The Indian Railway Network: A Lifeline Across the Subcontinent
Related Articles: The Indian Railway Network: A Lifeline Across the Subcontinent
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Indian Railway Network: A Lifeline Across the Subcontinent. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indian Railway Network: A Lifeline Across the Subcontinent
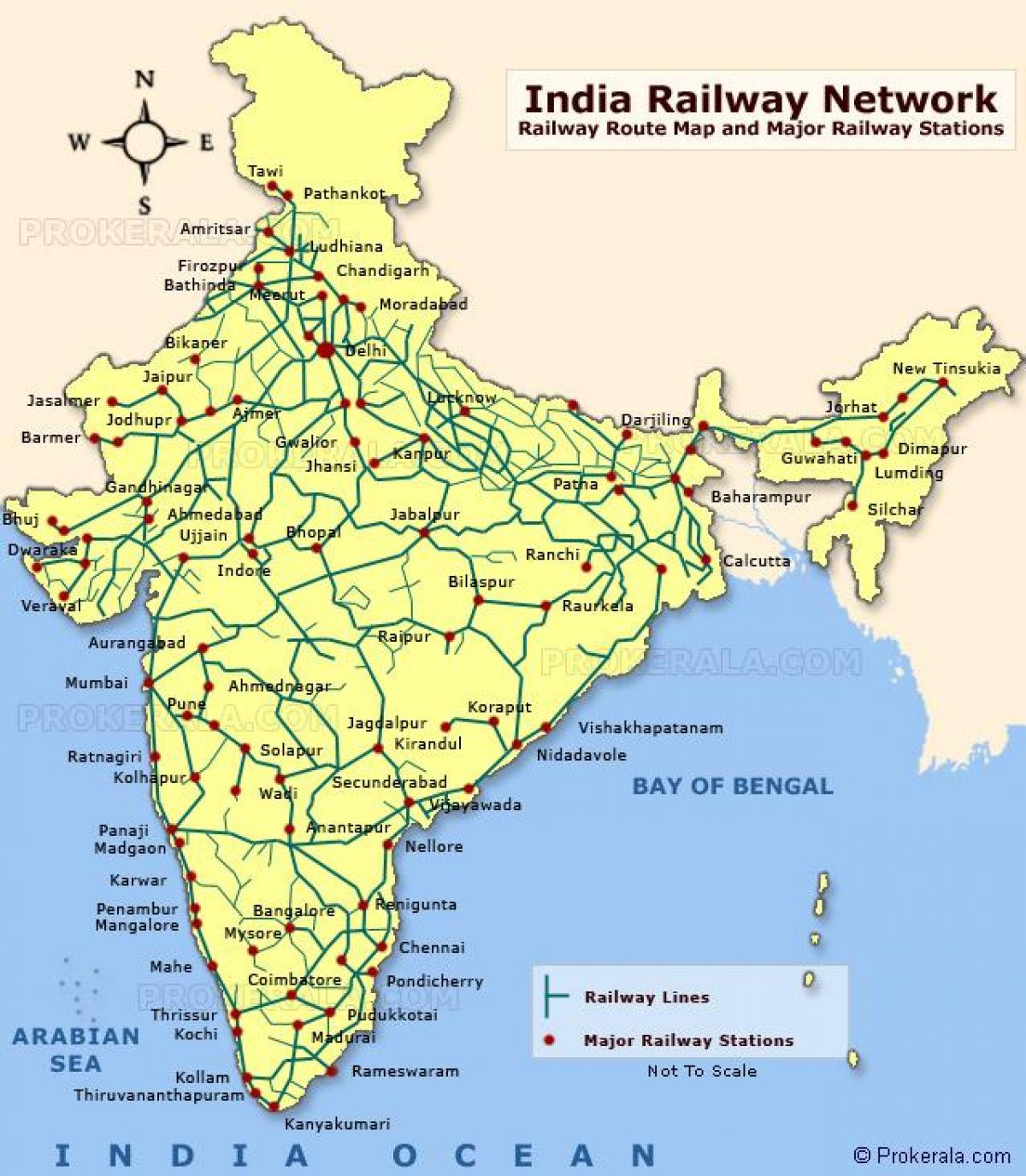
The Indian Railway network, one of the largest and most extensive in the world, is a vital artery that pulsates with the lifeblood of the nation. Spanning over 67,000 kilometers, it connects the far corners of the country, facilitating trade, tourism, and the movement of people. Understanding the intricate tapestry of this network requires delving into its history, structure, and impact on the Indian economy and society.
A Legacy of Rails:
The genesis of the Indian Railways can be traced back to the British colonial era. The first train journey in India took place in 1853, a momentous occasion that marked the beginning of a transformative journey for the nation. The initial purpose of the railways was to connect major cities and ports for efficient transportation of goods and troops. However, the network rapidly expanded, reaching into the hinterland and playing a crucial role in the development of infrastructure and industries.
The Modern Network: A Complex Web of Connections:
Today, the Indian Railway network operates under the auspices of the Ministry of Railways, a sprawling organization with a complex structure. The network is divided into 18 zones, each managed by a General Manager, who is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the zone. These zones are further subdivided into divisions, each headed by a Divisional Railway Manager. This hierarchical structure ensures efficient administration and coordination across the vast network.
The Lifeline of India: A Multifaceted Role:
The Indian Railways play a multifaceted role in the Indian economy and society. It is a major employer, providing livelihoods to millions of people across the country. The network is a crucial facilitator of trade and commerce, enabling the transportation of goods and raw materials across vast distances. It also plays a vital role in tourism, providing affordable and accessible travel options for millions of domestic and international tourists.
The Map: A Visual Representation of Connectivity:
The map of the Indian Railway network is a testament to the interconnectedness of the nation. It depicts the intricate web of lines that crisscross the country, connecting cities, towns, and villages. The map highlights major railway junctions, important stations, and key routes. It is a valuable tool for understanding the flow of passengers and goods across the network, identifying potential bottlenecks, and planning future expansions.
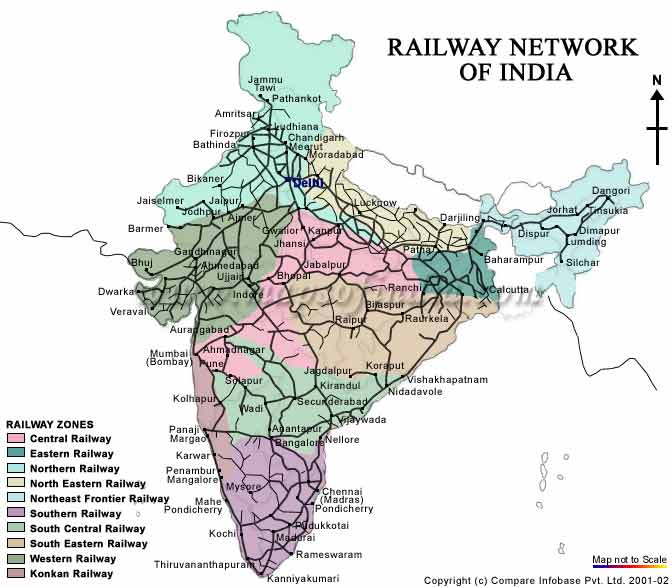
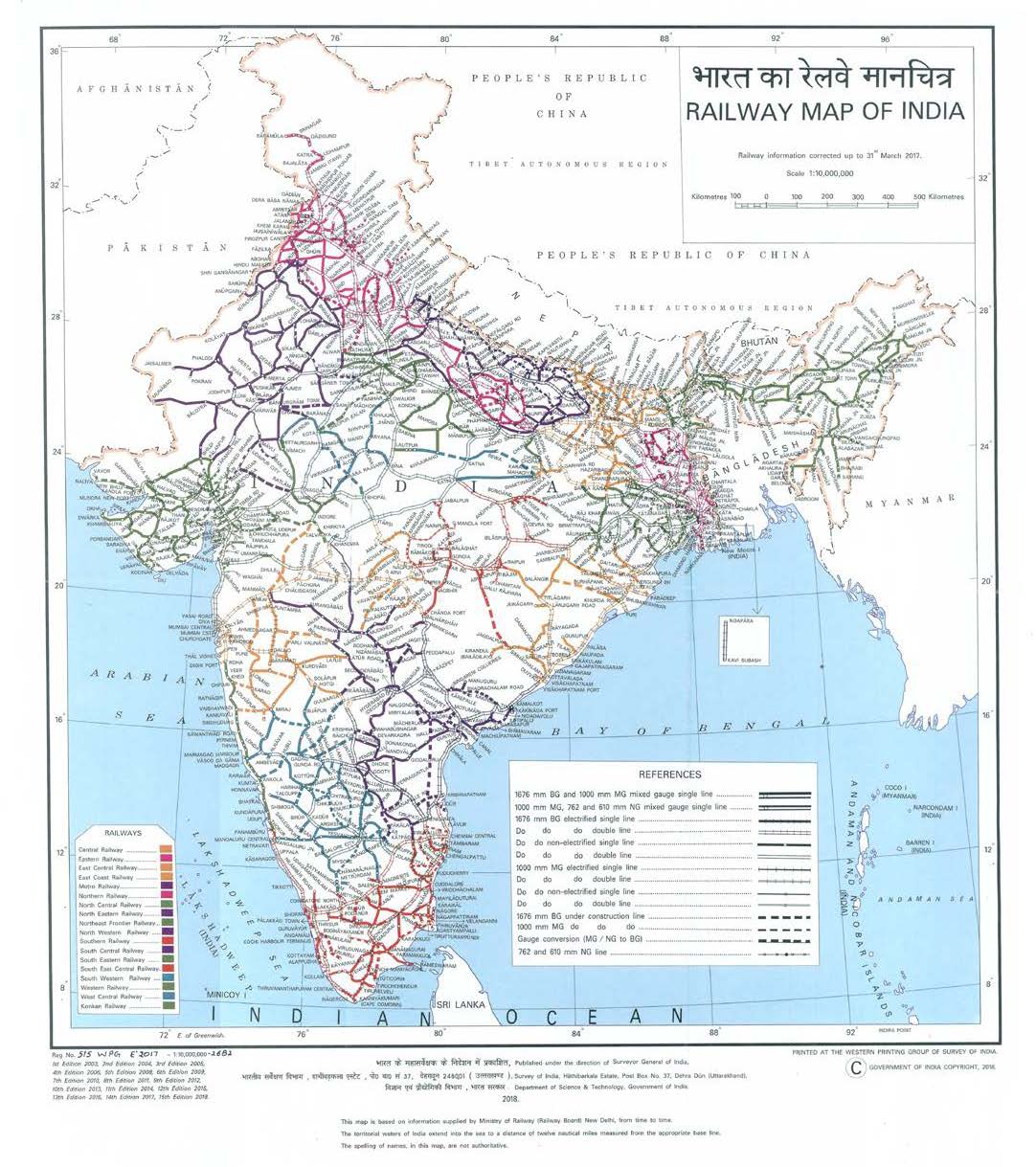
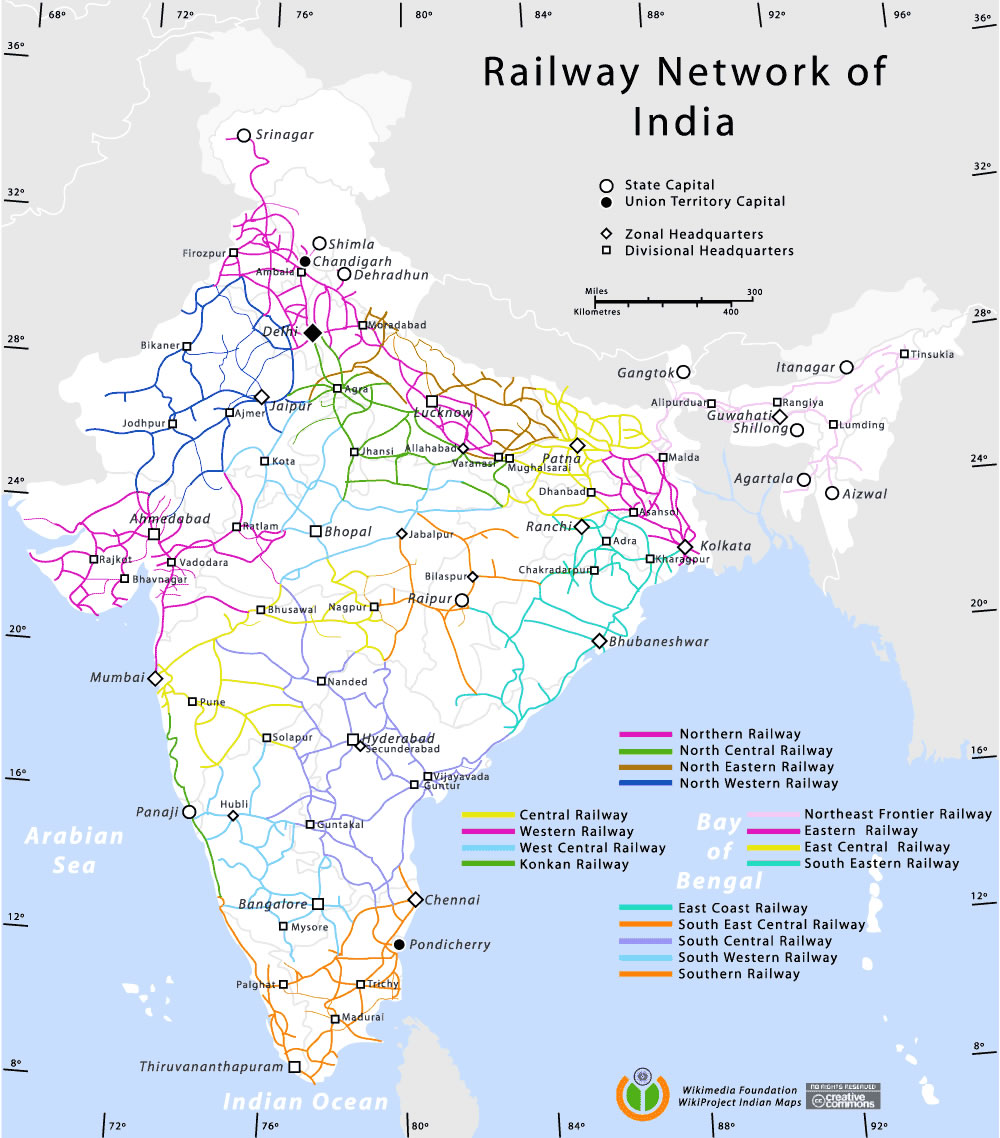
Key Features of the Map:
- Gauge: The map highlights the different gauges used in the Indian Railway network, including broad gauge, meter gauge, and narrow gauge.
- Electrified Lines: The map indicates the electrified lines, which are crucial for efficient and environmentally friendly transportation.
- Double and Triple Lines: The map shows the double and triple lines, which are used to increase capacity and reduce congestion.
- Major Stations: The map identifies major railway stations, which are crucial hubs for passenger and freight traffic.
- Railway Zones: The map displays the 18 railway zones, highlighting the administrative divisions of the network.
The Future of the Indian Railways:
The Indian Railways are undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and the government’s focus on modernization. The focus is on increasing capacity, improving safety, and enhancing the passenger experience. The government is investing heavily in infrastructure development, including high-speed rail lines, dedicated freight corridors, and the modernization of existing lines.
FAQs about the Indian Railway Network:
1. What are the different gauges used in the Indian Railway network?
The Indian Railway network utilizes three main gauges: broad gauge (1.676 meters), meter gauge (1 meter), and narrow gauge (0.762 meters). The majority of the network is broad gauge, while meter gauge lines are primarily found in the northeastern and western regions. Narrow gauge lines are mostly used for local and tourist purposes.
2. How many railway zones are there in India?
The Indian Railway network is divided into 18 zones, each managed by a General Manager. These zones are further subdivided into divisions, each headed by a Divisional Railway Manager.
3. What are the key challenges faced by the Indian Railways?
The Indian Railways face numerous challenges, including:
- Congestion: The network is often congested, particularly during peak hours.
- Safety: Accidents are a major concern, and improving safety standards is a priority.
- Financial Sustainability: The railways are facing financial challenges, and the government is seeking ways to make them more financially sustainable.
- Modernization: The network requires significant modernization to keep pace with technological advancements.
4. What are the government’s plans for the future of the Indian Railways?
The government is investing heavily in the modernization of the Indian Railways, focusing on:
- High-speed rail lines: The government is developing high-speed rail lines to connect major cities and reduce travel time.
- Dedicated freight corridors: The government is building dedicated freight corridors to improve the efficiency of freight transportation.
- Modernization of existing lines: The government is investing in the modernization of existing lines, including track renewal, electrification, and signaling upgrades.
- Improving passenger experience: The government is focusing on improving the passenger experience, including better amenities, improved cleanliness, and enhanced security.
Tips for Using the Indian Railway Network:
- Plan your journey in advance: Booking tickets in advance is essential, especially during peak season.
- Check the train schedule: The Indian Railways have a comprehensive website and mobile app where you can check train schedules and book tickets.
- Arrive at the station early: It is important to arrive at the station early to allow time for security checks and boarding.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Be vigilant about your belongings and surroundings, especially in crowded areas.
- Follow the instructions of railway staff: Follow the instructions of railway staff to ensure a safe and enjoyable journey.
Conclusion:
The Indian Railway network is a vital lifeline for the nation, connecting people, goods, and ideas across the vast subcontinent. Its intricate web of lines, spanning over 67,000 kilometers, stands as a testament to the country’s infrastructure and its commitment to connectivity. As the network continues to evolve and modernize, it will play an increasingly important role in the economic and social development of India. The map of the Indian Railway network serves as a visual representation of this vital infrastructure, highlighting its importance and its potential for future growth.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indian Railway Network: A Lifeline Across the Subcontinent. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!