Unveiling Europe’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at Elevation Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Europe’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at Elevation Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Europe’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at Elevation Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Europe’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at Elevation Maps
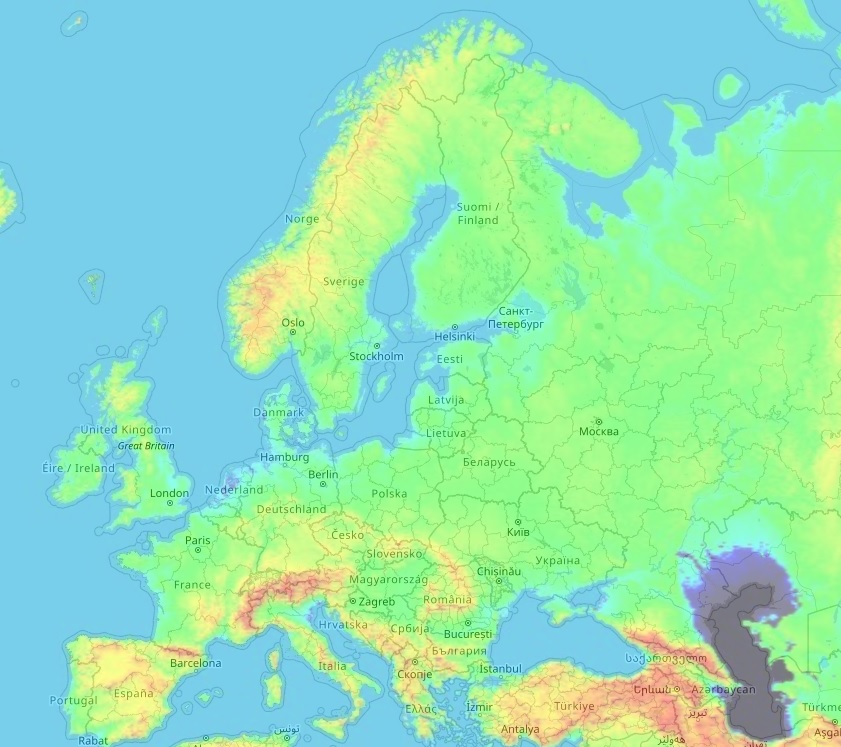
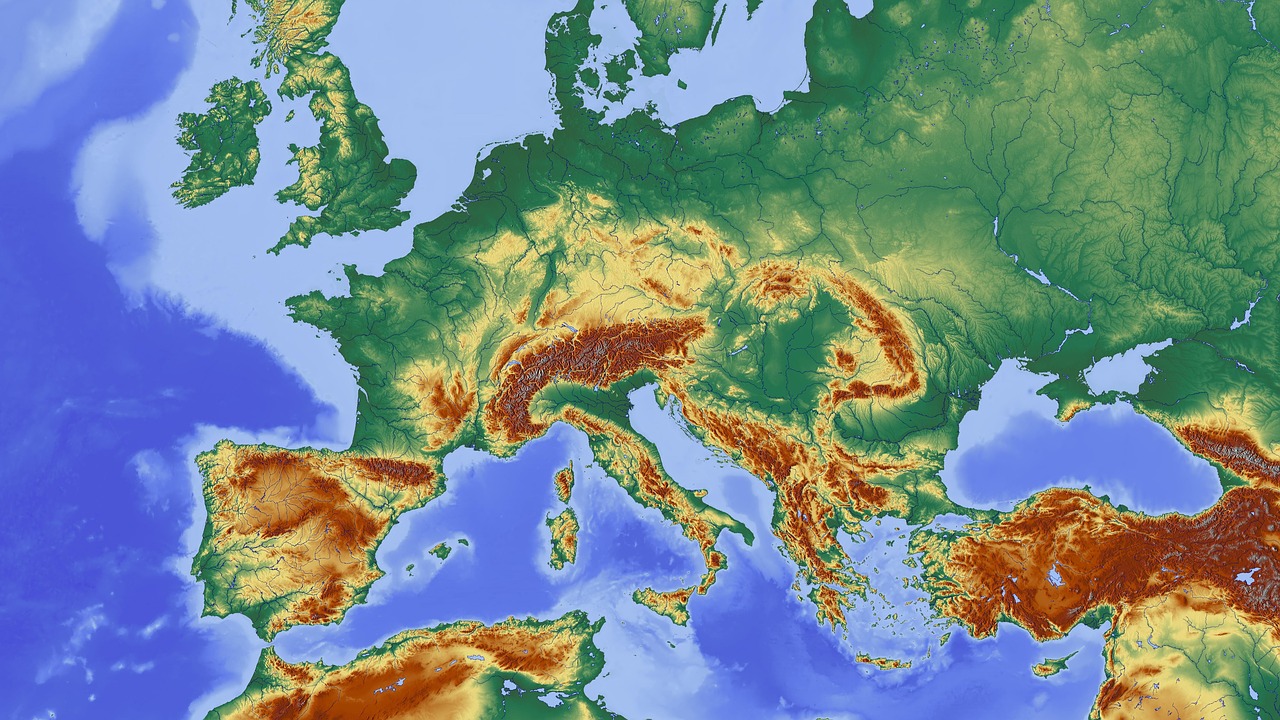
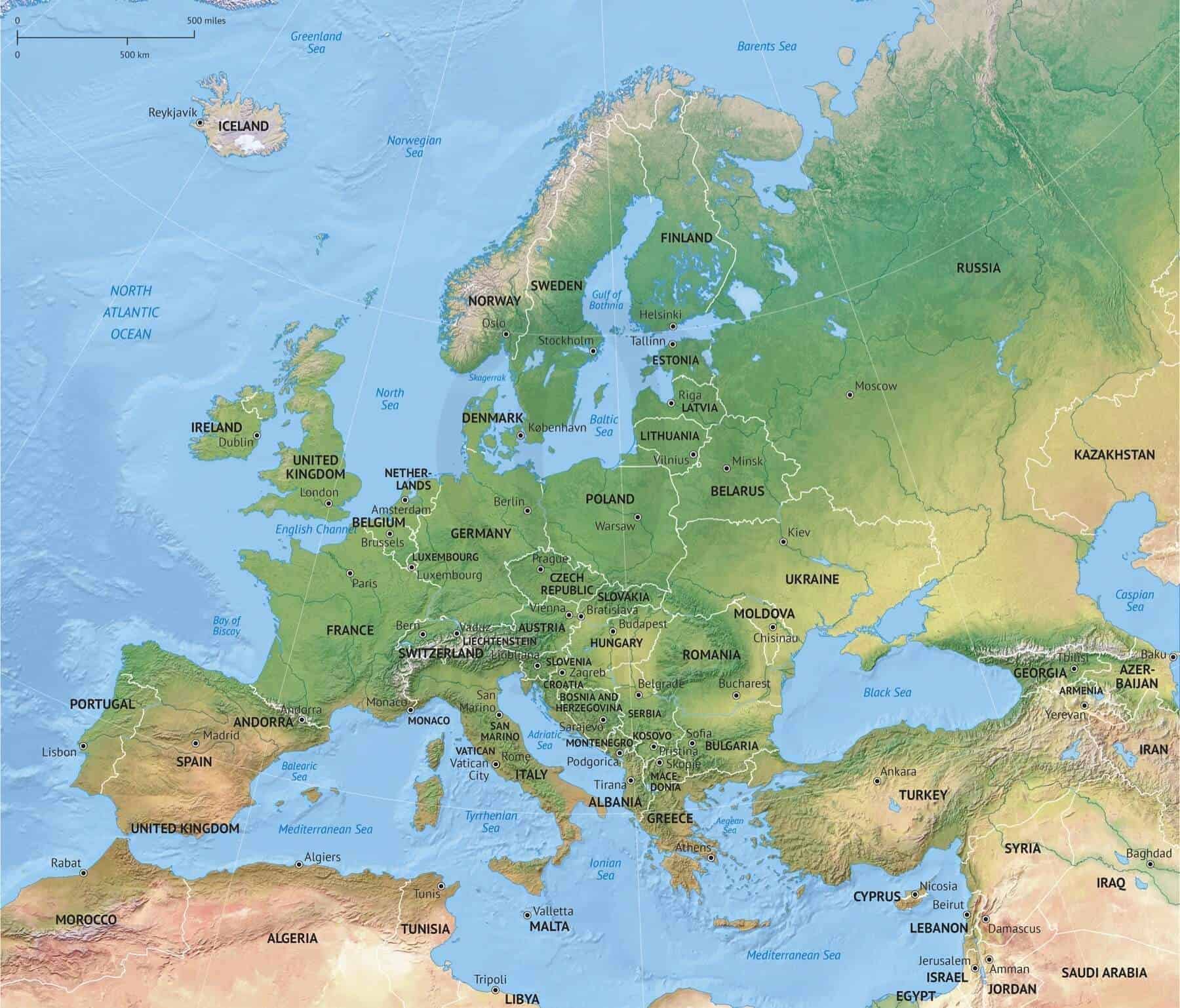
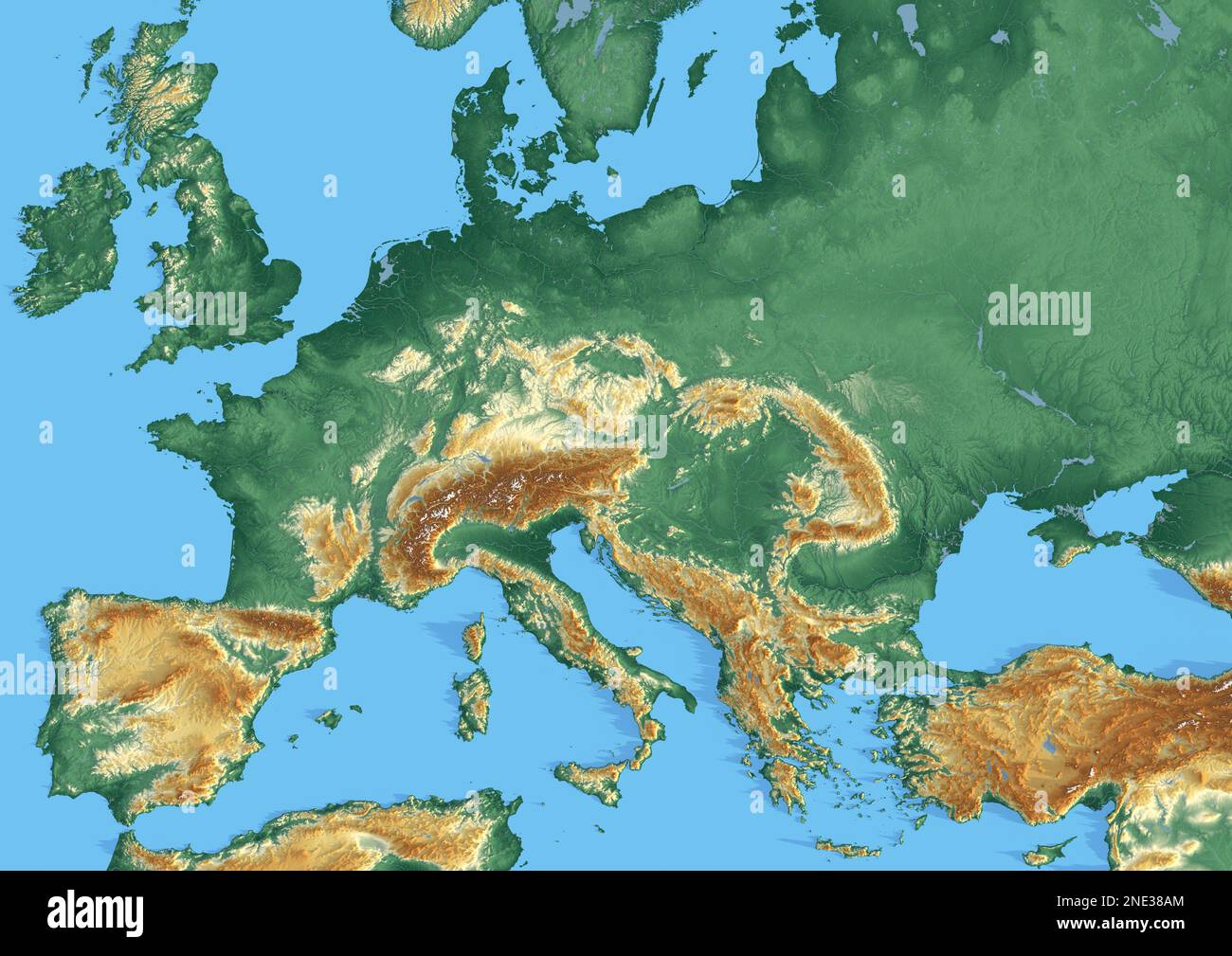
Europe, a continent of diverse landscapes, boasts a rich tapestry of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines. Understanding the distribution of elevation across this vast expanse is crucial for various disciplines, from geography and geology to environmental science and urban planning. Elevation maps, meticulously crafted representations of land height above sea level, provide a visual and quantifiable means to comprehend the continent’s complex topography.
A Visual Journey Through European Elevation:
Elevation maps of Europe depict a fascinating interplay of contrasting features. The towering Alps, stretching from the Mediterranean to the Adriatic Sea, dominate the central and southern portions, reaching heights of over 4,000 meters. The Pyrenees, a formidable mountain range separating France and Spain, rise to altitudes exceeding 3,000 meters. The Carpathian Mountains, curving through Central Europe, present a distinct arc of peaks and valleys.
Moving eastward, the Caucasus Mountains, a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, boast Mount Elbrus, the highest peak in Europe, reaching an impressive 5,642 meters. Further east, the Ural Mountains, marking the traditional border between Europe and Asia, rise to heights exceeding 1,800 meters.
Beyond the lofty peaks, Europe’s elevation map reveals vast plains. The Great European Plain, stretching from France through Germany and Poland, encompasses fertile farmlands and major river systems. The North European Plain, encompassing Denmark, the Netherlands, and parts of Germany, features flat landscapes and coastal areas.
The Iberian Peninsula, home to Spain and Portugal, exhibits a diverse topography, with the Pyrenees in the north and the Sierra Nevada range in the south. The Apennine Mountains, traversing the length of Italy, showcase a rugged and mountainous landscape. The Balkan Peninsula, encompassing countries like Greece, Bulgaria, and Romania, features a complex mosaic of mountains, valleys, and coastal areas.
Unveiling the Importance of Elevation Maps:
Elevation maps serve as invaluable tools for a multitude of applications, providing insights into:
1. Geographical Understanding:
- Identifying key landforms: Mountains, plains, valleys, and plateaus are clearly delineated, enabling a comprehensive understanding of Europe’s geographical features.
- Understanding regional variations: Elevation maps highlight the differences in terrain across various regions, revealing how topography influences local climates, vegetation, and human settlements.
- Analyzing drainage patterns: River networks and their associated valleys are evident, providing insights into water flow, erosion, and sedimentation processes.
2. Environmental Analysis:
- Assessing climate patterns: Elevation plays a significant role in determining temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. Elevation maps enable analysis of climate zones and their impact on ecosystems.
- Mapping biodiversity hotspots: Elevation influences species distribution, with different flora and fauna thriving at specific altitudes. Elevation maps help identify areas with high biodiversity and prioritize conservation efforts.
- Monitoring land use changes: Elevation maps provide a baseline for tracking changes in land use patterns over time, including deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion.
3. Infrastructure Planning and Development:
- Siting infrastructure: Elevation maps assist in identifying suitable locations for roads, railways, pipelines, and other infrastructure projects, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing efficiency.
- Managing water resources: Elevation maps contribute to understanding water flow patterns, aiding in dam construction, irrigation systems, and flood control measures.
- Planning urban development: Elevation maps help determine suitable locations for residential areas, commercial zones, and transportation networks, considering factors like slope, drainage, and natural hazards.
4. Geological Research:
- Mapping tectonic activity: Elevation maps reveal the distribution of fault lines and mountain ranges, providing insights into tectonic activity and the forces shaping the Earth’s surface.
- Analyzing geological formations: Elevation data can be used to map rock types, soil composition, and mineral deposits, aiding in geological exploration and resource extraction.
- Understanding landform evolution: Elevation maps provide a historical record of landform development, revealing how erosion, deposition, and other geological processes have shaped the landscape over time.
FAQs about Elevation Maps of Europe:
Q: What is the highest point in Europe?
A: Mount Elbrus, located in the Caucasus Mountains, is the highest peak in Europe, reaching an altitude of 5,642 meters above sea level.
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Europe?
A: Europe is home to several prominent mountain ranges, including the Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, Caucasus Mountains, Ural Mountains, Apennine Mountains, and the Scandinavian Mountains.
Q: How do elevation maps contribute to climate change research?
A: Elevation maps are crucial for understanding how climate change impacts various regions. By analyzing elevation data, researchers can assess the potential for glacial retreat, sea-level rise, and changes in precipitation patterns, informing adaptation strategies and mitigation efforts.
Q: What are some applications of elevation maps in urban planning?
A: Elevation maps are valuable tools for urban planners, aiding in:
- Identifying areas prone to flooding: Elevation data helps identify low-lying areas susceptible to flooding, allowing for targeted mitigation measures.
- Planning sustainable transportation networks: Elevation maps assist in determining optimal routes for roads, railways, and public transportation systems, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing efficiency.
- Designing green spaces: Elevation data helps identify suitable locations for parks, green corridors, and urban forests, promoting biodiversity and enhancing the urban environment.
Tips for Using Elevation Maps of Europe:
- Understanding the scale and resolution: Different elevation maps have varying scales and resolutions, affecting the level of detail they provide.
- Consulting multiple sources: Combining data from different elevation maps can provide a more comprehensive picture of the terrain.
- Utilizing specialized software: Geographic information system (GIS) software enables advanced analysis and visualization of elevation data.
- Integrating with other data sets: Combining elevation maps with other data sets, such as climate data, population density, and land use patterns, can reveal more nuanced insights.
Conclusion:
Elevation maps of Europe serve as a vital tool for understanding the continent’s complex topography, its influence on climate, biodiversity, and human activities. By providing a visual and quantifiable representation of land height, these maps empower researchers, planners, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding environmental protection, infrastructure development, and resource management. As technology advances, the accuracy and accessibility of elevation data continue to improve, offering even greater potential for unlocking the secrets of Europe’s diverse and dynamic landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Europe’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at Elevation Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!