Understanding Europe and Ukraine: A Geographic Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding Europe and Ukraine: A Geographic Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Europe and Ukraine: A Geographic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Europe and Ukraine: A Geographic Perspective

The map of Europe is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories, interwoven by a network of shared experiences and challenges. Within this intricate mosaic lies Ukraine, a nation whose strategic location has profoundly shaped its destiny and continues to hold significant implications for the continent’s geopolitical landscape.
A Geographic Overview of Europe
Europe, a continent spanning over 10 million square kilometers, encompasses a diverse array of geographical features. From the rugged peaks of the Alps to the vast plains of Eastern Europe, from the icy landscapes of Scandinavia to the sun-drenched shores of the Mediterranean, Europe’s physical geography has profoundly influenced its history, culture, and development.
Key Geographic Features of Europe:
- Peninsulas: Europe is characterized by numerous peninsulas, including the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, the Balkan Peninsula, and the Scandinavian Peninsula. These peninsulas have historically served as gateways for cultural exchange and trade, fostering unique identities and fostering economic growth.
- Mountain Ranges: The continent is home to several significant mountain ranges, such as the Alps, the Pyrenees, the Carpathians, and the Caucasus Mountains. These mountainous regions have acted as natural barriers, shaping political boundaries and influencing local climates.
- Rivers: Europe boasts a vast network of rivers, including the Danube, the Rhine, the Volga, and the Vistula. These waterways have historically served as transportation routes, facilitating trade and communication, and have also played a crucial role in the development of agriculture and industry.
- Climate: Europe experiences a wide range of climates, from the temperate oceanic climate of Western Europe to the cold continental climate of Eastern Europe. This variation in climate has influenced the continent’s agricultural production, biodiversity, and cultural development.
Ukraine’s Geographic Position
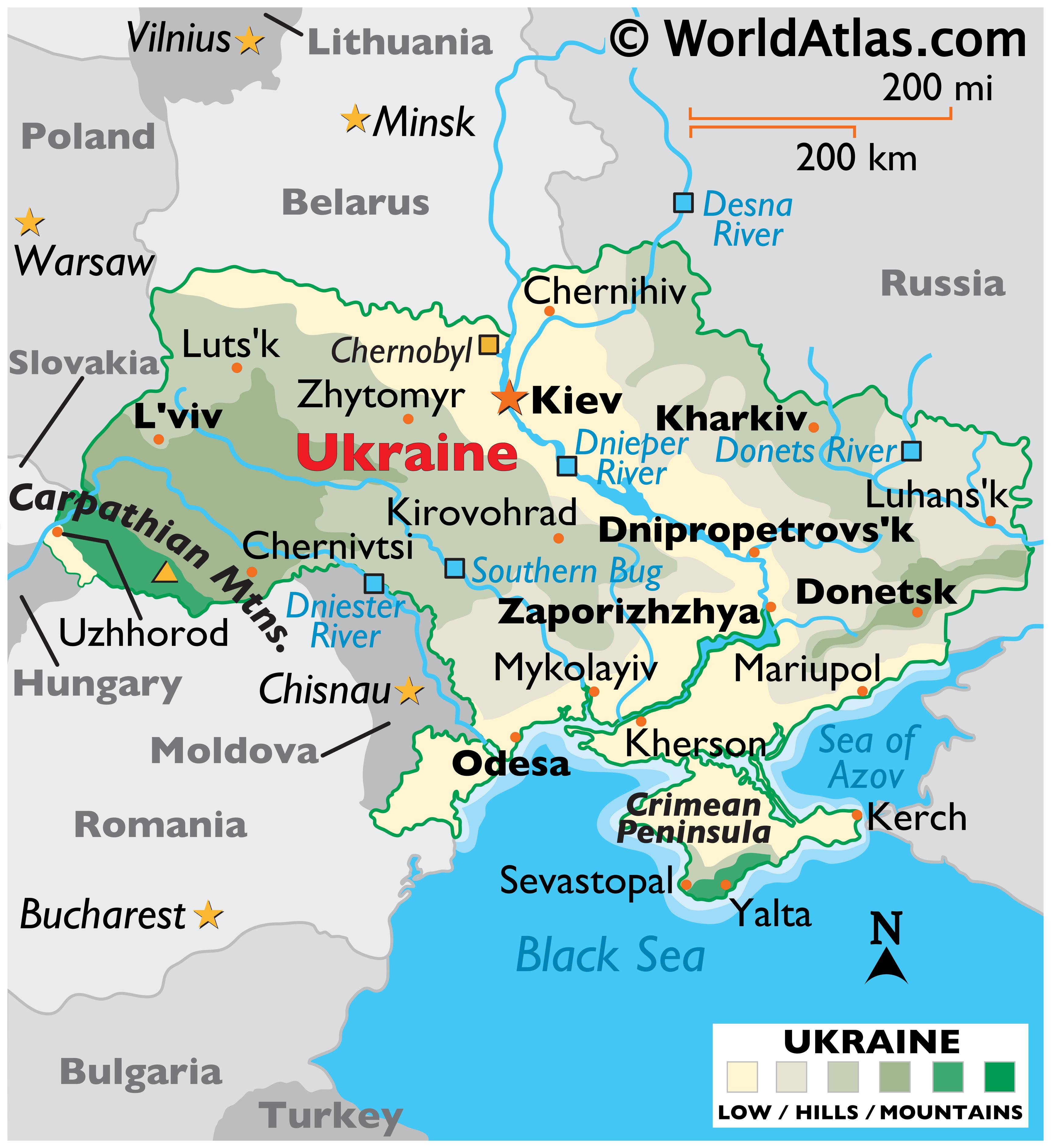
Ukraine, a country with a land area of over 603,700 square kilometers, occupies a crucial position in Eastern Europe. Its location, stretching from the Carpathian Mountains in the west to the vast steppes of the east, and bordered by Russia to the east and north, Belarus to the north, Poland, Slovakia, Hungary, and Romania to the west, and Moldova and the Black Sea to the south, has historically made it a bridge between East and West, a crossroads of cultures, and a focal point of geopolitical tensions.
Key Geographic Features of Ukraine:
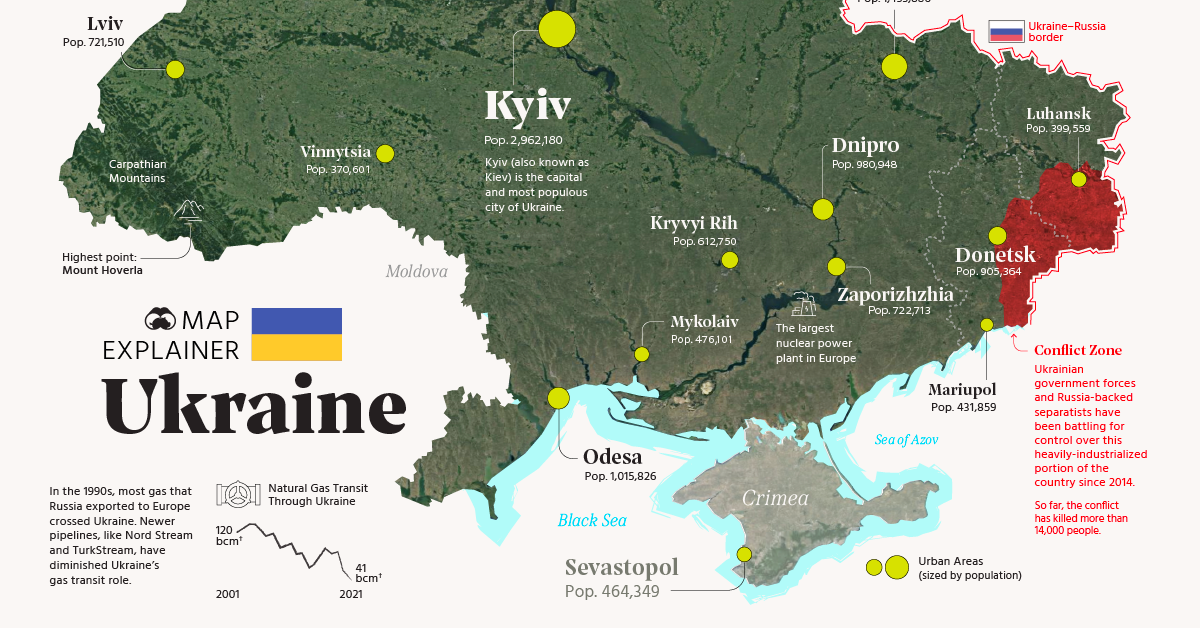
- Black Sea Coastline: Ukraine’s southern coastline along the Black Sea provides access to vital shipping routes and connects it to the wider Mediterranean region. This strategic location has historically played a significant role in trade and economic development.
- Fertile Steppes: The vast Ukrainian steppes, renowned for their fertile soils, have been a major agricultural region for centuries, contributing significantly to the country’s economy and food production.
- Carpathian Mountains: The Carpathian Mountains, which stretch across the western part of Ukraine, offer a diverse range of landscapes, including forests, meadows, and mountain ranges. They provide a natural barrier and a source of natural resources.
- Dnieper River: The Dnieper River, one of Europe’s longest rivers, flows through Ukraine, providing a vital transportation route and a source of water for agriculture and industry.
The Importance of Understanding the Map of Europe and Ukraine
Understanding the map of Europe and Ukraine is crucial for comprehending the historical, political, and economic dynamics of the region.
Historical Perspective:
- The Map as a Witness to History: The map of Europe and Ukraine reflects centuries of conflict and cooperation, migration and cultural exchange. From the rise and fall of empires to the tumultuous events of the 20th century, the map has been a silent witness to pivotal moments in European history.
- Understanding Border Disputes and Territorial Claims: The map reveals historical border disputes and territorial claims, which continue to shape the political landscape of the region. Understanding the historical context of these disputes is essential for comprehending the complexities of contemporary international relations.
- Tracing Cultural Influences and Connections: The map highlights the interconnectedness of cultures across Europe and Ukraine. It reveals the flow of ideas, art, and trade, shaping the unique identities of different regions.
Contemporary Significance:
- Geopolitical Implications: The map highlights Ukraine’s strategic location at the crossroads of Eastern and Western Europe. Its relationship with Russia, the European Union, and NATO has profound implications for the security and stability of the continent.
- Economic and Trade Relations: The map illustrates the intricate web of economic and trade relations that connect Europe and Ukraine. Understanding these connections is crucial for comprehending the economic interdependence of the region.
- Environmental Concerns: The map reveals shared environmental challenges, such as climate change, pollution, and resource scarcity, which require collaborative efforts across borders to address.
FAQs on the Map of Europe and Ukraine
1. What is the significance of Ukraine’s location in Eastern Europe?
Ukraine’s location at the crossroads of Eastern and Western Europe makes it strategically important for both regions. It has historically been a bridge between Russia and the West, and its current geopolitical situation is a matter of global concern.
2. How has the map of Europe changed over time?
The map of Europe has undergone significant transformations over centuries, with changes in borders, political systems, and the rise and fall of empires. These changes reflect the dynamic nature of European history and the ongoing process of shaping the continent’s identity.
3. What are the main challenges facing Ukraine today?
Ukraine faces a range of challenges, including the ongoing conflict with Russia, economic instability, and political reforms. Understanding these challenges is essential for comprehending the country’s future prospects and the implications for the wider region.
4. How does the map of Europe and Ukraine contribute to understanding the continent’s cultural diversity?
The map reveals the rich tapestry of cultures across Europe and Ukraine, highlighting the influence of history, geography, and migration on the development of distinct identities. Understanding these cultural nuances is essential for promoting intercultural dialogue and cooperation.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Europe and Ukraine
- Use Interactive Maps: Utilize online interactive maps to explore the geography of Europe and Ukraine in detail. These maps often provide additional information, such as population density, economic indicators, and historical data.
- Study Historical Maps: Examining historical maps can provide valuable insights into the evolution of borders, political systems, and cultural influences over time.
- Read Historical Accounts: Engaging with historical accounts and narratives can help to understand the context behind the geographic features and political boundaries depicted on the map.
- Explore Geographic Data: Accessing and analyzing geographic data, such as satellite imagery, climate information, and population statistics, can enhance your understanding of the region’s physical and human landscapes.
Conclusion
The map of Europe and Ukraine is more than just a static representation of geographical features. It is a dynamic tool for understanding the complex interplay of history, politics, culture, and geography that shapes the region’s identity and destiny. By studying the map and engaging with its historical and contemporary context, we gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing Europe and Ukraine, and the implications for the wider world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Europe and Ukraine: A Geographic Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!