Navigating Montana’s Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to Reservations
Related Articles: Navigating Montana’s Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to Reservations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Montana’s Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to Reservations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Montana’s Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to Reservations
Montana’s landscape, a tapestry of rugged mountains, vast plains, and shimmering rivers, holds within its embrace a rich and diverse cultural heritage. This heritage is intricately woven with the presence of nine sovereign Native American nations, each with its own unique history, traditions, and governance. Understanding the geography of these nations, their historical context, and their ongoing significance is crucial for appreciating Montana’s multifaceted identity.
A Tapestry of Sovereignty: Exploring Montana’s Reservations
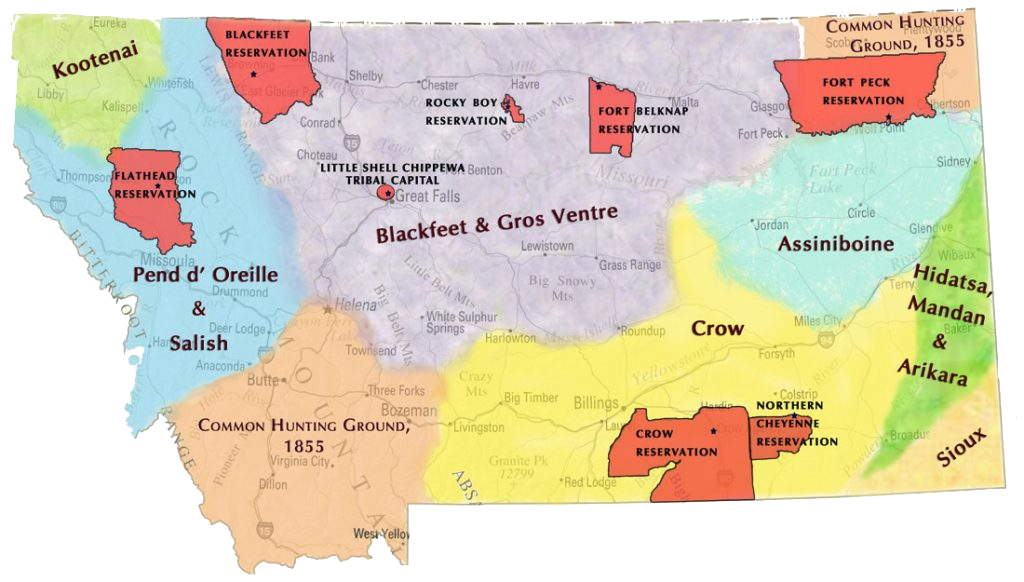
Montana’s reservations, encompassing a significant portion of the state’s landmass, are not merely geographical entities; they are vibrant communities, each with its own distinct cultural tapestry. These reservations are:
- The Blackfeet Nation: Situated in the northwest corner of Montana, the Blackfeet Nation encompasses the Blackfeet Indian Reservation, home to the Blackfeet people, known for their equestrian skills and rich cultural traditions.
- The Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes: Located in the western part of the state, the Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes govern the Flathead Indian Reservation, where the Salish, Kootenai, and Pend d’Oreille peoples have resided for centuries.
- The Crow Nation: In southeastern Montana, the Crow Nation governs the Crow Indian Reservation, a vast expanse known for its historical significance and the Crow people’s enduring connection to the land.
- The Fort Belknap Indian Community: Situated in north-central Montana, the Fort Belknap Indian Community governs the Fort Belknap Reservation, a shared home for the Assiniboine and Gros Ventre peoples, known for their resilience and cultural continuity.
- The Fort Peck Tribes: Located in northeastern Montana, the Fort Peck Tribes govern the Fort Peck Reservation, home to the Assiniboine and Sioux peoples, united by their shared history and cultural traditions.
- The Northern Cheyenne Tribe: Situated in southeastern Montana, the Northern Cheyenne Tribe governs the Northern Cheyenne Reservation, a place of historical significance and cultural resilience for the Cheyenne people.
- The Rocky Boy’s Indian Reservation: Situated in north-central Montana, the Rocky Boy’s Indian Reservation is home to the Chippewa Cree people, known for their cultural vibrancy and strong sense of community.
- The Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana: Recognized by the state of Montana, the Little Shell Tribe is a distinct group of Chippewa people who have long resided in the state, seeking federal recognition for their unique history and cultural heritage.
- The Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Reservation: A distinct tribal entity within the Fort Peck Reservation, the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes maintain their own governance and cultural practices.
Navigating the Map: Understanding the Significance of Reservations
A Montana reservation map serves as a vital tool for understanding the geographical context of these sovereign nations. It provides a visual representation of their boundaries, locations, and relationships to surrounding communities. However, the map is more than just a geographical tool; it is a representation of the enduring presence of Native American culture in Montana, highlighting the following key aspects:
- Sovereignty and Self-Governance: Montana’s reservations are sovereign entities, meaning they have the right to self-governance within their respective territories. This sovereignty extends to various aspects of life, including law enforcement, education, and economic development.
- Cultural Preservation and Heritage: Reservations are vital centers for the preservation and revitalization of Native American cultures. They serve as hubs for language immersion programs, cultural events, and the transmission of traditional knowledge from generation to generation.
- Economic Development and Self-Sufficiency: Reservations are actively engaged in economic development initiatives, aiming to create sustainable livelihoods for their members. These initiatives encompass various sectors, including tourism, agriculture, and renewable energy.
- Historical Significance and Land Rights: Reservations represent the historical and cultural connection of Native American tribes to their ancestral lands. They serve as reminders of the enduring relationship between these tribes and the land, and they highlight the ongoing fight for land rights and resource management.
Beyond the Map: Engaging with Montana’s Native American Communities
While a map provides a visual representation of reservations, it is crucial to recognize that these are living communities with diverse populations, histories, and aspirations. Engaging with these communities requires respect, understanding, and a willingness to learn. Here are some key points to consider:
- Respecting Tribal Sovereignty: Approaching interactions with Native American communities with an understanding of their sovereignty is essential. This means recognizing their right to self-governance and respecting their cultural practices and traditions.
- Understanding Historical Context: Learning about the history of Native American tribes in Montana, including their treaties, struggles, and resilience, is crucial for fostering meaningful relationships.
- Supporting Economic Development: Supporting businesses owned and operated by Native Americans within reservations contributes to their economic well-being and self-sufficiency.
- Engaging in Cultural Exchange: Participating in cultural events, learning about traditional arts and crafts, and engaging in dialogue with tribal members fosters understanding and appreciation for Native American cultures.
Frequently Asked Questions: Unraveling Common Inquiries about Montana Reservations
Q: Are reservations open to the public?
A: Reservations are sovereign territories, and access may be restricted in certain areas. It is important to respect tribal laws and regulations, obtain necessary permits, and seek permission before visiting or exploring reservation lands.
Q: How can I learn more about specific tribes and their cultures?
A: Many tribes have websites, museums, and cultural centers dedicated to sharing their history and traditions. Engaging with tribal members, attending cultural events, and participating in educational programs are excellent ways to deepen your understanding.
Q: How can I contribute to the well-being of Montana’s Native American communities?
A: Supporting tribal businesses, advocating for policies that promote tribal sovereignty and self-determination, and raising awareness about the challenges and successes of Native American communities are all valuable contributions.
Tips for Responsible Engagement with Montana’s Reservations
- Respect tribal sovereignty and laws.
- Obtain necessary permits and permissions before visiting or exploring reservation lands.
- Be mindful of cultural sensitivities and appropriate attire.
- Support tribal businesses and economic initiatives.
- Engage in respectful dialogue with tribal members and learn about their history and traditions.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Resilience and Cultural Vibrancy
Montana’s reservation map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a testament to the enduring presence and resilience of Native American cultures within the state. Understanding the history, sovereignty, and cultural significance of these reservations is essential for appreciating the rich tapestry of Montana’s heritage. By engaging with these communities with respect and understanding, we can foster a more inclusive and informed appreciation of the state’s multifaceted identity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Montana’s Heritage: A Comprehensive Guide to Reservations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!