Navigating the World: Understanding the International Time Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the International Time Zone Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding the International Time Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding the International Time Zone Map

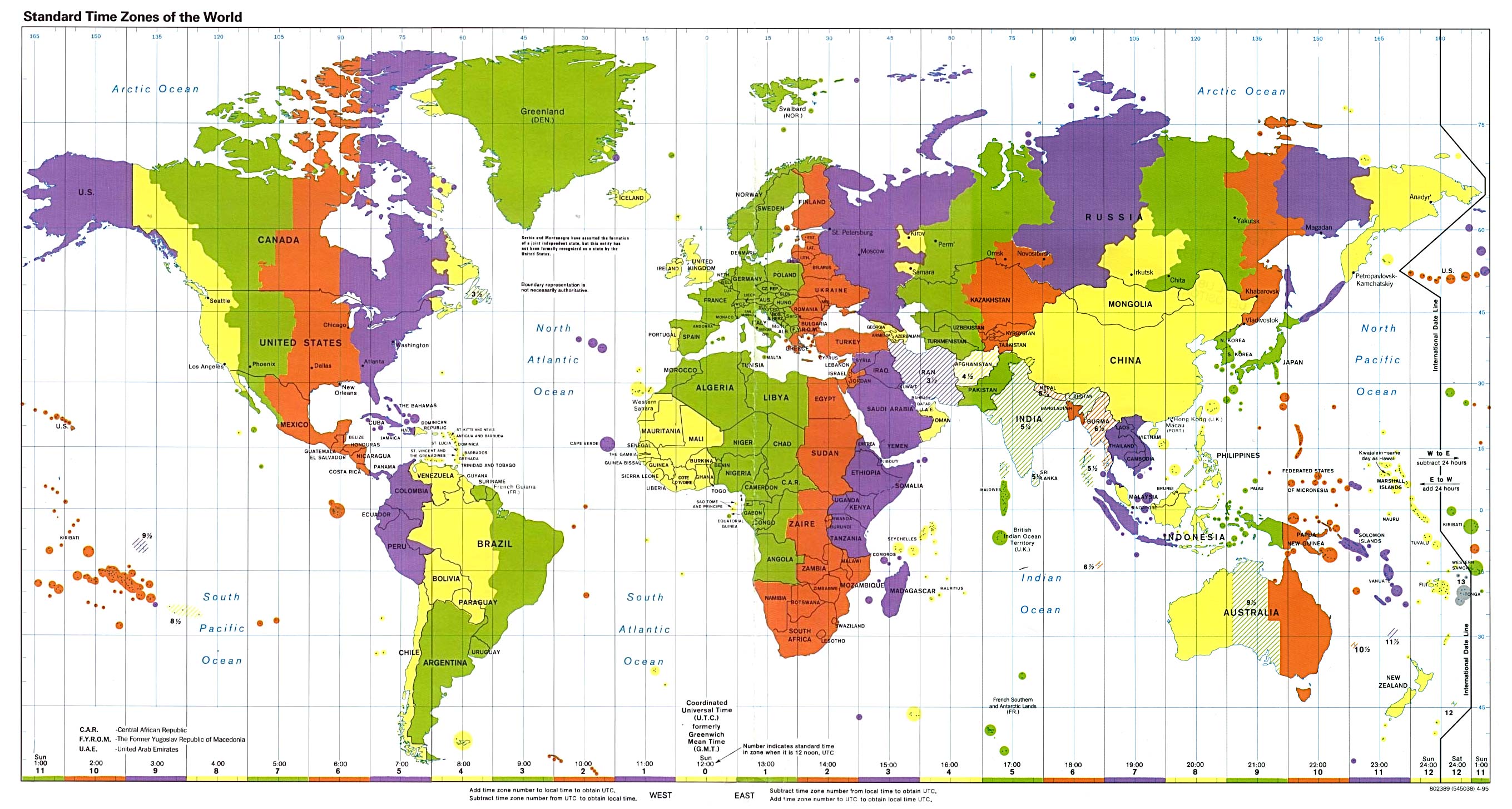
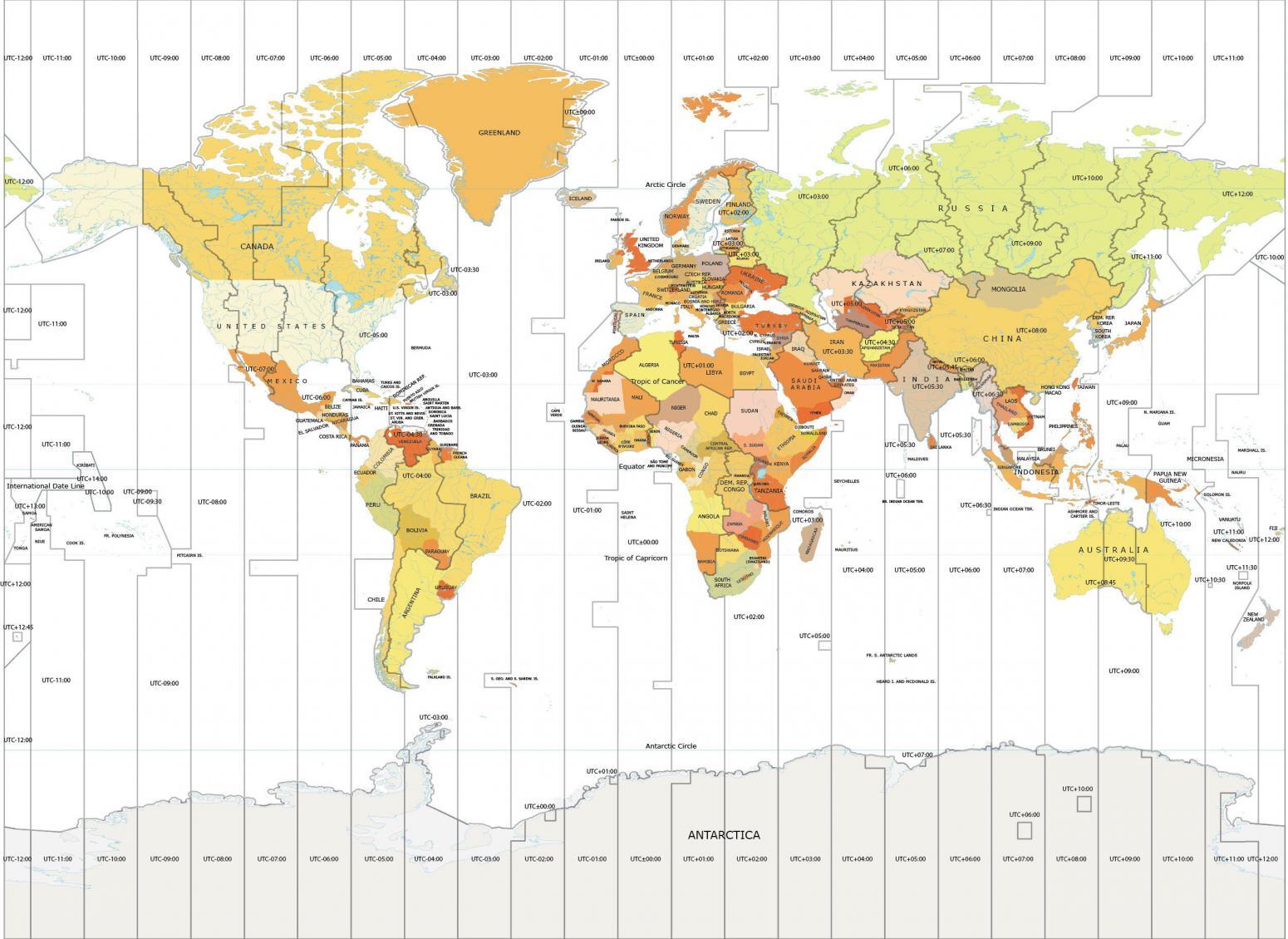
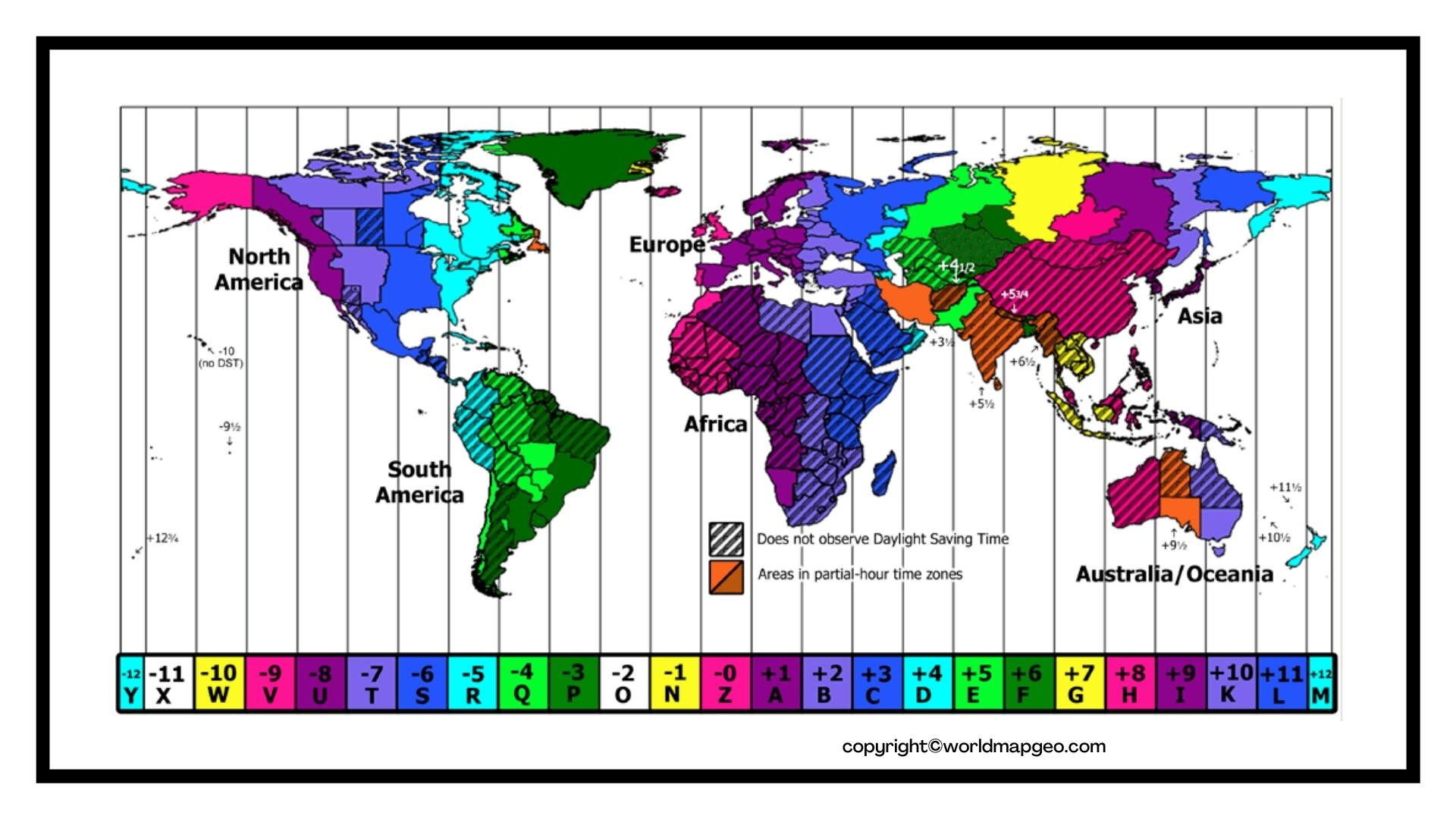
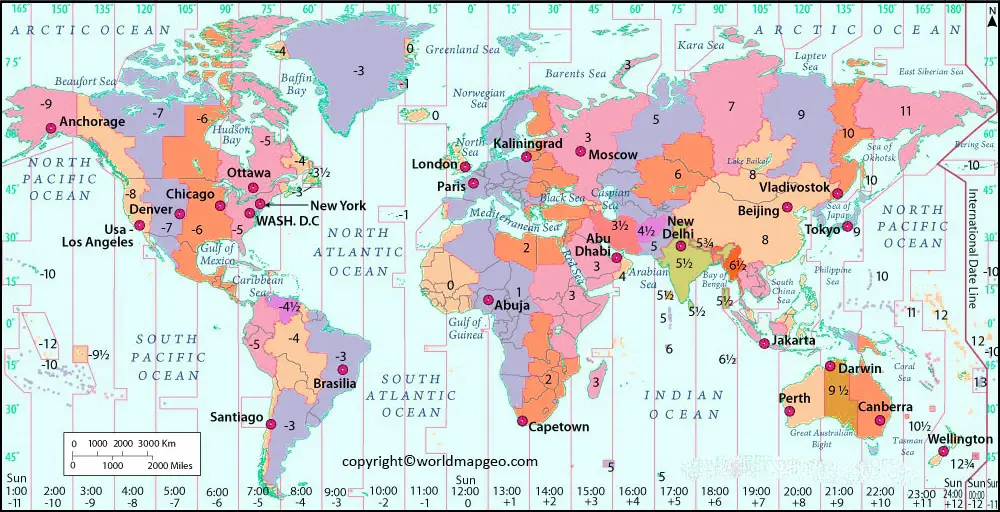
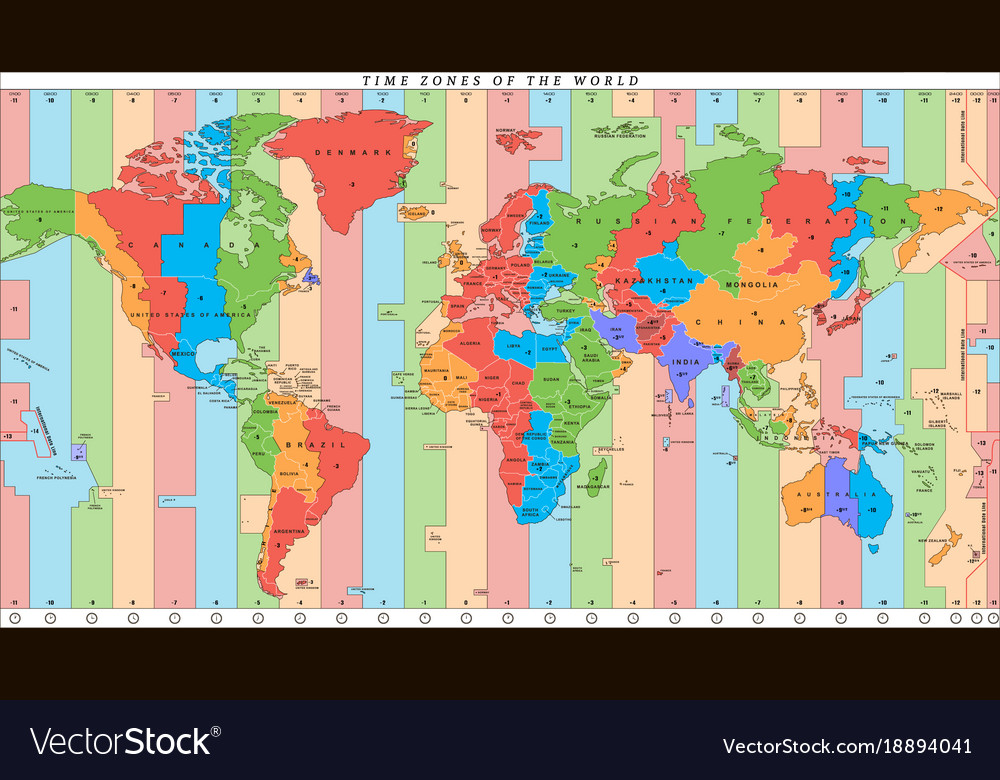
The Earth, a sphere rotating on its axis, experiences the sun’s rays at different times depending on its position. This simple fact is the foundation for the complex system of time zones that govern our daily lives. An international time zone map is a visual representation of this system, depicting the world divided into 24 time zones, each corresponding to a specific hour of the day.
A Global Grid: The Foundation of Time Zones
Imagine a grid drawn over the Earth, with lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole, marking 15-degree intervals of longitude. Each of these lines represents a time zone. This grid, while seemingly arbitrary, is based on the Earth’s rotation. The planet completes one full rotation in approximately 24 hours, and each time zone represents a single hour of this rotation.
The Prime Meridian: The Starting Point
The starting point of this global grid is the Prime Meridian, a line of longitude that passes through Greenwich, England. It marks the 0° longitude and serves as the reference point for all other time zones.
Standard Time: A Global Agreement
To maintain order and avoid confusion, each time zone adheres to a standard time. This standard time is based on the solar time at the center of the time zone. For instance, the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the standard time for the time zone encompassing the Prime Meridian.
The International Date Line: Where Yesterday Meets Tomorrow
The International Date Line, roughly following the 180° meridian, marks the boundary between two consecutive days. When crossing the International Date Line eastward, one gains a day, while crossing it westward results in losing a day. This seemingly paradoxical phenomenon is a consequence of the Earth’s rotation.
The Importance of Time Zones: A Global Network
The international time zone map is not merely a geographical curiosity; it is a vital tool for facilitating communication, commerce, and travel across the globe. It enables individuals, businesses, and governments to coordinate activities, schedule meetings, and conduct transactions across time zones.
Understanding Time Zones: A Practical Guide
- UTC: The Universal Time Standard: UTC, or Coordinated Universal Time, is the primary time standard used worldwide. It is based on atomic clocks and serves as the reference time for all other time zones.
- Time Zone Abbreviations: Each time zone has a unique abbreviation, such as EST (Eastern Standard Time) or PST (Pacific Standard Time). These abbreviations facilitate communication and understanding across time zones.
- Daylight Saving Time: Many countries implement Daylight Saving Time (DST) during certain months to make better use of daylight hours. During DST, clocks are moved forward by one hour.
- Time Zone Converters: Numerous online tools and mobile applications offer convenient time zone converters, allowing users to quickly determine the current time in different locations around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why are there 24 time zones?
A: The Earth rotates 360 degrees in approximately 24 hours. Each time zone represents a 15-degree segment of this rotation, resulting in 24 time zones.
Q: Why do some countries have multiple time zones?
A: Countries that span a significant longitudinal distance may have multiple time zones to account for the varying solar times across their territory.
Q: How do I calculate the time difference between two time zones?
A: The time difference between two time zones is determined by the number of 15-degree longitude intervals between them. Each interval represents one hour.
Q: What is the difference between GMT and UTC?
A: GMT is the standard time for the time zone encompassing the Prime Meridian. UTC is the primary time standard used worldwide, based on atomic clocks. While GMT and UTC are often used interchangeably, UTC is more precise and is the preferred standard for scientific and technical applications.
Q: What is the International Date Line and why is it important?
A: The International Date Line, roughly following the 180° meridian, marks the boundary between two consecutive days. It is essential for maintaining a consistent calendar system across the globe.
Tips for Navigating Time Zones
- Utilize online time zone converters: These tools allow you to quickly determine the current time in different locations.
- Familiarize yourself with time zone abbreviations: Understanding time zone abbreviations will help you communicate effectively across time zones.
- Plan ahead for international travel: Factor in the time difference when scheduling meetings, flights, and other activities.
- Be mindful of Daylight Saving Time: Remember to adjust your clocks accordingly when DST is implemented.
- Use a world clock app: Many mobile apps offer world clock features, displaying the current time in multiple locations simultaneously.
Conclusion
The international time zone map is a vital tool for navigating the complexities of time across the globe. By understanding the system of time zones, we can effectively communicate, conduct business, and travel across different regions, fostering a more interconnected and efficient world. As technology continues to advance, the importance of time zones will only grow, ensuring that our global society can function seamlessly despite the Earth’s rotation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding the International Time Zone Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!