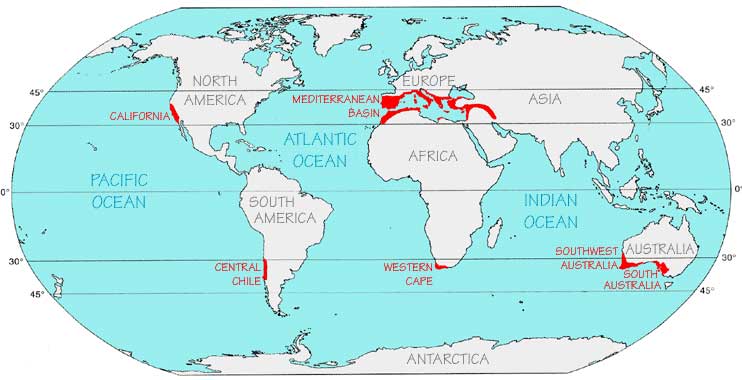
Global Distribution of the Mediterranean Climate
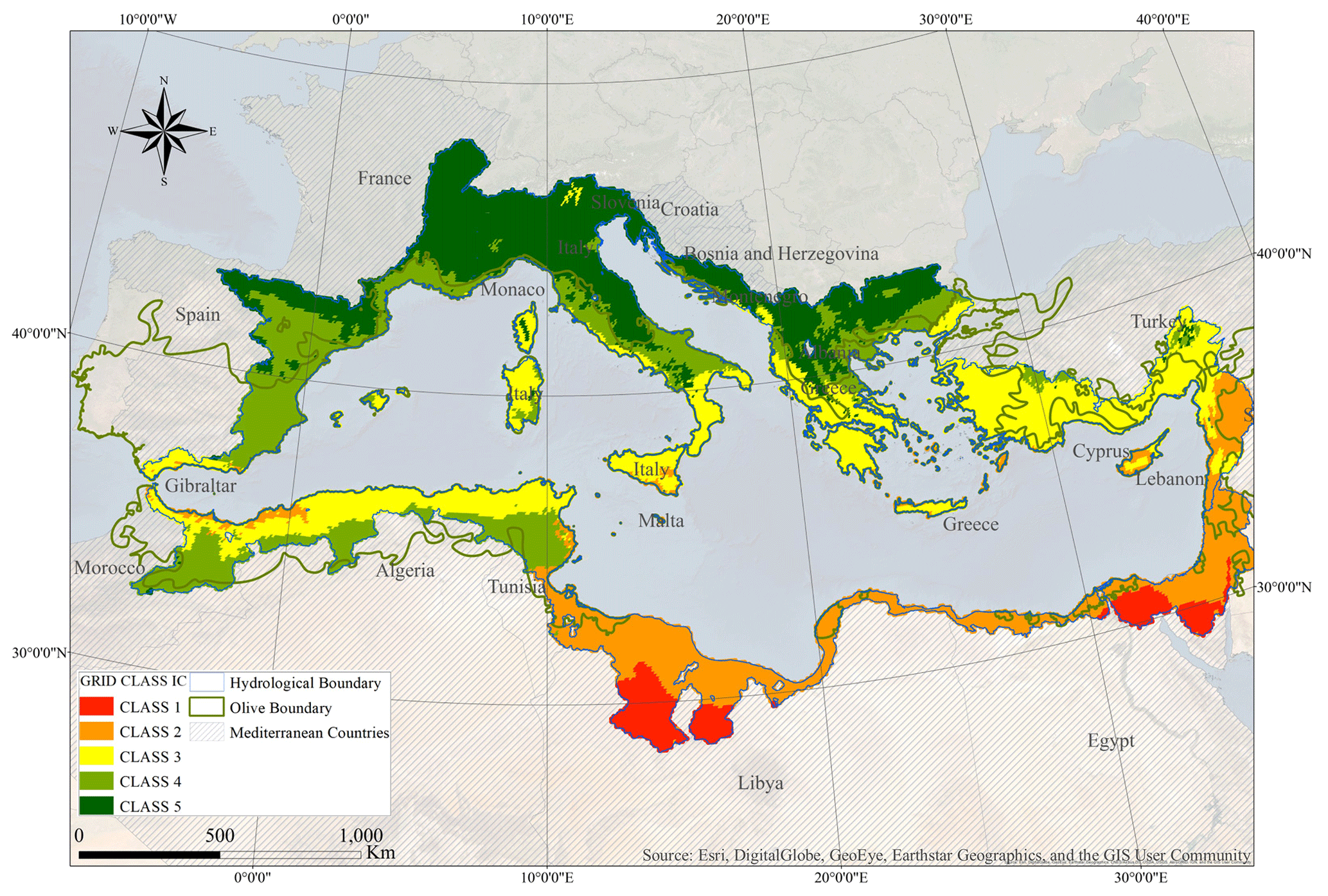
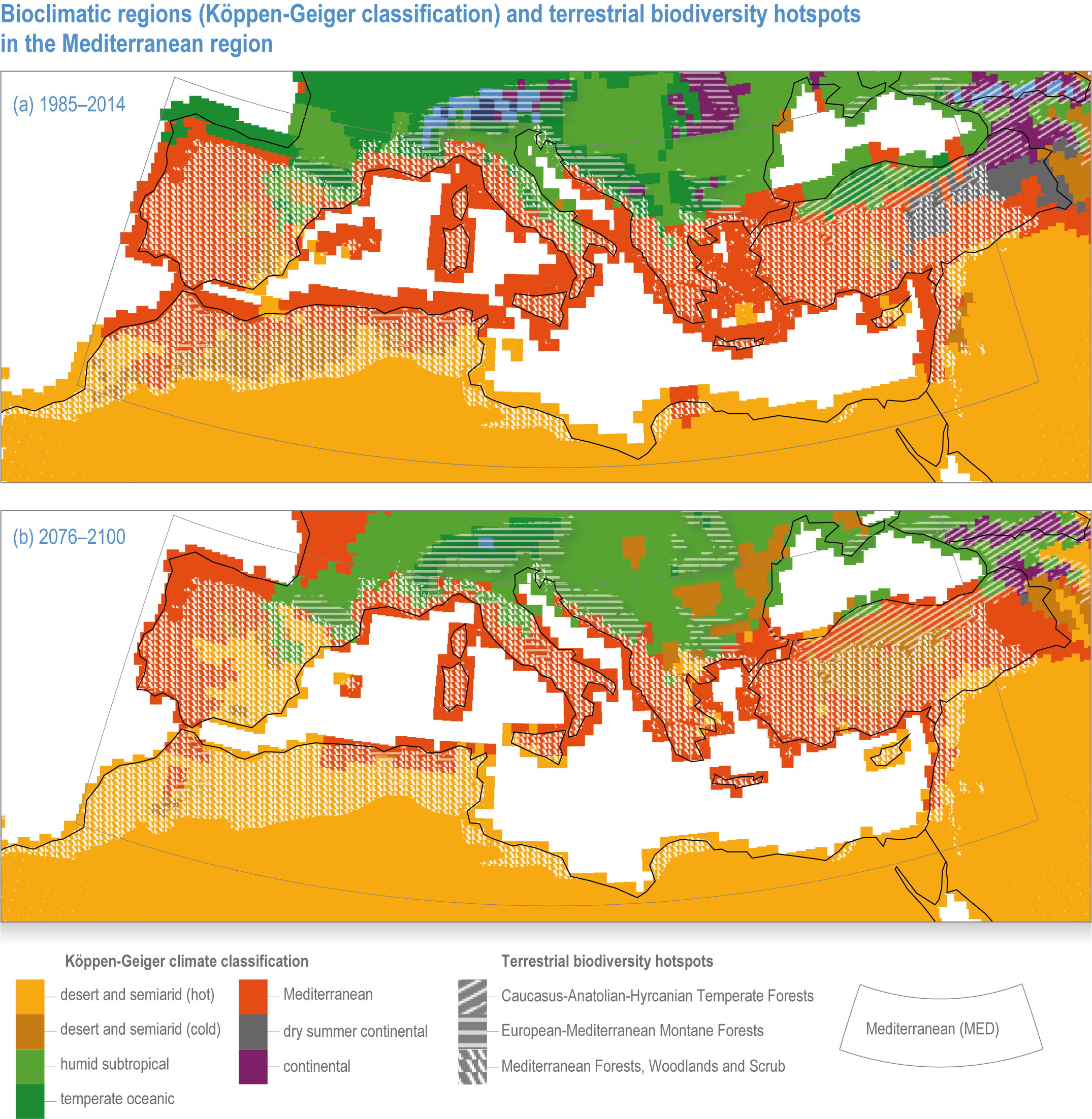
The Mediterranean climate map reveals a fascinating distribution pattern, with five distinct regions showcasing this climate type:
- The Mediterranean Basin: The namesake region, encompassing countries like Italy, Greece, Spain, Portugal, and parts of France, Turkey, and North Africa, is the most well-known example of the Mediterranean climate.
- California: The western coast of the United States, from Southern California to the San Francisco Bay Area, exhibits a Mediterranean climate, characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
- Central Chile: The central region of Chile, stretching from Valparaíso to Concepción, experiences a Mediterranean climate, with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
- Southwestern Australia: The southwestern corner of Australia, including Perth and surrounding areas, displays a Mediterranean climate, characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
- South Africa’s Cape Region: The southwestern tip of South Africa, known as the Cape Floral Kingdom, experiences a Mediterranean climate, with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
The Importance of the Mediterranean Climate Map
The Mediterranean climate map holds significant importance for a variety of disciplines:
- Climate Science: It provides a valuable tool for understanding climate patterns, identifying regions with similar climatic conditions, and studying the impact of climate change on these regions.
- Agriculture and Forestry: The map helps farmers and foresters identify suitable areas for specific crops and tree species, optimizing agricultural practices and forestry management.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The map highlights areas with unique ecosystems, supporting a diversity of plant and animal life, guiding conservation efforts and habitat management.
- Urban Planning: The map assists urban planners in designing cities and infrastructure that are adapted to the specific challenges and opportunities presented by the Mediterranean climate.
- Tourism and Recreation: The map helps identify regions with favorable weather conditions, attracting tourists and providing valuable insights for tourism development and outdoor recreation.
FAQs about the Mediterranean Climate Map
1. Why are there distinct Mediterranean climate regions around the world?
The Mediterranean climate is primarily influenced by global atmospheric circulation patterns, specifically the subtropical high-pressure cells that dominate these regions during the summer. These cells bring dry, stable air, resulting in warm, dry summers. During the winter, the subtropical high-pressure cells weaken, allowing for the passage of frontal systems from higher latitudes, bringing moisture and precipitation.
2. What are the challenges associated with the Mediterranean climate?
The Mediterranean climate presents challenges such as:
- Drought and Water Scarcity: The extended summer drought can lead to water scarcity, particularly in regions with high population density and agricultural activity.
- Fire Risk: The combination of dry vegetation and hot, dry summers creates a heightened risk of wildfires, requiring careful management and fire prevention strategies.
- Soil Erosion: The combination of heavy rainfall during winter and dry, exposed soil during summer can lead to soil erosion, impacting agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
3. How does the Mediterranean climate influence plant and animal life?
The Mediterranean climate has shaped the evolution of unique plant and animal communities:
- Sclerophyllous Vegetation: Plants have adapted to the dry summers with tough, leathery leaves, deep roots, and fire-resistant properties.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: The Mediterranean climate supports a high level of biodiversity, with a rich array of endemic species found in these regions.
- Migratory Patterns: Many bird species migrate to Mediterranean regions during the winter, taking advantage of the milder temperatures and abundant food resources.
4. What are the future implications of climate change for Mediterranean regions?
Climate change is predicted to exacerbate existing challenges in Mediterranean regions:
- Increased Drought: Warmer temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns are expected to intensify drought conditions, impacting water availability and agricultural productivity.
- More Frequent and Intense Wildfires: Climate change is likely to increase the frequency and intensity of wildfires, leading to significant ecological and economic damage.
- Sea Level Rise: Rising sea levels pose a threat to coastal communities and ecosystems in Mediterranean regions, increasing the risk of flooding and erosion.
Tips for Living in a Mediterranean Climate
- Water Conservation: Implement water-saving practices in homes, gardens, and agricultural activities to mitigate the effects of drought.
- Fire Prevention: Practice fire safety measures, including clearing vegetation around homes and following local fire regulations.
- Sustainable Land Management: Promote sustainable agricultural practices and forestry management to protect soil health and biodiversity.
- Climate Adaptation: Plan for future climate change impacts, including investing in water infrastructure and adapting urban planning strategies.
Conclusion
The Mediterranean climate map provides a vital framework for understanding the distribution, characteristics, and implications of this unique climate type. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of climate, ecosystems, and human societies. By recognizing the challenges and opportunities presented by the Mediterranean climate, we can work towards sustainable management of these regions, ensuring their continued vitality for future generations. The map serves as a powerful tool for promoting understanding, fostering collaboration, and guiding responsible stewardship of these diverse and fascinating regions.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Mediterranean Climate: A Map of Sunshine and Diversity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!