North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads of History
Related Articles: North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads of History
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads of History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads of History

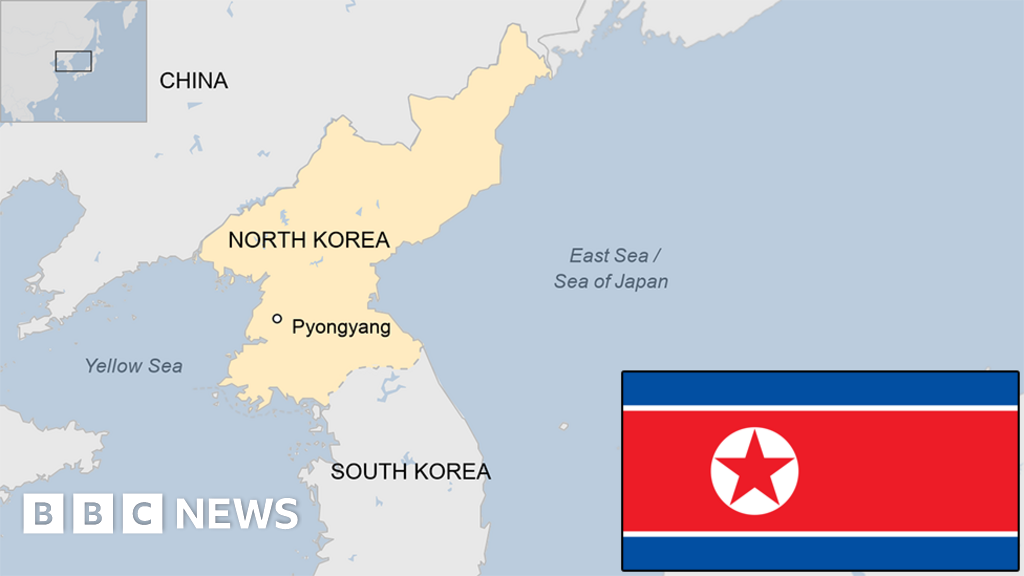
North Korea, officially the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), occupies the northern portion of the Korean Peninsula, a landmass jutting out from the eastern coast of Asia. Its strategic location, nestled between powerful neighbors, has shaped its history and continues to influence its current political and economic landscape.
A Geographic Overview:
North Korea’s geography is a mix of rugged mountains, fertile plains, and a long coastline. The Taebaek Mountains, a major mountain range that extends across the Korean Peninsula, dominate the country’s interior, with Mount Paektu, considered a sacred mountain in Korean culture, reaching a height of 2,744 meters. These mountains create a barrier between the east and west, influencing the country’s climate and accessibility.
The country’s eastern coastline, facing the Sea of Japan, is characterized by dramatic cliffs, rocky inlets, and numerous islands. The western coastline, bordering the Yellow Sea, is relatively flat and features extensive tidal flats. These diverse coastal areas offer potential for fishing and aquaculture, though their development has been limited by political and economic factors.
A Nation Divided:
The Korean Peninsula was historically a single entity, but it was divided following World War II. The 38th parallel, a line of latitude established by the Allied powers, became the dividing line between North Korea, backed by the Soviet Union, and South Korea, supported by the United States. This division, solidified by the Korean War (1950-1953), has resulted in a complex geopolitical situation with lasting ramifications.
Neighboring Countries:
North Korea’s geographic location places it in the midst of a complex web of international relations. It shares borders with China, its largest trading partner and a major source of economic and political support, to the north and Russia, another important ally, to the northeast. To the south, it is separated from South Korea by a heavily fortified demilitarized zone (DMZ), a testament to the ongoing Cold War legacy.
Key Cities and Regions:
- Pyongyang, the capital city, is located in the western part of the country on the Taedong River. It is the center of government, industry, and culture.
- Wonsan, a port city on the east coast, is known for its scenic beauty and its potential for tourism development.
- Hamhung, the second-largest city, is an industrial center with a focus on chemical production and heavy industries.
- Kaesong, located near the DMZ, is a historic city known for its ancient temples and its role as a special economic zone for inter-Korean cooperation.
The Impact of Geography:
North Korea’s mountainous terrain has made transportation and communication challenging. It has also influenced the country’s agricultural practices, with rice cultivation being the mainstay in the plains while the mountainous areas are suitable for forestry and livestock farming.
The country’s proximity to China and Russia has provided it with access to key resources and markets, but it has also made it vulnerable to regional power dynamics. The division from South Korea has created a unique geopolitical situation, with the DMZ becoming a symbol of the Cold War and a barrier to economic and social integration.
Understanding the Significance:
North Korea’s location at the heart of Northeast Asia makes it a critical player in regional security and stability. Its nuclear program, its complex relationship with the United States, and its economic ties with China and Russia all contribute to the geopolitical significance of the country.
Understanding where North Korea is on the map is crucial for comprehending its history, its current situation, and its potential future trajectory. Its location shapes its interactions with its neighbors, its access to resources, and its role in the global political landscape.
FAQs:
Q: What is the capital of North Korea?
A: The capital of North Korea is Pyongyang.
Q: What is the official name of North Korea?
A: The official name of North Korea is the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK).
Q: What is the population of North Korea?
A: The estimated population of North Korea is around 25 million.
Q: What is the currency of North Korea?
A: The currency of North Korea is the North Korean won.
Q: What is the primary language spoken in North Korea?
A: The primary language spoken in North Korea is Korean.
Q: What is the political system of North Korea?
A: North Korea is a socialist state with a one-party system led by the Workers’ Party of Korea.
Q: What is the climate like in North Korea?
A: North Korea experiences a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The winters are cold and dry, while the summers are hot and humid.
Q: What are some of the major industries in North Korea?
A: North Korea’s economy is heavily reliant on heavy industries such as mining, manufacturing, and energy production. Agriculture also plays a significant role.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing North Korea?
A: North Korea faces numerous challenges, including economic stagnation, political isolation, food shortages, and a lack of human rights.
Tips:
- Use a reliable map: Utilize a world map or an online mapping service to pinpoint North Korea’s location.
- Look for neighboring countries: Identify China, Russia, and South Korea on the map to understand North Korea’s geographical context.
- Explore the Korean Peninsula: Examine the Korean Peninsula as a whole to grasp the historical and political factors that led to the division between North and South Korea.
- Read about North Korean history: Research the Korean War, the division of the peninsula, and the rise of the DPRK to gain a deeper understanding of the country’s past and present.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up with news and developments related to North Korea to stay informed about its evolving political and economic landscape.
Conclusion:
North Korea’s location on the map is not just a geographical marker; it is a key element in understanding its history, its current challenges, and its potential future. Its strategic location, its divided past, and its complex relationships with neighboring countries continue to shape its destiny. By understanding where North Korea is on the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of this enigmatic nation and its role in the ever-changing global landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads of History. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
