Navigating the Tapestry of Indigenous America: A Guide to the Native American Tribe Map of the United States
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Indigenous America: A Guide to the Native American Tribe Map of the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Indigenous America: A Guide to the Native American Tribe Map of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Indigenous America: A Guide to the Native American Tribe Map of the United States

The United States is a land rich with diverse cultures, landscapes, and histories. Among these interwoven threads, the legacy of Native American tribes stands out as a vital and often overlooked component of the nation’s identity. Understanding the geographical distribution of these tribes, their unique traditions, and their enduring presence is crucial for appreciating the complexities of American history and fostering a more inclusive and respectful society.
A Visual Guide to Indigenous America:
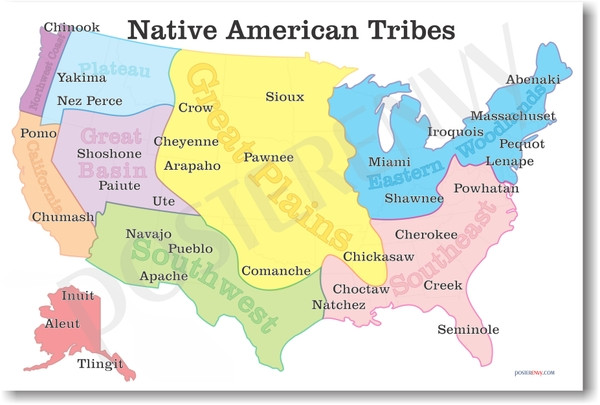
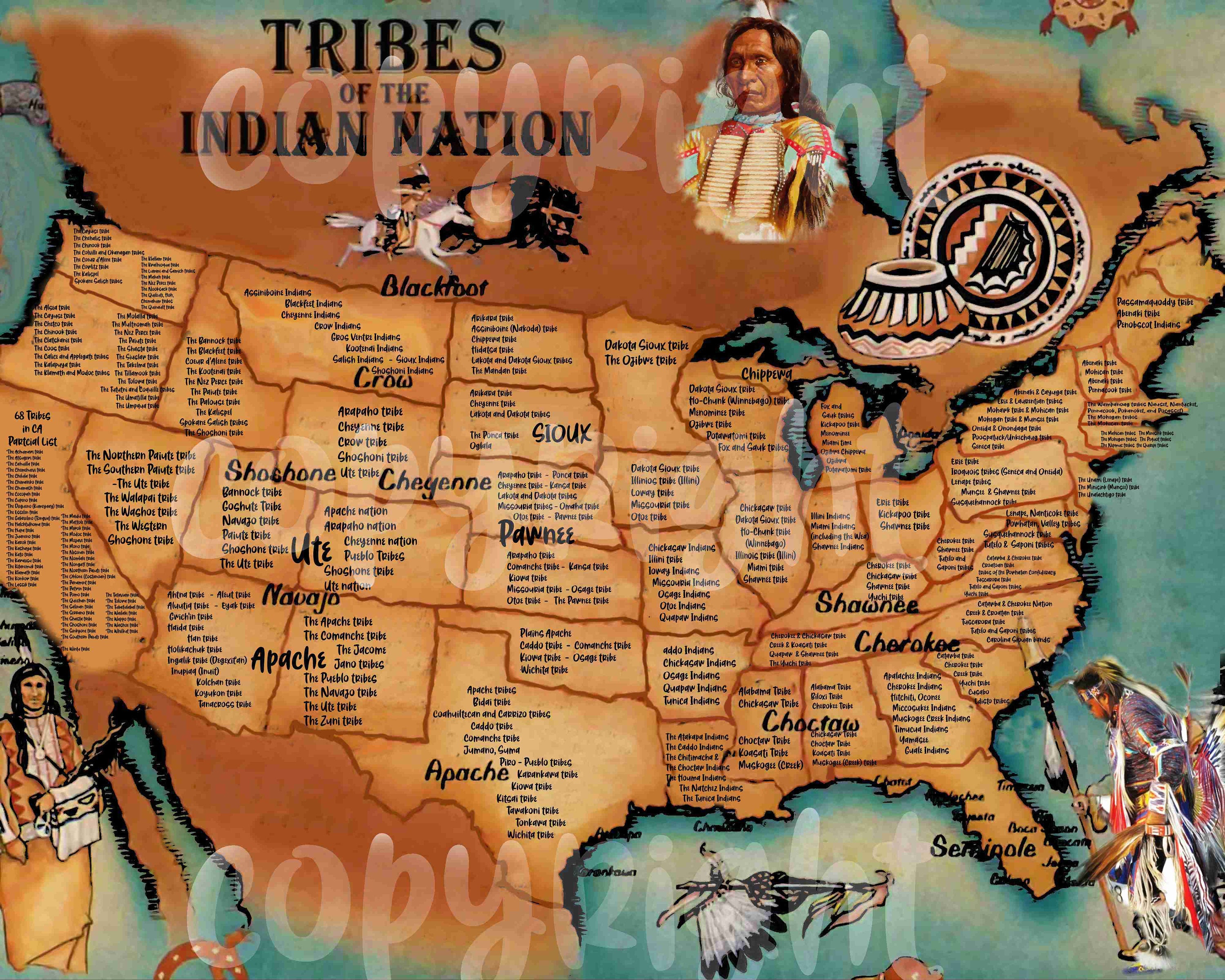
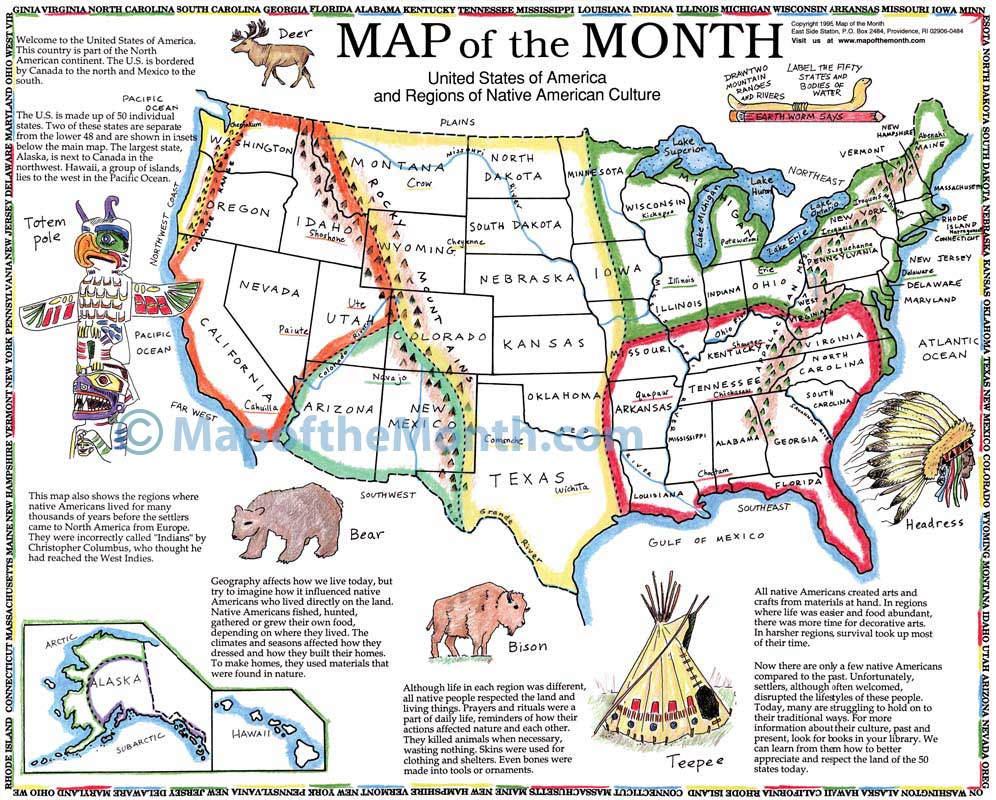
The Native American Tribe Map of the United States serves as a powerful tool for visualizing the vibrant tapestry of indigenous cultures across the country. It reveals the intricate network of tribal lands, reservations, and historical territories, offering a glimpse into the diverse linguistic families, cultural practices, and political structures that have shaped the nation’s landscape.
Beyond Borders: The Significance of the Map:
The map transcends its role as a mere geographical representation. It serves as a vital resource for:
- Historical Understanding: The map provides a tangible connection to the past, revealing the pre-colonial presence of indigenous peoples and their complex relationships with the land. It highlights the profound impact of colonization and forced displacement on tribal nations, prompting reflection on the injustices of the past and the ongoing struggles for self-determination.
- Cultural Preservation: The map emphasizes the continued existence of distinct tribal cultures and languages, celebrating their resilience and adaptability. It serves as a guide for understanding the diverse traditions, ceremonies, and art forms that have been passed down through generations, fostering respect and appreciation for indigenous heritage.
- Political Recognition: The map underscores the sovereignty of tribal nations, acknowledging their unique legal status and their right to self-governance. It highlights the importance of respecting tribal treaty rights and engaging in meaningful consultation with tribal leaders on issues that affect their communities.
- Educational Awareness: The map serves as a valuable tool for education, promoting understanding and empathy for indigenous peoples. It encourages critical thinking about historical narratives and fosters a more inclusive and accurate representation of American history.
- Community Building: The map fosters connections between tribal communities and non-native individuals, promoting dialogue and collaboration. It encourages the sharing of knowledge and resources, fostering a spirit of mutual respect and understanding.
Navigating the Map: A Comprehensive Overview:
The Native American Tribe Map of the United States is a complex and dynamic representation, reflecting the ongoing evolution of tribal identities and the diverse landscapes they inhabit. To fully appreciate its richness, it is essential to understand the following key elements:
- Tribal Territories: The map identifies the traditional territories of various tribes, encompassing vast areas that extend beyond current reservation boundaries. These territories represent the ancestral homelands of indigenous peoples, reflecting their deep connection to the land and its resources.
- Reservations: The map designates the locations of federally recognized reservations, which are areas set aside for tribal use and governance. Reservations serve as centers of cultural and political life for many tribes, providing a space for self-determination and community building.
- Tribal Nations: The map acknowledges the distinct identities and sovereignty of individual tribal nations, each with its own unique history, language, culture, and governance structure. Recognizing the diversity of tribal nations is crucial for respecting their distinct identities and promoting cultural preservation.
- Linguistic Families: The map highlights the diverse linguistic families represented within the United States, showcasing the richness and complexity of indigenous languages. Understanding the linguistic landscape of the country provides a deeper appreciation for the cultural heritage of Native Americans.
- Historical Events: The map can be used to explore the historical context of tribal territories and reservations, highlighting the impact of colonization, treaties, and forced removal on indigenous communities. Understanding these events is essential for recognizing the ongoing challenges faced by tribal nations and advocating for their rights.
FAQs Regarding the Native American Tribe Map of the United States:
Q: What is the difference between a tribe and a nation?
A: The terms "tribe" and "nation" are often used interchangeably, but there is a distinction. "Tribe" refers to a group of people sharing a common language, culture, and territory. "Nation" emphasizes the political and legal status of a group, acknowledging their right to self-governance and sovereignty.
Q: Why are there so many different tribes in the United States?
A: The diversity of tribes in the United States reflects the vast and varied landscapes of the country, as well as the long history of indigenous peoples inhabiting these lands. Each tribe developed unique cultural practices, languages, and traditions in response to their specific environment and historical experiences.
Q: Are all Native American tribes federally recognized?
A: No, not all Native American tribes are federally recognized. Federal recognition is a complex process that involves meeting specific criteria established by the Bureau of Indian Affairs. Tribes that are federally recognized have access to certain benefits and legal protections, but many tribes remain unrecognized.
Q: What is the significance of treaty rights?
A: Treaty rights are agreements between the United States government and individual tribes, outlining specific rights and responsibilities. These treaties often address land ownership, resource management, and self-governance. Treaty rights are legally binding and play a crucial role in protecting tribal sovereignty and ensuring the well-being of indigenous communities.
Q: How can I learn more about specific tribes?
A: There are numerous resources available for learning about specific tribes, including tribal websites, museums, and educational institutions. Many tribes have dedicated websites that provide information about their history, culture, and current initiatives.
Tips for Using the Native American Tribe Map of the United States:
- Engage in Critical Thinking: Approach the map with an open mind, recognizing that it represents a complex and evolving landscape. Be mindful of the historical context and the ongoing challenges faced by indigenous communities.
- Respect Tribal Sovereignty: Acknowledge the unique legal status of tribal nations and their right to self-governance. Engage in respectful dialogue and consultation with tribal leaders on issues that affect their communities.
- Promote Cultural Awareness: Use the map as a tool for promoting understanding and appreciation of indigenous cultures. Explore the diverse traditions, languages, and art forms of Native American tribes.
- Support Tribal Communities: Seek out opportunities to support tribal businesses, organizations, and initiatives. Advocate for policies that promote tribal self-determination and economic development.
Conclusion:
The Native American Tribe Map of the United States serves as a powerful reminder of the enduring presence of indigenous peoples in the nation’s history and landscape. It underscores the importance of recognizing tribal sovereignty, promoting cultural preservation, and fostering respectful dialogue and collaboration between indigenous communities and non-native individuals. By understanding the complexities of the map and engaging with its narratives, we can contribute to a more inclusive and equitable future for all Americans.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Indigenous America: A Guide to the Native American Tribe Map of the United States. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!