Mesopotamia: Cradle of Civilization
Related Articles: Mesopotamia: Cradle of Civilization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mesopotamia: Cradle of Civilization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mesopotamia: Cradle of Civilization

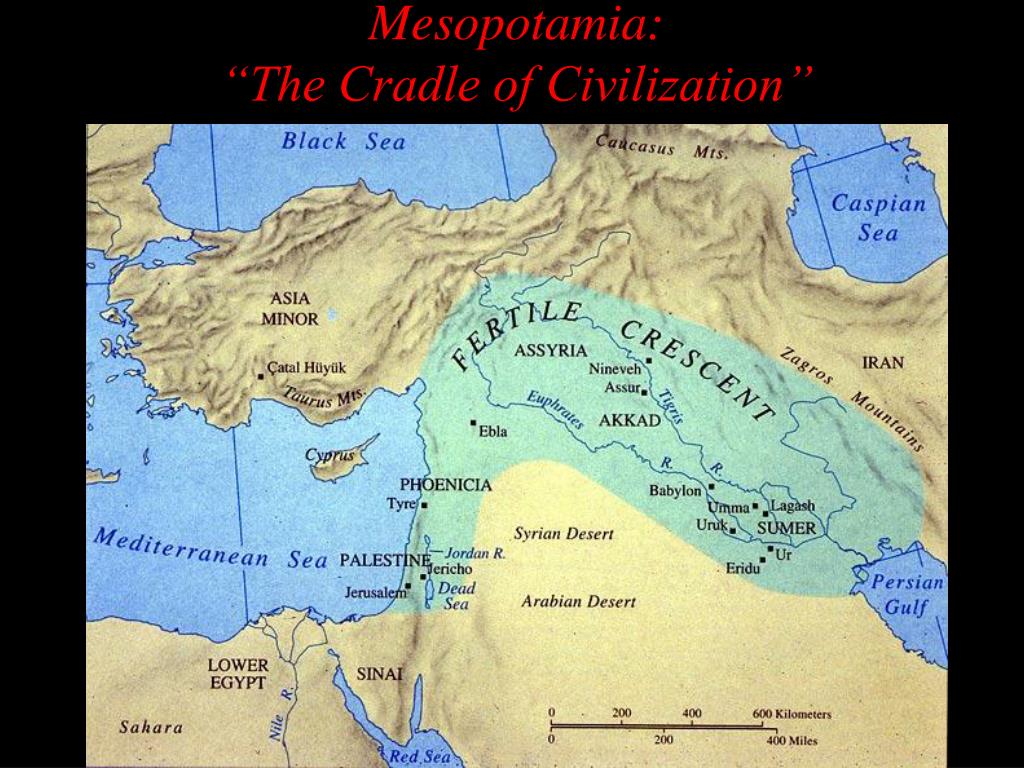
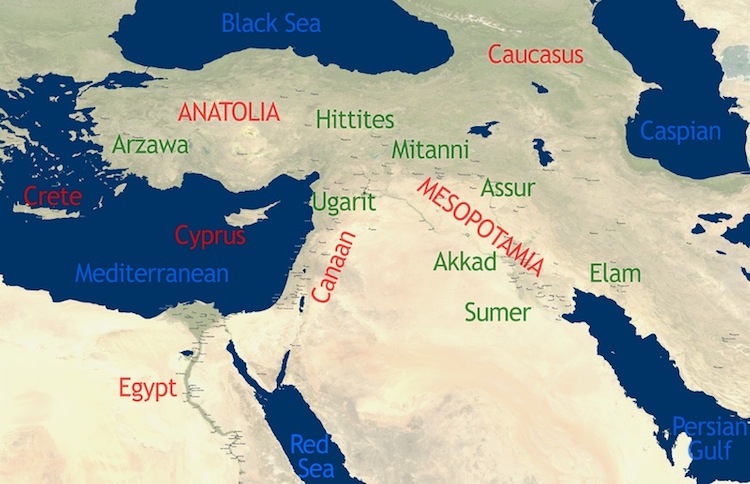
Mesopotamia, a name derived from Greek words meaning "land between rivers," occupies a pivotal position in the annals of human history. This ancient civilization, renowned as the "cradle of civilization," flourished in the fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, a region encompassing modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, parts of Turkey, Syria, and Iran.
Geographical Location and Significance:
Mesopotamia’s strategic location, nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, provided the foundation for its remarkable development. The rivers, acting as lifelines, supplied water for irrigation, facilitated trade, and provided fertile land for agriculture. The fertile plains, known as the "Mesopotamian Marshes," allowed for the cultivation of crops like wheat, barley, and dates, forming the basis of a thriving agricultural society.
The region’s geographical location also facilitated trade and cultural exchange. Situated at the crossroads of major trade routes, Mesopotamia became a hub for the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. This interaction with other civilizations played a crucial role in the development of Mesopotamian culture, art, and innovation.
Key Features of Mesopotamian Civilization:
Mesopotamia witnessed the rise and fall of numerous powerful city-states, each leaving behind a rich legacy of achievements. The Sumerian civilization, the first known urban civilization, emerged in the 4th millennium BCE, laying the groundwork for future advancements.
Some of the key features that characterized Mesopotamian civilization include:
- Urbanization: Mesopotamia was home to some of the earliest cities in the world, including Ur, Uruk, and Kish. These cities boasted sophisticated infrastructure, including temples, palaces, and irrigation systems, demonstrating the advanced level of organization and planning.
- Writing: The Sumerians developed the world’s first known writing system, cuneiform, using wedge-shaped symbols pressed into clay tablets. This invention revolutionized communication, record-keeping, and the transmission of knowledge.
- Agriculture: The fertile land between the rivers allowed for the development of intensive agriculture. The invention of the plow, irrigation systems, and the domestication of animals led to surplus food production, supporting a growing population and enabling specialization of labor.
- Trade and Commerce: Mesopotamia’s strategic location facilitated trade with neighboring civilizations. The region became a hub for the exchange of goods, including textiles, metals, and agricultural products. This trade network fostered economic growth and cultural exchange.
- Law and Governance: Mesopotamian societies developed complex legal systems codified in written laws. The Code of Hammurabi, a collection of laws from the Babylonian period, is a testament to the sophisticated legal framework of the time.
- Art and Architecture: Mesopotamian art and architecture reflected the civilization’s advancements. From massive ziggurats dedicated to their gods to intricate sculptures and reliefs, their artistic expressions showcased their skills and beliefs.
Legacy of Mesopotamia:
Mesopotamia’s legacy extends far beyond its geographical boundaries. The civilization’s inventions, innovations, and cultural achievements laid the foundation for later civilizations in the region and beyond. The development of writing, mathematics, astronomy, and law, along with advancements in agriculture and engineering, had a profound impact on the course of human history.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major rivers in Mesopotamia?
A: The two main rivers of Mesopotamia are the Tigris and Euphrates. These rivers played a crucial role in the development of the civilization, providing water for irrigation, facilitating trade, and shaping the landscape.
Q: What were the main cities in Mesopotamia?
A: Mesopotamia was home to numerous important cities, including Ur, Uruk, Kish, Akkad, Babylon, and Nineveh. These cities were centers of political power, economic activity, and cultural development.
Q: What is the significance of cuneiform writing?
A: Cuneiform writing, developed by the Sumerians, was the world’s first known writing system. It revolutionized communication, record-keeping, and the transmission of knowledge, playing a pivotal role in the development of Mesopotamian civilization.
Q: What are the major contributions of Mesopotamian civilization?
A: Mesopotamia’s contributions to human civilization include the development of writing, mathematics, astronomy, law, agriculture, and engineering. These advancements laid the foundation for future civilizations and shaped the course of human history.
Tips for Understanding Mesopotamia:
- Study Maps: Refer to historical maps to visualize the location of Mesopotamia and its surrounding regions. This will provide context for understanding the civilization’s trade routes, cultural interactions, and geographical influences.
- Explore Ancient Texts: Explore translations of ancient Mesopotamian texts, such as the Code of Hammurabi, to gain insights into their legal systems, social structures, and beliefs.
- Visit Museums: Visit museums that house Mesopotamian artifacts, such as the British Museum or the Louvre, to experience firsthand the civilization’s artistic achievements and material culture.
- Read Historical Accounts: Read accounts of Mesopotamian history written by historians and archaeologists to gain a comprehensive understanding of the civilization’s rise, development, and decline.
Conclusion:
Mesopotamia, the land between the rivers, stands as a testament to the ingenuity and resilience of humankind. Its legacy, etched in the sands of time, continues to inspire and inform us today. From the world’s first writing system to complex legal codes and advancements in agriculture and engineering, Mesopotamia’s contributions to human civilization are immeasurable. By studying this ancient civilization, we gain valuable insights into the origins of our own culture and the enduring power of human innovation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mesopotamia: Cradle of Civilization. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!