Mapping the World of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Data Visualization
Related Articles: Mapping the World of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Data Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the World of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Data Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the World of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Data Visualization
The world is awash in data, and making sense of it is a critical challenge across various fields. Map data visualization offers a powerful tool for unlocking the insights hidden within this deluge of information. By leveraging the inherent spatial relationships of data, map visualization transforms complex datasets into easily understandable and compelling visual narratives.
Understanding the Fundamentals
At its core, map data visualization involves representing data geographically. This might seem simple, but the possibilities are vast and versatile. The process involves:
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from various sources, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
- Data Preparation: Cleaning, transforming, and structuring the data to be suitable for visualization.
- Map Selection: Choosing an appropriate map projection and basemap that effectively represents the geographic context of the data.
- Data Mapping: Applying the data to the map using various techniques, such as choropleth maps (using color intensity), dot density maps (using dot size), and flow maps (using arrows or lines).
- Visualization Design: Selecting appropriate colors, symbols, legends, and other visual elements to ensure clarity and impact.
- Interpretation: Analyzing the visualized data to draw meaningful conclusions and identify trends, patterns, and anomalies.
The Benefits of Map Data Visualization
The power of map data visualization lies in its ability to translate complex data into readily digestible information, revealing insights that might otherwise remain hidden. Its benefits are manifold:
- Enhanced Understanding: By placing data in a geographic context, map visualization makes it easier to understand spatial relationships, patterns, and trends. This allows users to grasp complex information quickly and intuitively.
- Improved Communication: Visualizations can effectively convey complex data to diverse audiences, regardless of their technical expertise. This facilitates communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By revealing spatial patterns and anomalies, map data visualization empowers decision-makers with actionable insights, leading to better informed choices and strategic planning.
- Problem Identification and Analysis: Visualizing data geographically can highlight areas of concern, identify potential problems, and provide valuable insights for targeted interventions and solutions.
- Trend Forecasting and Prediction: By analyzing spatial trends over time, map visualizations can help forecast future developments and predict potential outcomes.
Types of Map Data Visualization
The world of map data visualization encompasses a wide array of techniques, each suited for different types of data and purposes:
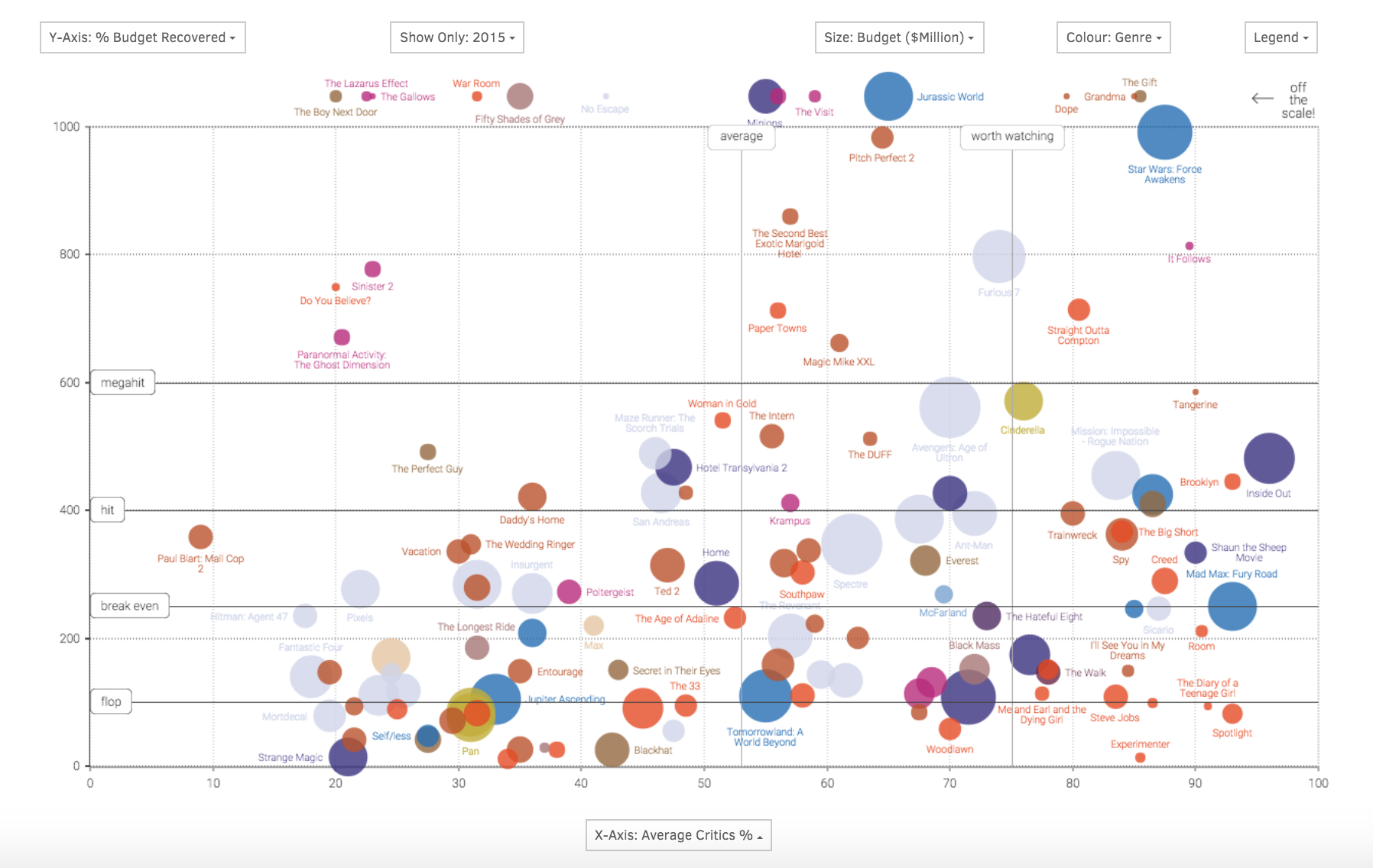
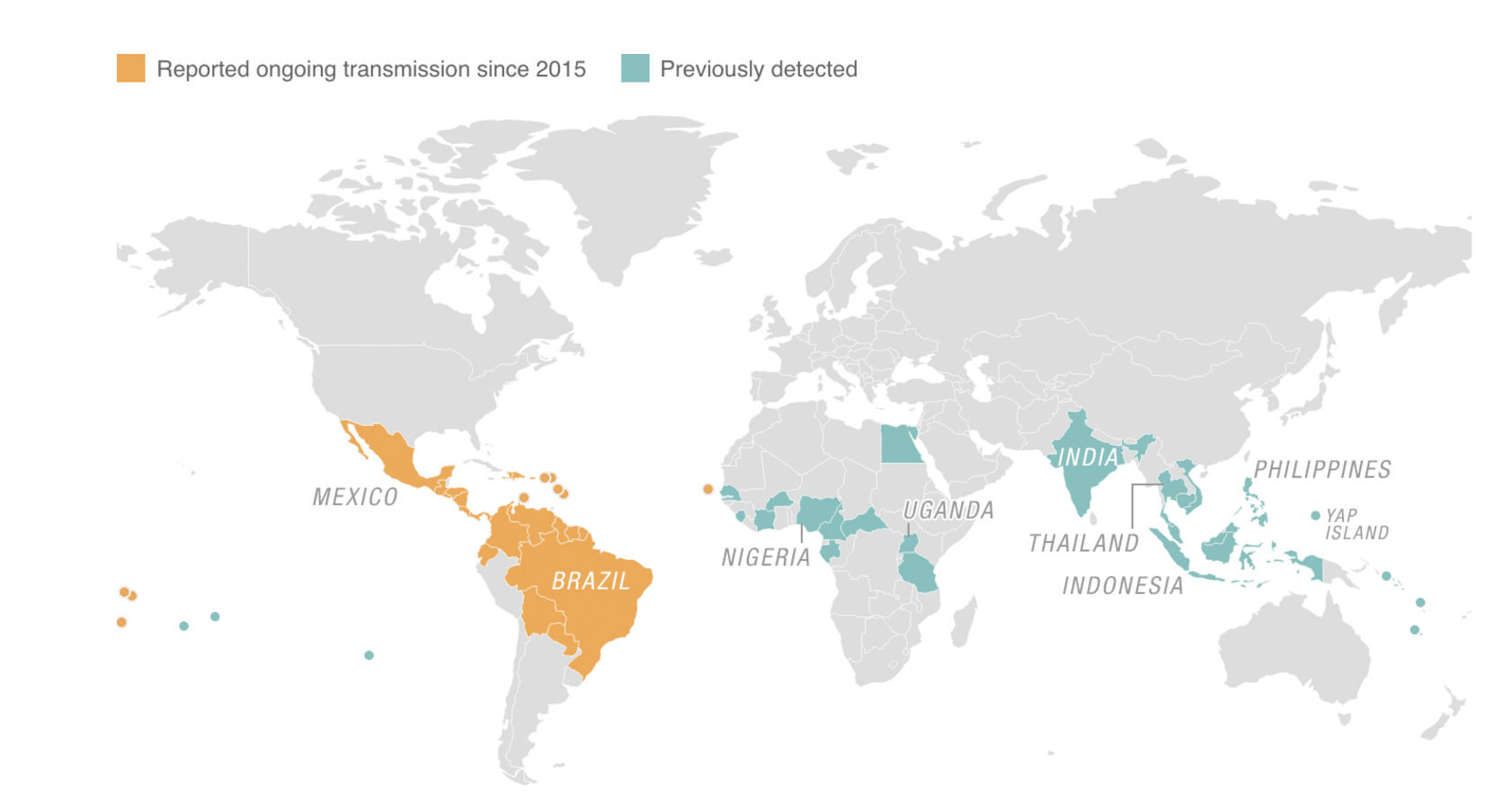
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use color intensity to represent data values across geographic areas. They are effective for visualizing continuous data like population density, income levels, or disease prevalence.
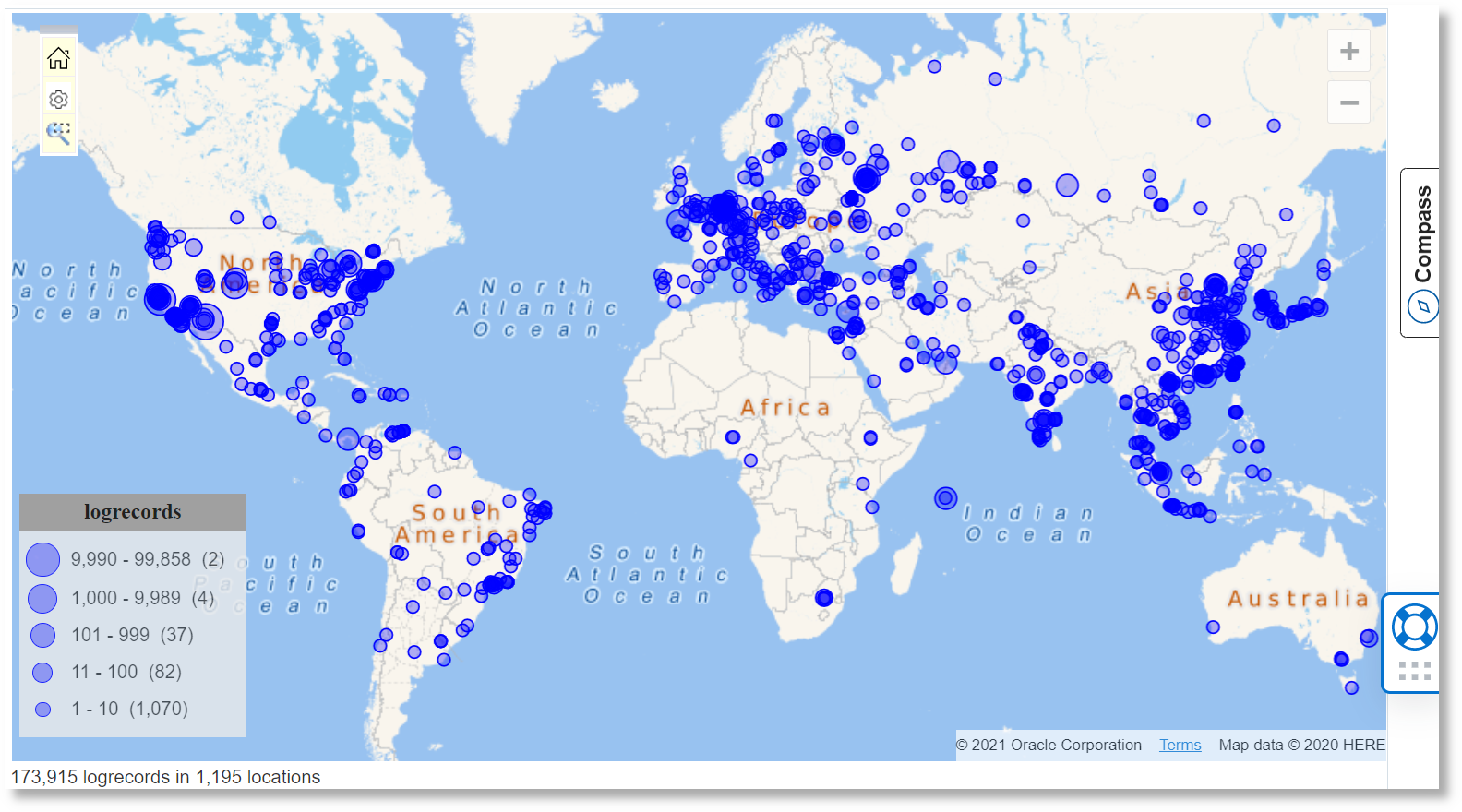
- Dot Density Maps: These maps use the density of dots to represent data values. They are useful for visualizing discrete data like population distribution, crime rates, or business locations.
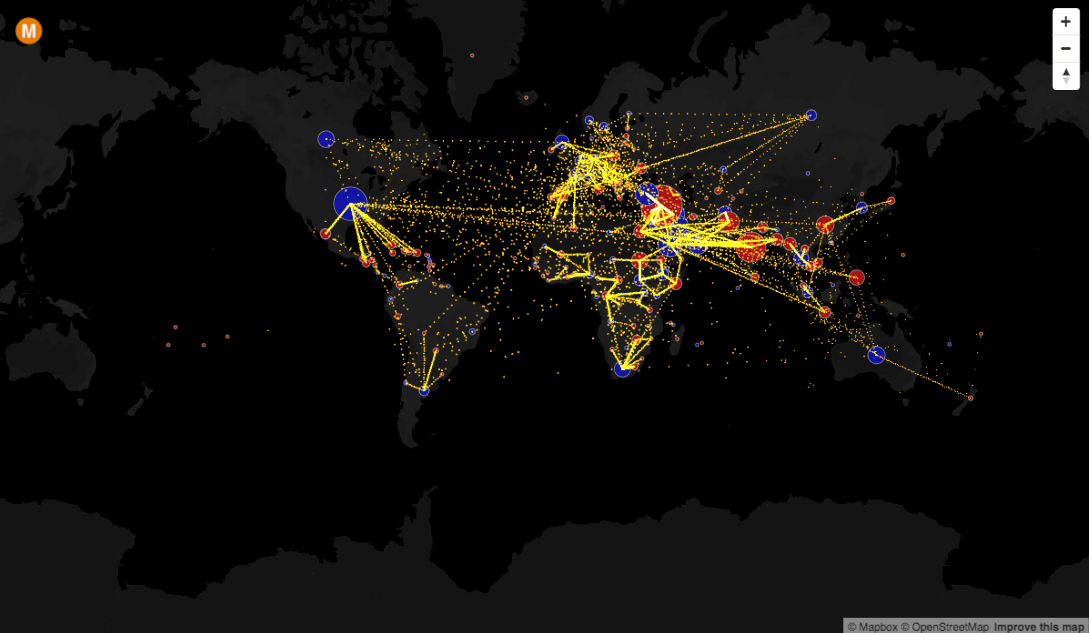
- Flow Maps: These maps use arrows or lines to represent movement or flow patterns. They are ideal for visualizing migration patterns, trade routes, or transportation networks.
- Isoline Maps: These maps use lines to connect points of equal value, creating contours that represent continuous data like elevation, temperature, or rainfall.
- Heat Maps: These maps use color gradients to represent data density or intensity, highlighting areas of high concentration. They are often used for visualizing user activity, traffic patterns, or customer demographics.
- Cartograms: These maps distort geographic areas to represent data values, emphasizing areas with high data values. They are useful for visualizing data where geographic size is not a primary concern.
Applications Across Fields
The versatility of map data visualization makes it a valuable tool across various fields:
- Business and Marketing: Understanding customer demographics, identifying market trends, and optimizing sales strategies.
- Public Health: Tracking disease outbreaks, monitoring health outcomes, and identifying areas in need of intervention.
- Urban Planning: Analyzing population growth, identifying transportation bottlenecks, and planning for sustainable development.
- Environmental Science: Mapping pollution levels, tracking deforestation, and assessing the impact of climate change.
- Social Sciences: Exploring demographic trends, analyzing social disparities, and understanding the impact of social policies.
- Government and Policy: Allocating resources, planning infrastructure projects, and monitoring the effectiveness of public programs.
FAQs on Map Data Visualization
Q: What are the essential tools for creating map data visualizations?
A: A range of software tools are available, each with its own strengths and features. Some popular options include:
- GIS Software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are powerful GIS software packages offering comprehensive data analysis and visualization capabilities.
- Data Visualization Platforms: Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio provide user-friendly interfaces for creating interactive and dynamic maps.
- Programming Languages: Python with libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn, and GeoPandas offers flexibility and customization for creating advanced visualizations.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy and reliability of my map data visualizations?
A: Accuracy and reliability are paramount. It is essential to:
- Source data from reputable sources: Use data from official government agencies, research institutions, or established organizations.
- Verify data accuracy: Cross-reference data from multiple sources and perform data quality checks.
- Consider potential biases: Be aware of potential biases in data collection and interpretation, and address them transparently.
- Use appropriate map projections: Select map projections that minimize distortion and accurately represent the geographic context.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective map data visualizations?
A: Effective map visualizations are clear, concise, and visually appealing. Consider these tips:
- Keep it simple: Avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information. Focus on the key insights you want to convey.
- Use color effectively: Choose a color scheme that is visually appealing and aids in data interpretation. Avoid overly saturated colors or overly complex color schemes.
- Employ clear labels and legends: Ensure all elements are clearly labeled and that a comprehensive legend is provided.
- Consider interactivity: Interactive maps can engage the audience and allow them to explore the data in greater detail.
- Tell a story: Use the visualization to tell a compelling story about the data, highlighting key trends and insights.
Conclusion
Map data visualization is a powerful tool for unlocking the insights hidden within data. By leveraging the spatial relationships of data, it transforms complex information into easily understandable and compelling visual narratives. From business intelligence to public health, environmental science, and beyond, map data visualization plays a vital role in empowering decision-making, fostering understanding, and driving progress. As the world continues to generate vast amounts of data, the ability to visualize it effectively will become increasingly important for navigating the complexities of our interconnected world.
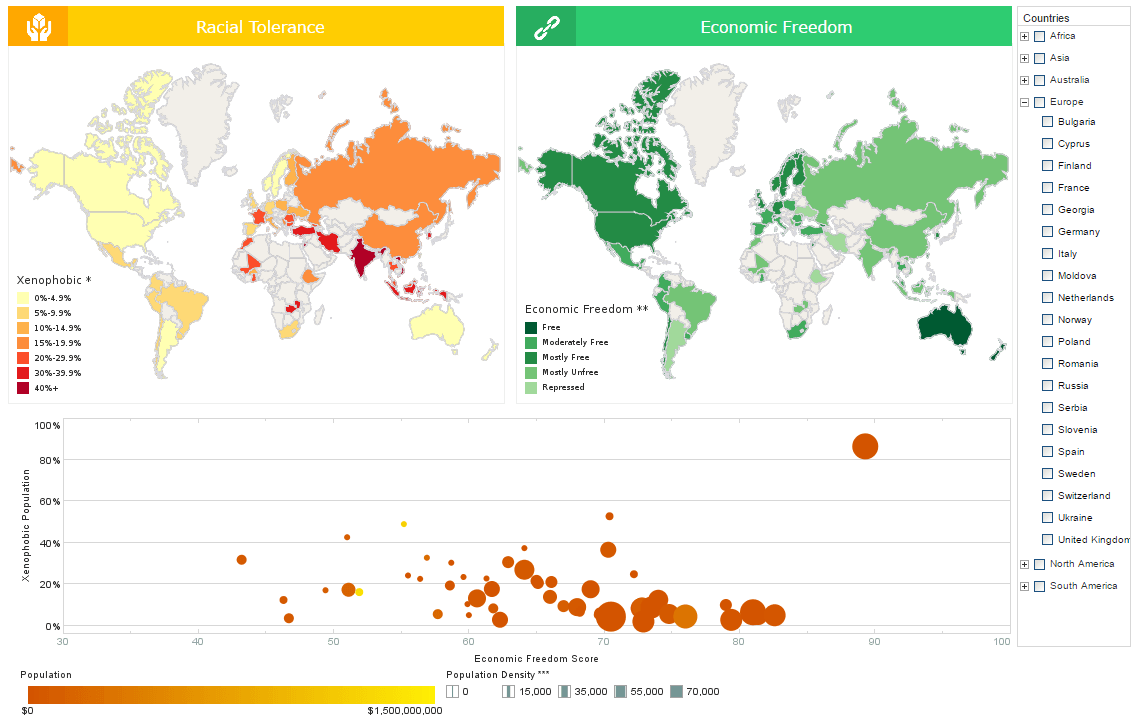
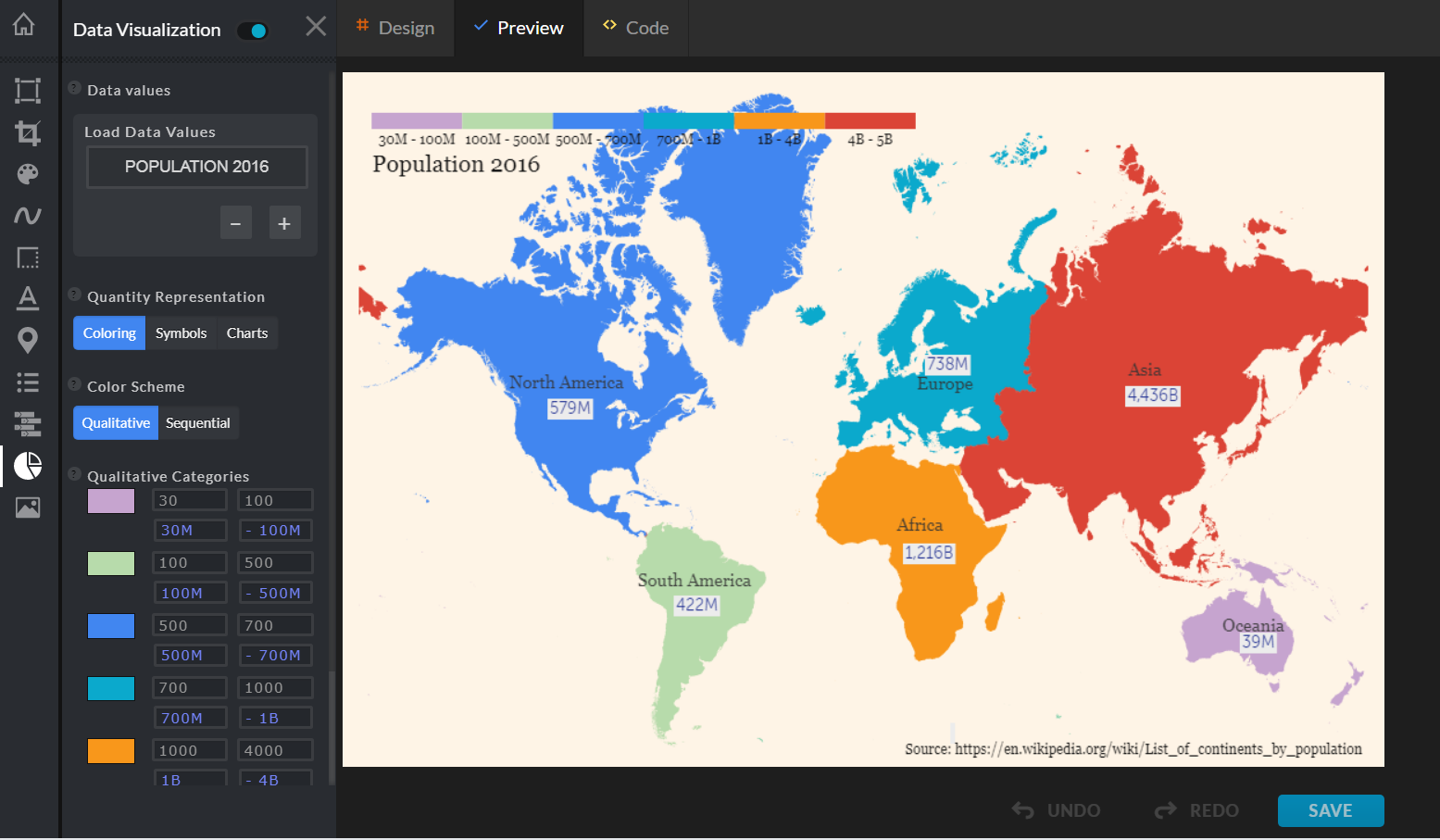
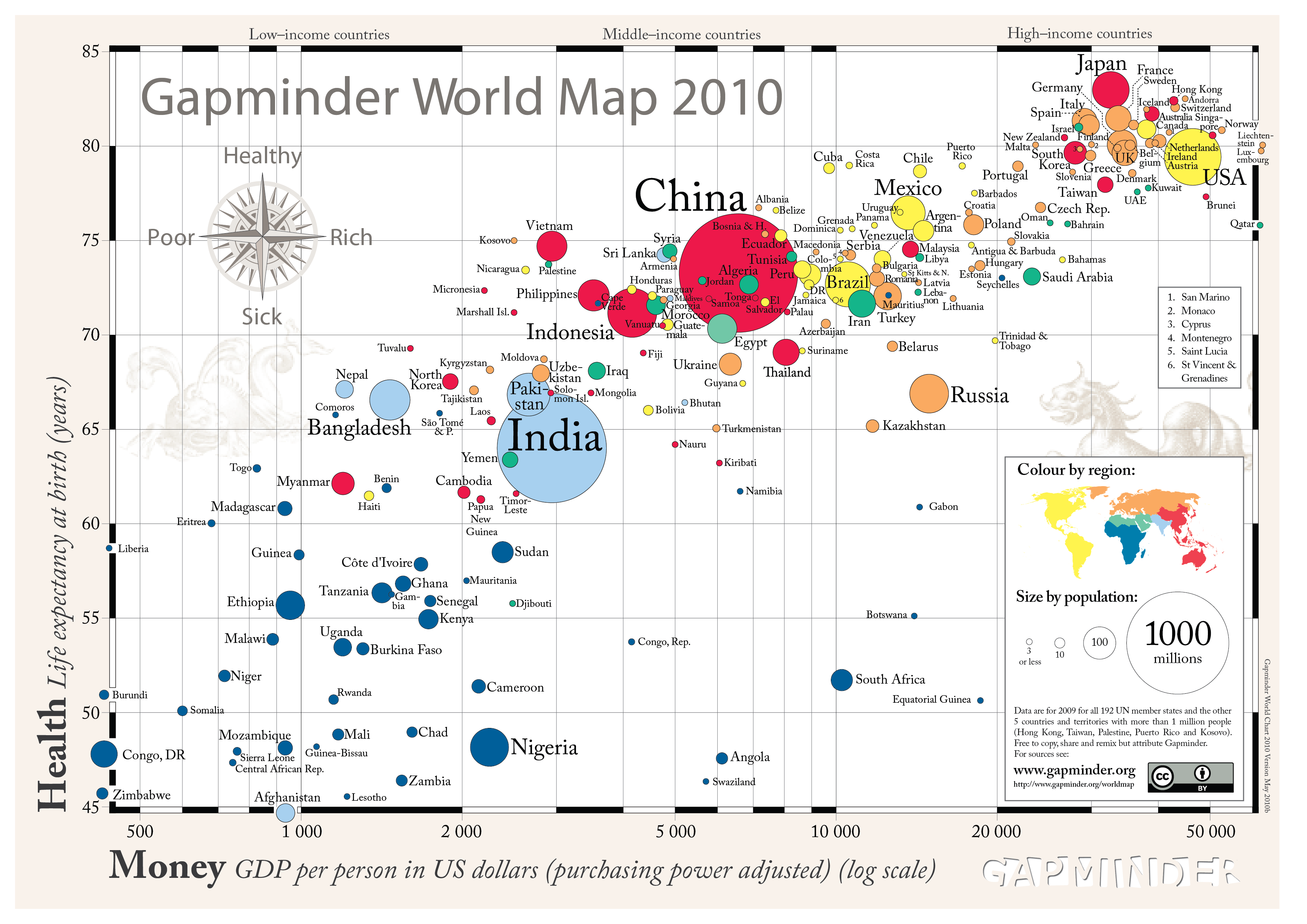

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the World of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Data Visualization. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!