Navigating the Flames: Understanding California’s Fire Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Flames: Understanding California’s Fire Zone Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Flames: Understanding California’s Fire Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Flames: Understanding California’s Fire Zone Map
![]()
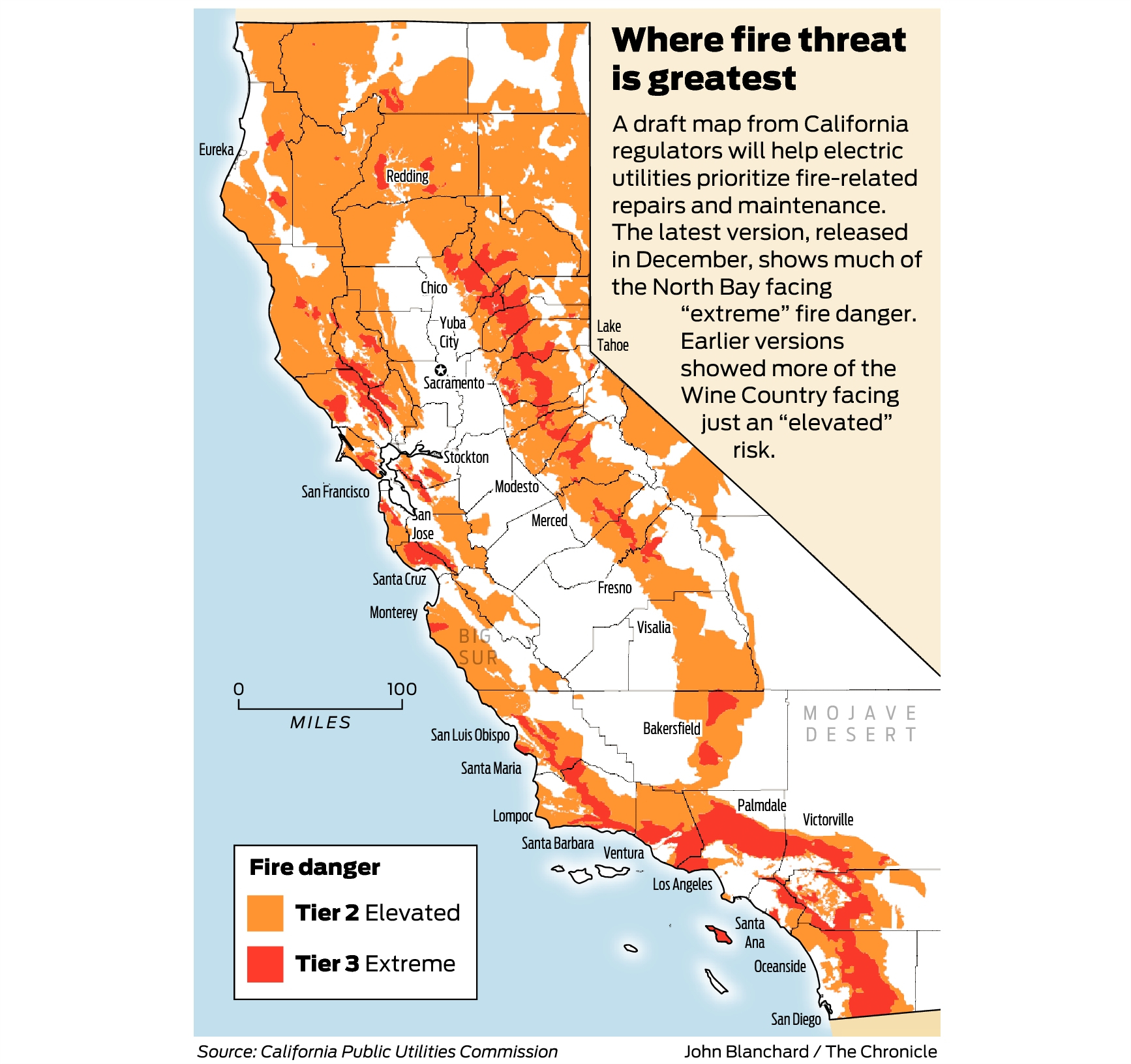
California, renowned for its diverse landscapes, also faces the stark reality of wildfire threats. These destructive forces, fueled by a combination of climate change, dry vegetation, and human activity, pose significant risks to life, property, and the environment. To better prepare for and mitigate these risks, the state utilizes a comprehensive tool: the California Fire Zone Map.
A Framework for Understanding Risk:
The Fire Zone Map, developed and maintained by the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire), classifies areas across the state based on their wildfire hazard potential. This classification system is crucial for various stakeholders, including:
- Homeowners: Understanding the fire hazard level of their property allows for informed decision-making regarding fire-resistant building materials, landscaping, and emergency preparedness plans.
- Insurance Companies: The map serves as a guide for assessing wildfire risk and setting insurance premiums.
- Emergency Responders: Firefighters and other first responders utilize the map to prioritize resources and develop effective fire suppression strategies.
- Land Managers: The map aids in identifying high-risk areas for preventative measures, such as controlled burns and fuel reduction projects.
- Local Governments: The map informs land-use planning and development decisions, ensuring responsible development practices in fire-prone areas.
Decoding the Map:
The California Fire Zone Map categorizes the state into seven distinct zones, each representing a different level of wildfire hazard:
Zone 1: Very Low Hazard
- Characterized by areas with minimal vegetation, such as urban areas with significant fire suppression capabilities and coastal regions with high humidity.
- These areas generally experience low wildfire risk.
Zone 2: Low Hazard
- Includes areas with moderate vegetation density and moderate fire suppression capabilities.
- Wildfires in these areas are less frequent and less intense compared to higher hazard zones.
Zone 3: Moderate Hazard
- Areas with a mix of vegetation types and a moderate to high risk of wildfire occurrence.
- Wildfires in these areas can be more frequent and potentially intense.
Zone 4: High Hazard
- Predominantly characterized by chaparral, grasslands, and forests with dense vegetation.
- Wildfires in these areas are more frequent and intense, often spreading rapidly and posing significant threats to life and property.
Zone 5: Very High Hazard
- Areas with extremely dense vegetation, steep slopes, and limited access for fire suppression.
- Wildfires in these areas are highly likely, often exhibiting rapid spread and extreme intensity.
Zone 6: Extreme Hazard
- Consists of areas with the highest risk of wildfire occurrence and intensity.
- These areas are characterized by extreme vegetation density, difficult terrain, and limited access for firefighting.
Zone 7: Wildland Urban Interface (WUI)
- This zone encompasses areas where wildland vegetation meets urban development.
- The WUI poses a unique challenge as wildfires can easily spread from wildland areas into residential neighborhoods, increasing the risk of property damage and loss of life.
Beyond the Zones:
The Fire Zone Map serves as a crucial starting point for understanding wildfire risk, but it is important to remember that it provides a broad overview. Factors not explicitly reflected on the map, such as weather conditions, topography, and human activity, can significantly influence wildfire behavior.
Utilizing the Map for Preparedness:
The California Fire Zone Map is a valuable tool for individuals, communities, and agencies to proactively address wildfire risks. By understanding the specific fire hazard level of their location, stakeholders can:
- Develop Personalized Fire Safety Plans: Tailored plans should address evacuation routes, fire-resistant landscaping, and emergency supplies.
- Implement Fire-Resistant Construction Practices: Utilizing fire-resistant building materials and landscaping can significantly reduce the risk of property damage.
- Engage in Community Wildfire Preparedness: Participating in community events, workshops, and drills helps foster awareness and preparedness.
- Support Fuel Reduction Projects: Collaborating with local authorities and land managers to reduce fuel loads in high-risk areas can mitigate the intensity and spread of wildfires.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions:
Q: How can I find my fire zone?
A: The California Fire Zone Map is accessible online through various resources, including the Cal Fire website and interactive maps. You can search by address or zip code to identify your specific zone.
Q: What does my fire zone tell me about my risk?
A: Your fire zone provides a general indication of wildfire risk based on factors like vegetation density, topography, and historical wildfire activity. However, it is crucial to consider local factors and stay informed about current fire danger levels.
Q: How often is the Fire Zone Map updated?
A: The Fire Zone Map is periodically updated by Cal Fire as new data becomes available and as wildfire risks evolve. It is recommended to check for the latest version of the map regularly.
Q: Is the Fire Zone Map a guarantee of safety?
A: The Fire Zone Map is a valuable tool for understanding wildfire risk, but it is not a guarantee of safety. Wildfires can occur in any area, and it is crucial to remain vigilant and prepared regardless of your fire zone.
Tips for Enhanced Wildfire Safety:
- Maintain a defensible space around your home: Clear vegetation and remove flammable materials from a minimum of 30 feet around structures.
- Regularly inspect and maintain your home’s fire safety systems: Ensure smoke detectors and sprinklers are functional and up-to-date.
- Stay informed about current fire danger levels and weather conditions: Pay attention to official alerts and warnings issued by local authorities.
- Develop a family evacuation plan: Practice evacuation routes and establish a designated meeting place.
- Be aware of potential ignition sources: Exercise caution when using outdoor equipment, disposing of cigarettes, and managing campfires.
Conclusion:
The California Fire Zone Map serves as a vital tool for navigating the complex and challenging landscape of wildfire risk in the state. By understanding the fire hazard level of their location and incorporating the map’s insights into their preparedness plans, individuals, communities, and agencies can take proactive steps to mitigate wildfire threats and protect lives, property, and the environment.
While the map provides valuable guidance, it is essential to remember that wildfire risk is dynamic and influenced by numerous factors. Continuous vigilance, responsible land management practices, and a strong commitment to community preparedness are crucial for safeguarding California’s future against the threat of wildfires.




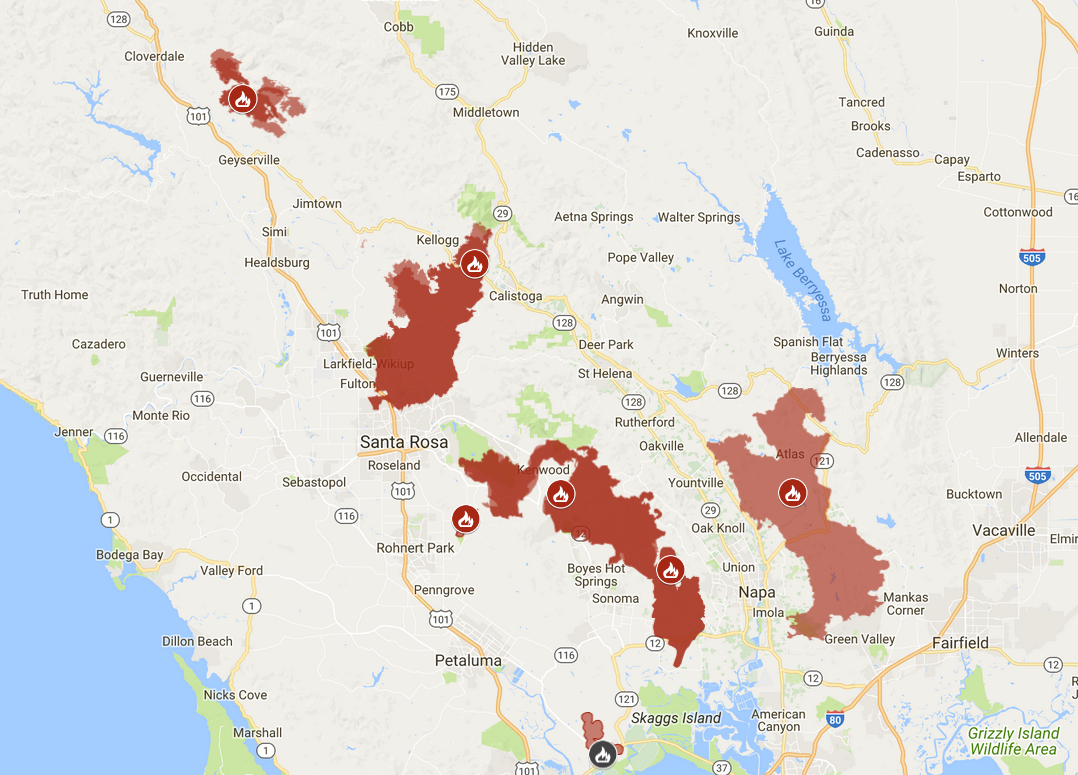
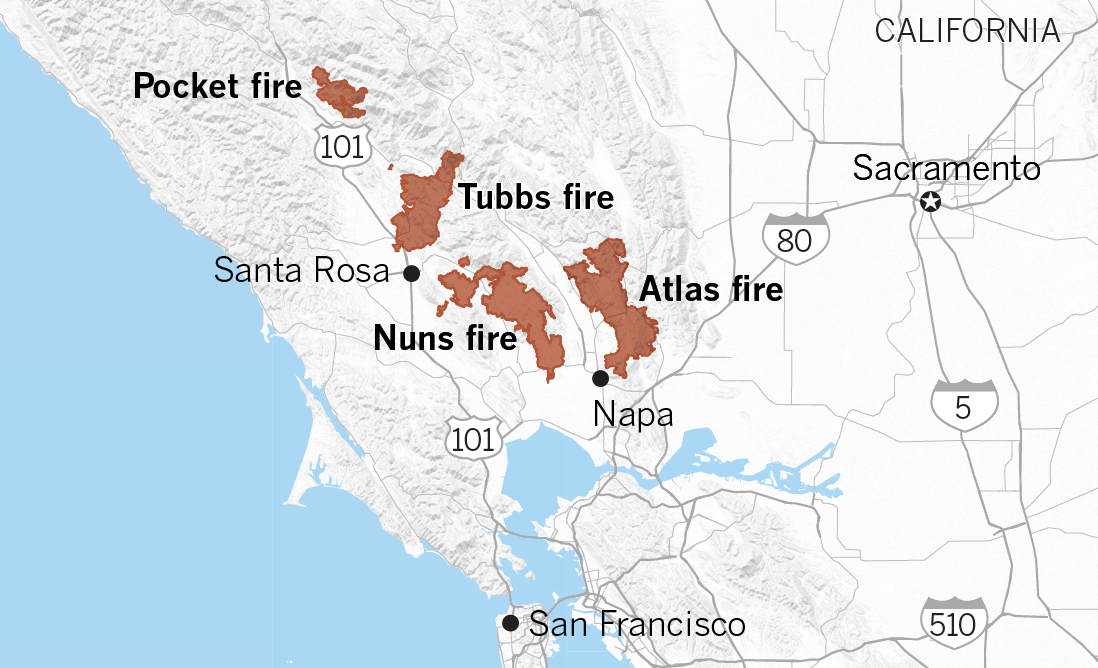

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Flames: Understanding California’s Fire Zone Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!