The Hexagon Map: A Versatile Tool for Visualization and Analysis
Related Articles: The Hexagon Map: A Versatile Tool for Visualization and Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Hexagon Map: A Versatile Tool for Visualization and Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Hexagon Map: A Versatile Tool for Visualization and Analysis
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Hexagon Map: A Versatile Tool for Visualization and Analysis
- 3.1 Understanding the Hexagon Map
- 3.2 Applications of Hexagon Maps
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions about Hexagon Maps
- 3.4 Tips for Using Hexagon Maps Effectively
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Hexagon Map: A Versatile Tool for Visualization and Analysis
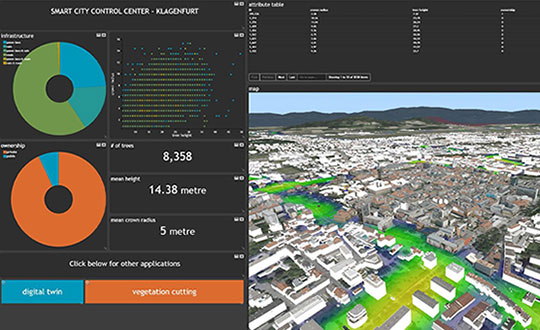
Hexagon maps, also known as hexagonal grids, are a unique and increasingly popular form of geographic representation. This article delves into the intricacies of this map type, exploring its advantages, applications, and the underlying principles that make it a powerful tool for diverse fields.
Understanding the Hexagon Map
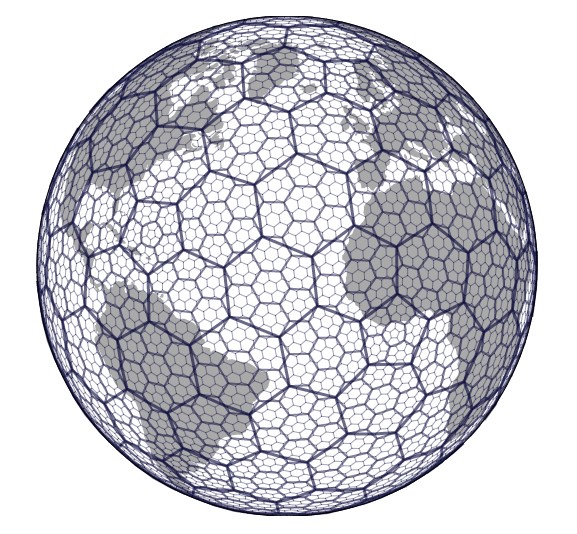
A hexagon map employs regular hexagons to represent geographic space. Unlike traditional square grids, which often result in distortion and uneven representation, hexagons seamlessly tessellate, creating a continuous, consistent grid without gaps or overlaps. This inherent property of hexagons makes them ideal for representing spatial data, particularly in situations where uniform distribution and accurate representation are crucial.
Key Advantages of Hexagon Maps:
- Uniformity and Consistency: Hexagons offer a more uniform representation of space compared to square grids, ensuring that each cell represents an equal area. This uniformity is particularly valuable for analyzing data where spatial distribution is critical.
- Reduced Distortion: Hexagon maps minimize distortion, especially near the poles, where traditional map projections often suffer from significant stretching. This makes them suitable for representing global data with greater accuracy.
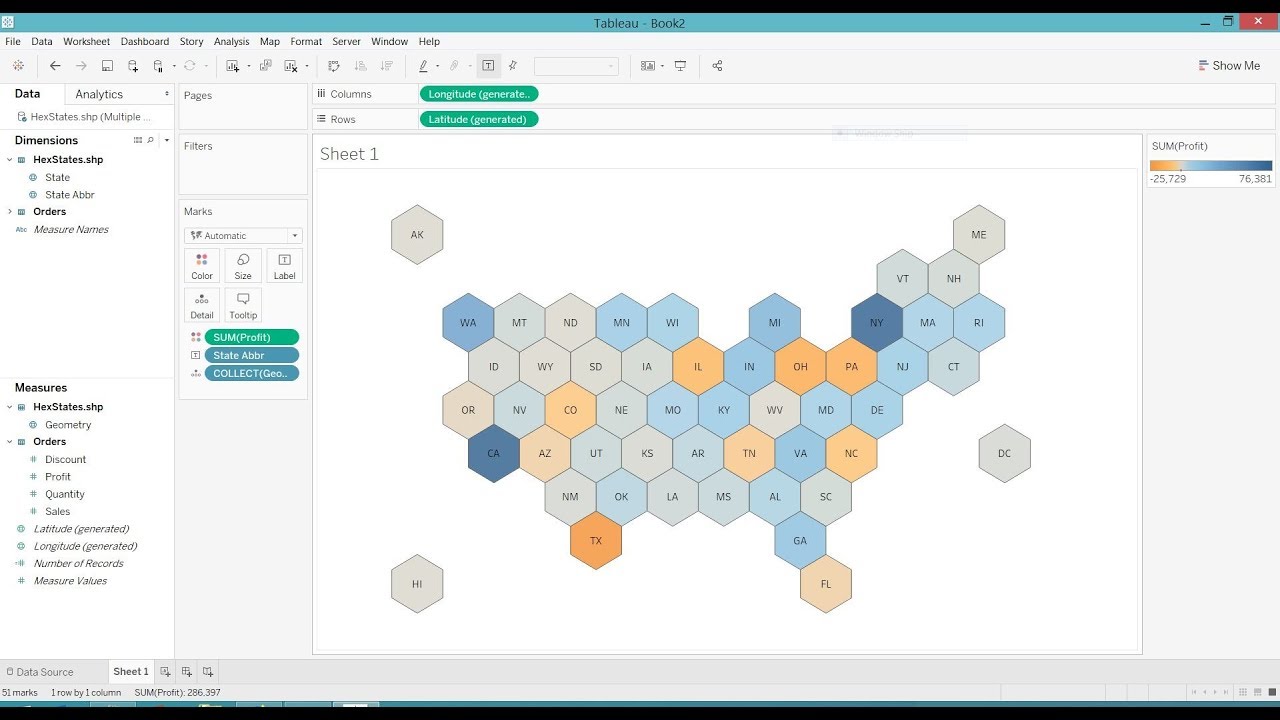
- Efficient Data Visualization: The unique shape of hexagons allows for visually appealing and informative data visualization. Data can be represented through color gradients, size variations, or other visual cues, making patterns and trends easily discernible.
- Enhanced Spatial Analysis: Hexagon maps facilitate robust spatial analysis by providing a consistent and uniform framework for data aggregation and analysis. This enables researchers to identify spatial patterns, correlations, and relationships within the data.
Applications of Hexagon Maps
The versatility of hexagon maps extends to numerous fields, including:
- Geography and Cartography: Hexagon maps are employed for representing geographical features, population density, land cover, and other spatial data. They are particularly useful for visualizing global data, where distortions are minimized.
- Urban Planning and Development: Planners utilize hexagon maps to analyze urban growth patterns, identify areas with high population density, and plan infrastructure development. The grid structure facilitates efficient allocation of resources and infrastructure.
- Environmental Studies: Hexagon maps are employed in environmental studies to represent data related to pollution levels, biodiversity, and climate change. The uniform grid structure allows for accurate analysis of spatial patterns and trends.
- Epidemiology and Public Health: Hexagon maps are crucial in epidemiological studies, enabling researchers to visualize disease outbreaks, identify high-risk areas, and track disease spread. The grid structure facilitates accurate mapping of disease incidence and prevalence.
- Marketing and Business Analytics: Hexagon maps are used in market research to analyze customer demographics, identify market segments, and optimize marketing strategies. The grid structure allows for efficient visualization of customer data and market trends.
- Game Development: Hexagon maps are widely used in video game development for creating game worlds, managing terrain generation, and optimizing pathfinding algorithms. The grid structure provides a predictable and efficient framework for game development.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hexagon Maps
1. What are the limitations of hexagon maps?
While hexagon maps offer numerous advantages, they also have limitations. One key limitation is the potential for distortion, especially when representing large-scale geographic areas. Another limitation is the difficulty in representing complex geometries, such as irregular coastlines or mountainous terrain.
2. How are hexagon maps created?
Hexagon maps can be created using various software tools, including geographic information system (GIS) software, mapping libraries, and specialized data visualization tools. The process typically involves defining the geographic extent, setting the hexagon size, and then projecting the data onto the hexagonal grid.
3. What are the best practices for using hexagon maps?
Effective use of hexagon maps requires careful consideration of the data being represented, the desired level of detail, and the intended audience. It’s important to choose an appropriate hexagon size, select appropriate data visualization techniques, and clearly label the map elements.
4. How do hexagon maps compare to other map types?
Compared to traditional square grids, hexagon maps offer greater uniformity, reduced distortion, and improved visual appeal. They are also more suitable for spatial analysis, particularly for identifying spatial patterns and correlations. However, they may not be as suitable for representing complex geometries or very small-scale features.
Tips for Using Hexagon Maps Effectively
- Choose the appropriate hexagon size: The size of the hexagon should be chosen based on the scale of the data and the desired level of detail.
- Use appropriate data visualization techniques: Different data visualization techniques, such as color gradients, size variations, and symbols, can be used to effectively represent different types of data.
- Clearly label map elements: Ensure that all map elements, including the legend, scale bar, and data labels, are clearly labelled and easily understandable.
- Consider the intended audience: The design and presentation of the hexagon map should be tailored to the intended audience, ensuring that the map is clear, informative, and engaging.
Conclusion
Hexagon maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data. Their unique properties, including uniformity, reduced distortion, and efficient data visualization, make them ideal for a wide range of applications. By understanding the advantages and limitations of hexagon maps, researchers, analysts, and professionals across various fields can leverage their potential to gain valuable insights from spatial data and make informed decisions.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Hexagon Map: A Versatile Tool for Visualization and Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!