Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Repeater Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Repeater Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Repeater Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Repeater Maps
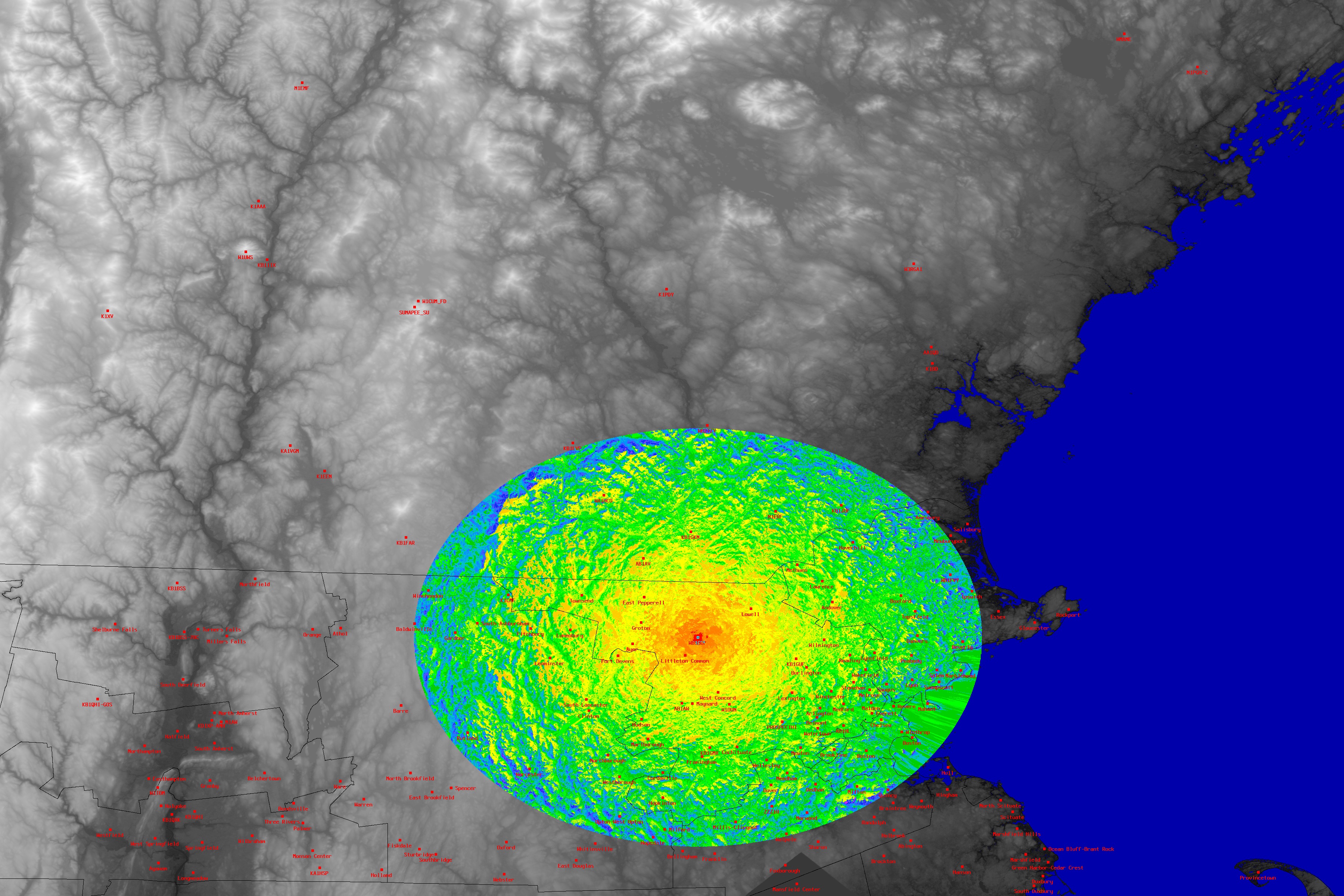
In the realm of wireless communication, the concept of signal propagation plays a pivotal role. Signals, whether they be radio waves, cellular data, or Wi-Fi, travel through the air, encountering obstacles and experiencing attenuation. This can lead to signal degradation, making it difficult for devices to communicate effectively. To overcome these challenges, repeaters are employed, acting as signal amplifiers, extending the reach of wireless networks.
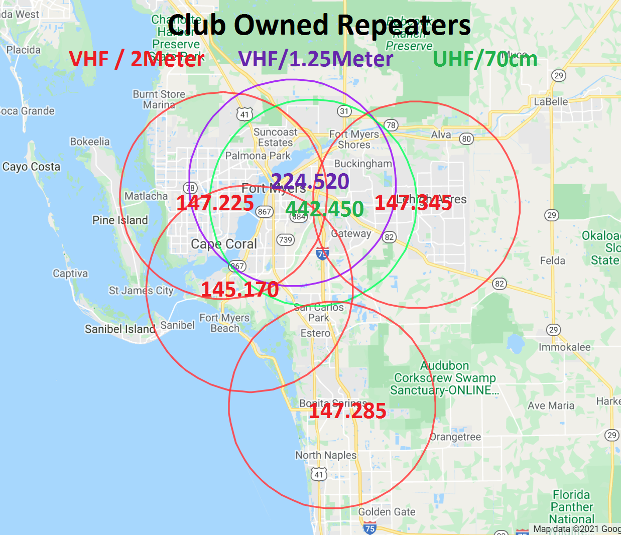
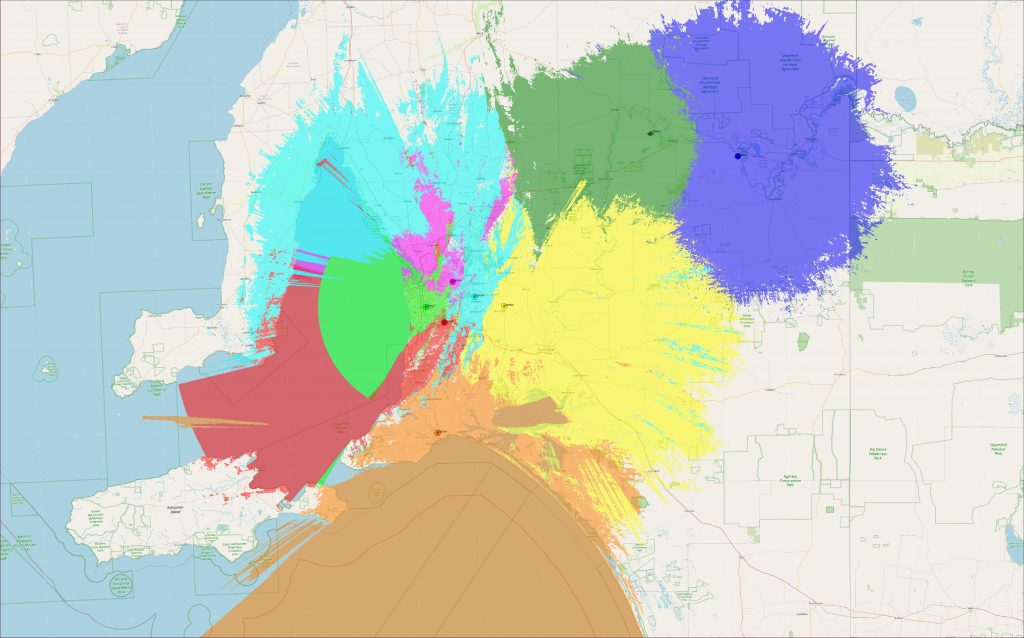
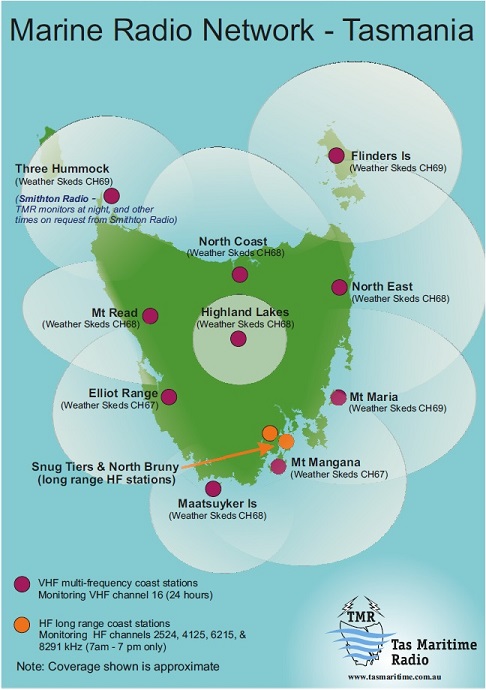
A repeater map, also known as a signal booster map, is a visual representation of the coverage area provided by repeaters within a specific region. These maps serve as essential tools for network operators, technicians, and individuals seeking to optimize their wireless connectivity. They offer a clear understanding of signal strength, potential blind spots, and the effectiveness of repeater deployment strategies.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Repeater Map
Repeater maps typically depict the following key elements:
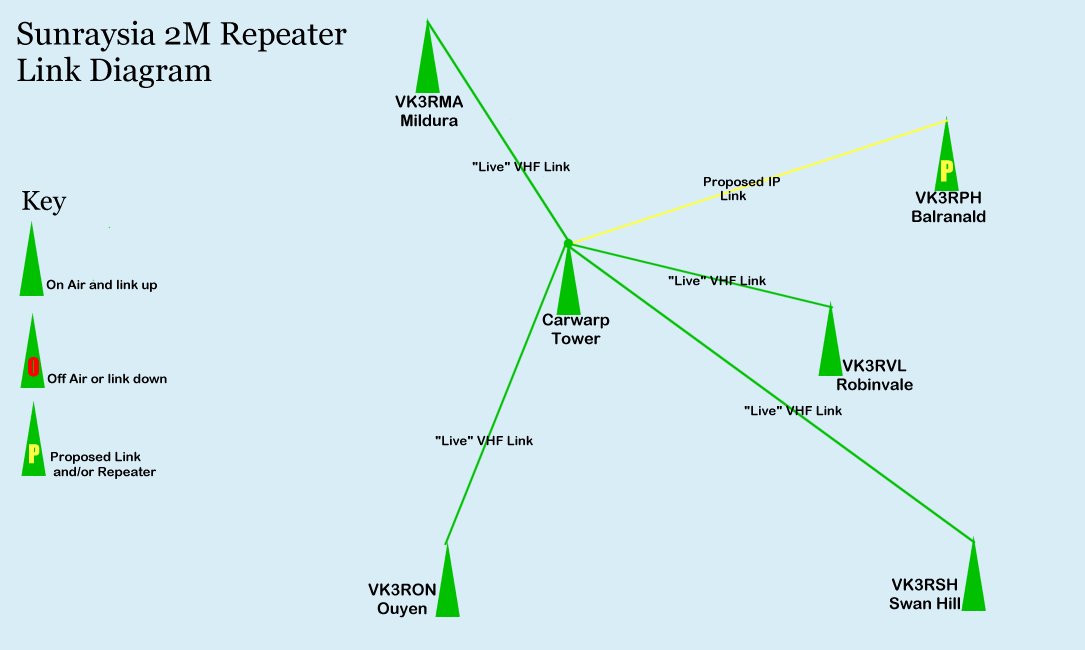
- Repeater Locations: The map clearly identifies the positions of repeaters within the covered area. This information is crucial for assessing the overall network infrastructure and identifying potential areas for improvement.
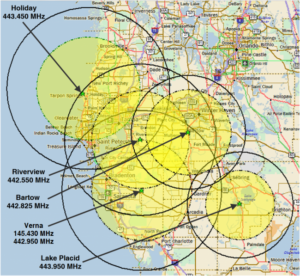
- Signal Strength Contours: The map uses color gradients or contour lines to represent the strength of the wireless signal at different locations. This visual representation allows users to identify areas with strong signal coverage, areas with weak signals, and areas that may require additional repeaters.
- Coverage Zones: The map defines distinct areas that are covered by specific repeaters. This information is particularly useful for network planning and troubleshooting, as it allows users to pinpoint the specific repeater responsible for a particular area.
- Terrain and Obstacles: The map often incorporates topographical information, including buildings, mountains, and other obstacles that can affect signal propagation. This information is essential for understanding the potential impact of the environment on signal strength and identifying areas that may require specialized repeater configurations.
- Network Types: The map may specify the type of wireless network being covered, such as cellular networks, Wi-Fi networks, or radio communication systems. This information helps users understand the specific applications and limitations of the repeater network.
The Importance of Repeater Maps
Repeater maps are indispensable tools for various stakeholders, including:
- Network Operators: They provide valuable insights into network performance, allowing operators to identify areas with poor coverage, optimize repeater placement, and ensure optimal signal strength across the network.
- Technicians: Repeaters maps are essential for troubleshooting network issues, identifying the root cause of signal problems, and selecting the appropriate repeater configuration to address specific challenges.
- Consumers: Individuals seeking to improve their home or office Wi-Fi coverage can utilize repeater maps to understand the existing signal strength in their area and determine if additional repeaters are necessary.
- Emergency Response Teams: In disaster scenarios, repeater maps play a crucial role in establishing reliable communication networks for emergency responders and coordinating relief efforts.
Benefits of Utilizing Repeater Maps
The use of repeater maps offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Network Coverage: By providing a clear understanding of signal strength and coverage areas, repeater maps enable network operators to strategically deploy repeaters, expanding network reach and eliminating blind spots.
- Improved Network Performance: Optimized repeater placement, guided by repeater maps, ensures efficient signal transmission and reception, leading to faster data speeds, fewer dropped calls, and enhanced overall network performance.
- Cost-Effective Network Management: Repeater maps facilitate efficient resource allocation by identifying areas where repeaters are most effective, reducing unnecessary deployments and minimizing operational costs.
- Enhanced User Experience: Improved signal coverage and network performance translate into a smoother and more reliable wireless experience for users, enhancing productivity and satisfaction.
FAQs about Repeater Maps
1. How are Repeater Maps Created?
Repeater maps are typically generated through a combination of site surveys, signal strength measurements, and specialized software. Site surveys involve physically visiting locations within the coverage area and collecting data on signal strength, while signal strength measurements are often conducted using drive tests or walk tests. The collected data is then processed by software that generates visual representations of the coverage area, highlighting signal strengths and potential blind spots.
2. What are the Different Types of Repeater Maps?
Repeater maps can be categorized based on the type of network they represent, the level of detail they provide, and the intended use. Some common types include:
- Cellular Network Maps: These maps depict the coverage area of cellular networks, providing information on signal strength, coverage zones, and the location of cell towers.
- Wi-Fi Network Maps: These maps illustrate the coverage area of Wi-Fi networks, highlighting areas with strong signal strength, areas with weak signals, and potential areas for repeater deployment.
- Radio Communication Maps: These maps focus on the coverage area of radio communication systems, such as those used by emergency responders or commercial businesses.
- Indoor Maps: These maps specifically target the coverage area within buildings, providing detailed information on signal strength and potential areas for repeater placement.
- Outdoor Maps: These maps focus on the coverage area outside buildings, considering the impact of terrain and obstacles on signal propagation.
3. Where Can I Find Repeater Maps?
Repeater maps are often provided by network operators, equipment manufacturers, and specialized mapping companies. Some online resources, such as websites dedicated to wireless network coverage, may also offer access to repeater maps for specific regions.
4. How Can I Use a Repeater Map to Improve My Wi-Fi Coverage?
By analyzing a repeater map, you can identify areas in your home or office with weak Wi-Fi signals. You can then strategically place a Wi-Fi repeater in these areas to extend the range of your existing Wi-Fi network and improve overall coverage.
5. Are Repeater Maps Always Accurate?
The accuracy of repeater maps depends on the quality of the data used to create them, the sophistication of the mapping software, and the dynamic nature of wireless signals. Factors such as weather conditions, building materials, and the presence of other wireless devices can influence signal strength and coverage. It’s important to note that repeater maps provide a general overview of signal coverage and may not accurately reflect real-time signal conditions.
Tips for Optimizing Repeater Deployment
- Consider the Environment: Before deploying repeaters, carefully assess the environment, taking into account factors such as building materials, obstacles, and terrain. This information will help you choose the appropriate repeater type and placement strategy.
- Choose the Right Repeater Type: Different types of repeaters are available, each designed for specific applications. Consider the type of wireless network you’re trying to extend, the desired coverage area, and the signal strength requirements to select the most suitable repeater.
- Optimize Repeater Placement: Strategic placement of repeaters is crucial for maximizing signal coverage and minimizing interference. Consider the location of the main router, the presence of obstacles, and the desired coverage area to determine the optimal positions for repeaters.
- Monitor Network Performance: After deploying repeaters, regularly monitor network performance to ensure they are functioning effectively. Identify any areas with weak signals or potential interference and adjust repeater placement or configuration accordingly.
Conclusion
Repeater maps are essential tools for navigating the complex world of wireless communication. By providing a visual representation of signal strength, coverage areas, and repeater locations, they empower network operators, technicians, and individuals to optimize their wireless networks, enhancing coverage, improving performance, and ensuring a seamless user experience. As technology advances and wireless communication becomes increasingly ubiquitous, the importance of repeater maps will only grow, serving as indispensable guides in building and managing robust and reliable wireless networks.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Repeater Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!