The Untamed Continent: Understanding the Territorial Claims on Antarctica
Related Articles: The Untamed Continent: Understanding the Territorial Claims on Antarctica
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Untamed Continent: Understanding the Territorial Claims on Antarctica. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Untamed Continent: Understanding the Territorial Claims on Antarctica
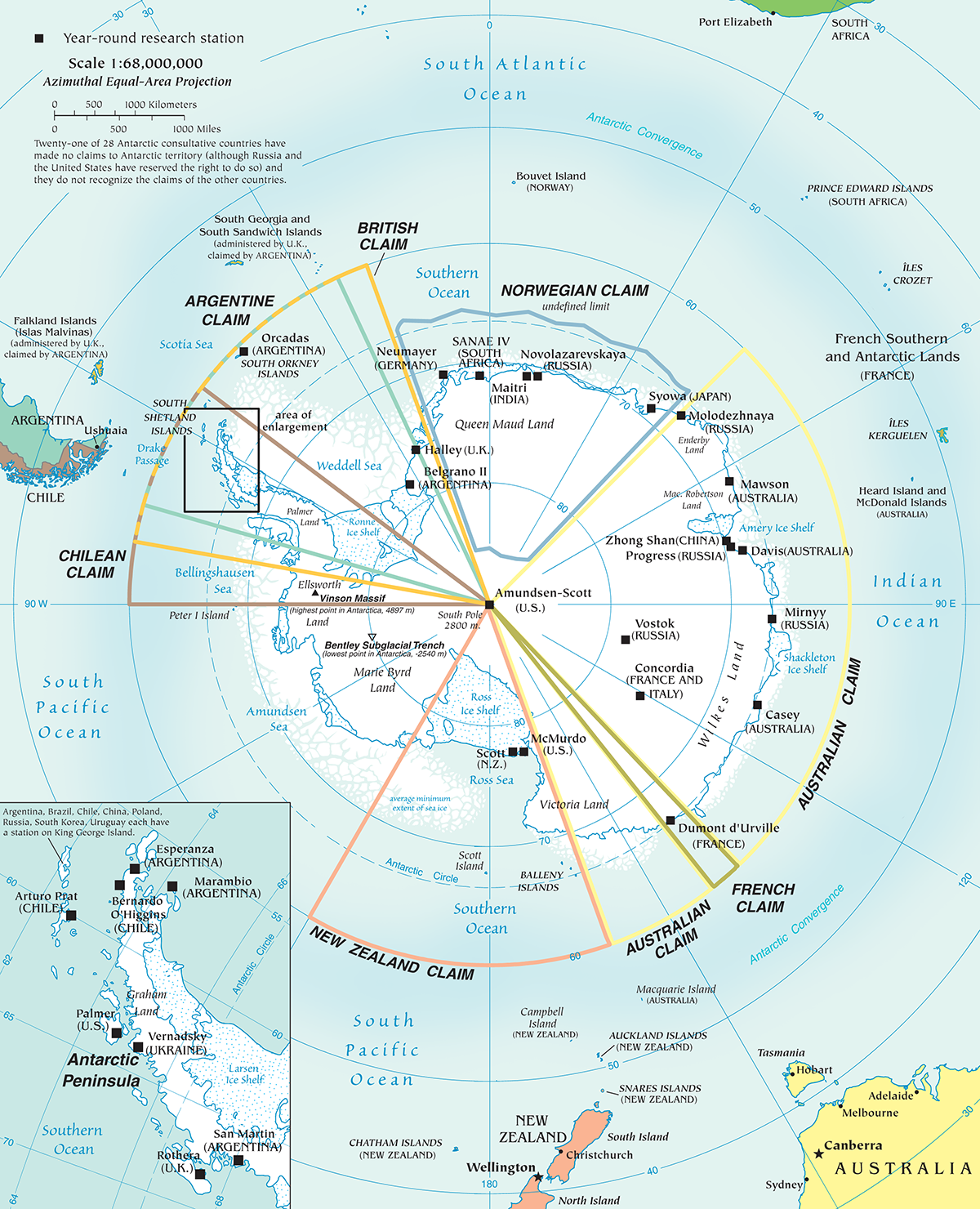
Antarctica, the Earth’s southernmost continent, remains a unique and enigmatic landmass. While its icy expanse evokes images of untouched wilderness, the continent is not devoid of human presence. Seven nations lay claim to portions of Antarctica, each with its own historical, scientific, and strategic interests. Understanding these claims requires a comprehensive look at the complex geopolitical landscape of this frozen continent.
A Continent of Claims:
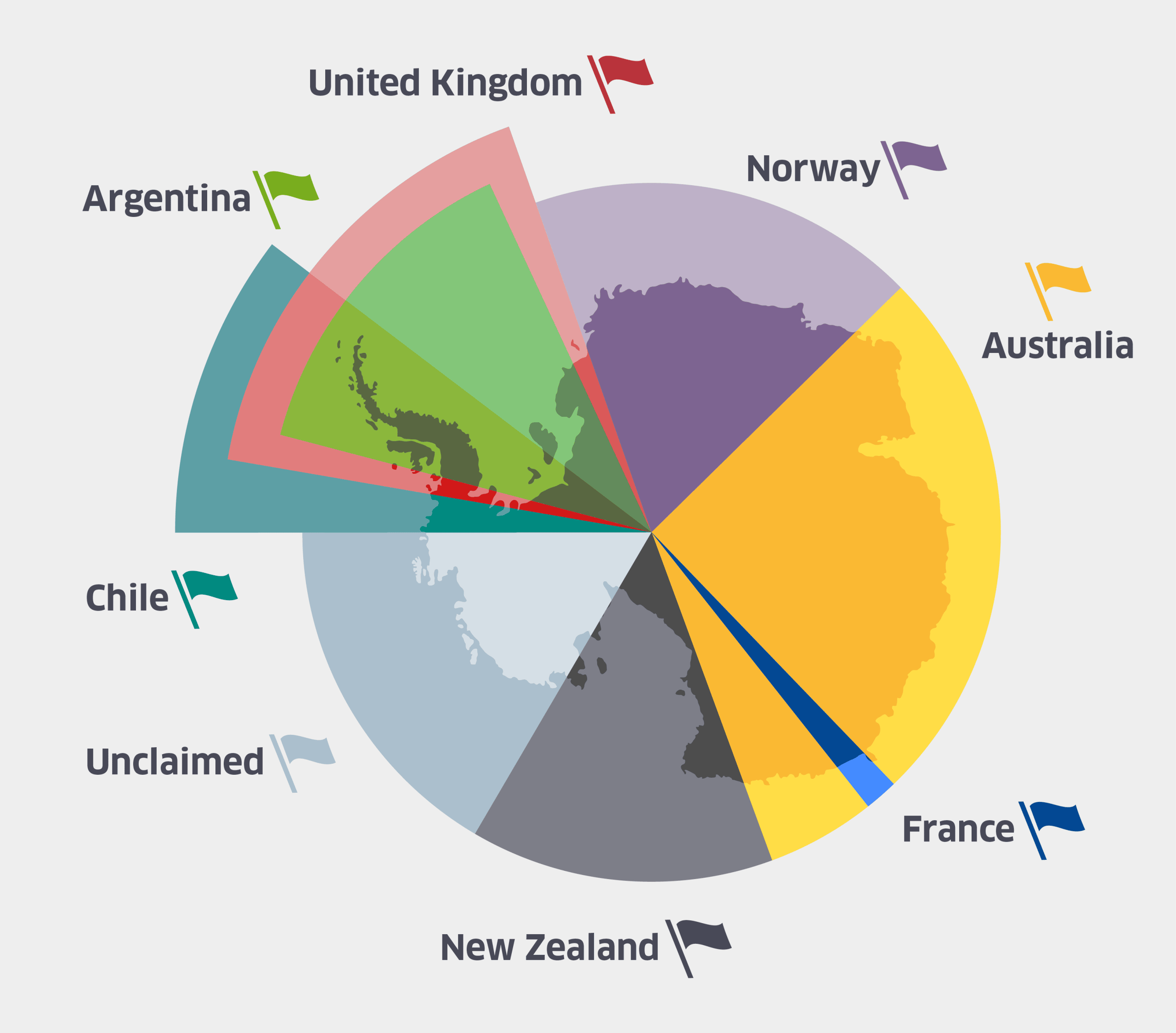
The Antarctic Treaty System, established in 1959, governs international relations on the continent. While the treaty prohibits territorial sovereignty claims and designates Antarctica for peaceful scientific research, seven nations maintain historical claims based on exploration and discovery:
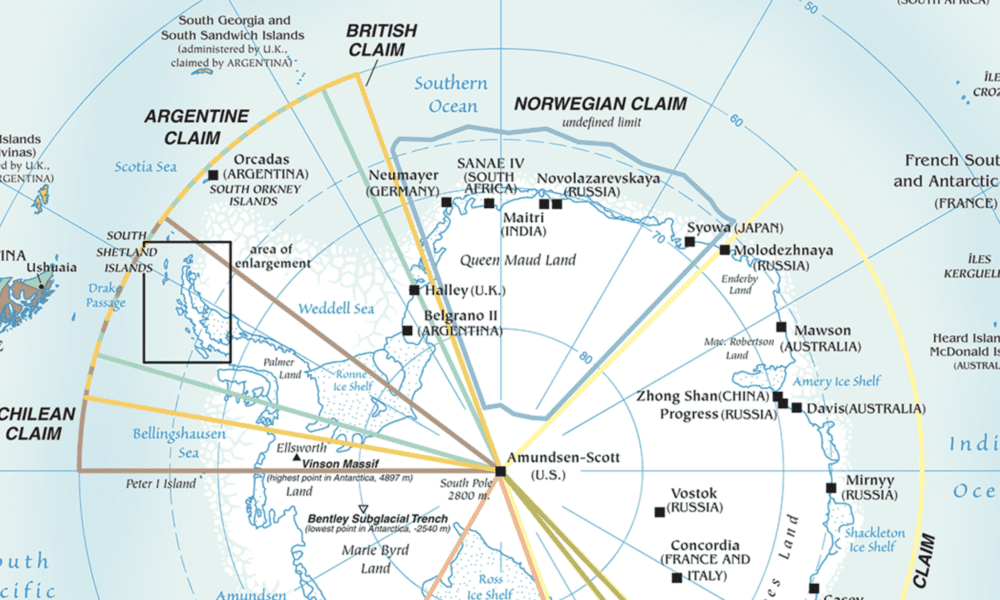
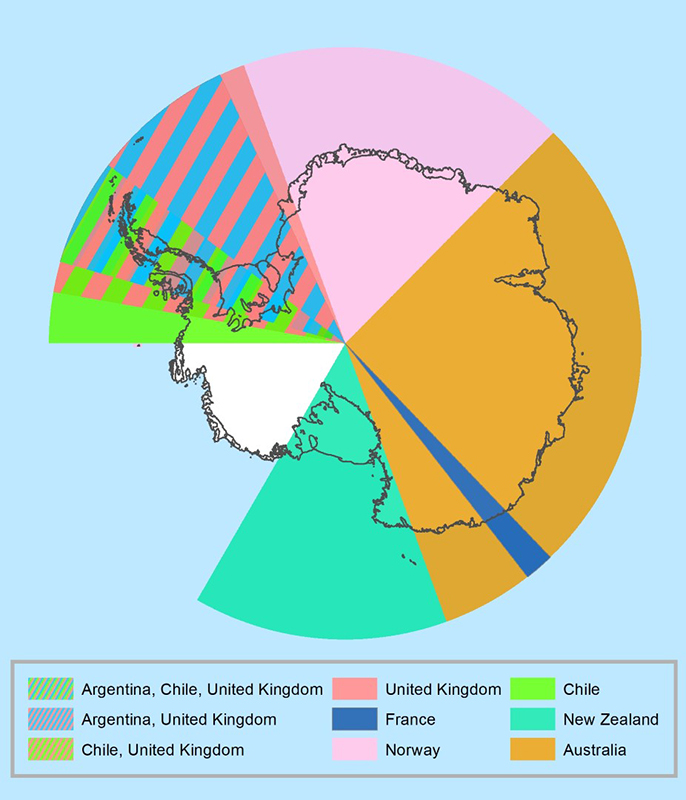
- Argentina: Claims the Antarctic Peninsula and adjacent islands, citing exploration by Argentine navigators in the 19th century.
- Australia: Claims a vast sector encompassing the East Antarctic coastline, citing exploration by Australian explorers in the early 20th century.
- Chile: Claims a sector overlapping with Argentina’s, based on Chilean exploration and scientific research in the region.
- France: Claims a sector encompassing Adélie Land, founded by French explorers in the 19th century.
- New Zealand: Claims a sector encompassing the Ross Sea region, citing exploration by New Zealand explorers in the 19th century.
- Norway: Claims Queen Maud Land, a sector along the Atlantic coast, based on Norwegian exploration and scientific research.
- United Kingdom: Claims a sector encompassing the South Orkney Islands and South Shetland Islands, citing British exploration in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Overlapping Claims and the Absence of Recognition:
The overlapping nature of these claims creates a complex geopolitical landscape. While these nations maintain their claims, no other country recognizes their territorial sovereignty. The Antarctic Treaty System acknowledges these claims but only for the purpose of scientific research and peaceful cooperation.
Beyond Territorial Claims: The Importance of Antarctica:
Despite the lack of recognized sovereignty, Antarctica holds significant importance for the world:
- Scientific Research: As a pristine environment, Antarctica provides a unique laboratory for studying climate change, glaciology, astronomy, and biodiversity. Research conducted in Antarctica contributes to global understanding of Earth’s systems and potential future scenarios.
- Environmental Conservation: Antarctica’s fragile ecosystem is home to unique flora and fauna. The Antarctic Treaty System emphasizes environmental protection and encourages scientific research that contributes to understanding and safeguarding this delicate ecosystem.
- Global Climate Regulation: Antarctica’s ice sheets play a crucial role in regulating global climate. Understanding the dynamics of these ice sheets is essential for predicting future sea level rise and its implications for coastal communities around the world.
- Resource Potential: While the Antarctic Treaty System prohibits resource exploitation, the continent holds potential for mineral and energy resources. The potential for resource extraction remains a sensitive issue, with ethical and environmental concerns requiring careful consideration.
Navigating the Future of Antarctica:
The future of Antarctica hinges on maintaining the balance between scientific research, environmental conservation, and responsible resource management. The Antarctic Treaty System serves as a framework for international cooperation, ensuring that the continent’s unique value is preserved for future generations.
FAQs Regarding Antarctica’s Territorial Claims:
1. Why are there overlapping claims in Antarctica?
Overlapping claims stem from historical exploration and discovery, with different nations claiming territories based on their respective explorations. The lack of a universally recognized framework for territorial claims in Antarctica contributes to the overlapping nature of these claims.
2. What are the implications of these overlapping claims?
While the Antarctic Treaty System acknowledges these claims, they remain unresolved. The overlapping nature of claims can potentially lead to disputes and conflicts in the future, particularly if resource exploitation becomes a possibility.
3. Does the Antarctic Treaty System prevent resource exploitation?
The Antarctic Treaty System prohibits resource exploitation, except for scientific research purposes. However, the potential for future resource extraction remains a sensitive issue, requiring careful consideration of ethical and environmental implications.
4. What is the future of Antarctica?
The future of Antarctica depends on maintaining the balance between scientific research, environmental conservation, and responsible resource management. The Antarctic Treaty System serves as a framework for international cooperation, ensuring that the continent’s unique value is preserved for future generations.
Tips for Understanding Antarctica’s Territorial Claims:
- Focus on the Antarctic Treaty System: This treaty governs international relations on the continent and provides a framework for understanding the current state of territorial claims.
- Explore the history of exploration and discovery: Understanding the historical context behind each nation’s claim provides valuable insights into the geopolitical landscape of Antarctica.
- Consider the environmental and scientific implications: Antarctica’s unique ecosystem and its role in global climate regulation are crucial factors to consider when evaluating territorial claims and future development.
Conclusion:
The map of Antarctica’s territorial claims reveals a complex geopolitical landscape. While the Antarctic Treaty System ensures international cooperation and peaceful scientific research, the future of this continent remains intertwined with the challenges of resource management, environmental conservation, and the potential for future disputes. Understanding the historical context, the scientific value, and the environmental significance of Antarctica is crucial for navigating the future of this unique and vital continent.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Untamed Continent: Understanding the Territorial Claims on Antarctica. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!