Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Identity: An Exploration of Tribal Maps
Related Articles: Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Identity: An Exploration of Tribal Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Identity: An Exploration of Tribal Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Identity: An Exploration of Tribal Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Identity: An Exploration of Tribal Maps
- 3.1 The Significance of Tribal Maps
- 3.2 The Diverse Forms of Tribal Maps
- 3.3 Understanding the Power of Tribal Maps
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Tribal Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using Tribal Maps Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Identity: An Exploration of Tribal Maps
Tribal maps, also known as indigenous maps, are powerful tools that go beyond simple geographical representations. They offer a profound glimpse into the intricate tapestry of indigenous cultures, histories, and relationships with the land. These maps are not merely static depictions of territory; they are dynamic narratives that embody the lived experiences, ancestral knowledge, and cultural practices of indigenous communities.
The Significance of Tribal Maps
Tribal maps hold immense significance for several reasons:
1. Historical Preservation and Documentation: They serve as invaluable historical records, preserving ancestral knowledge, oral traditions, and stories passed down through generations. They document the movement of indigenous populations, their traditional territories, and the historical events that shaped their lives.
2. Cultural Identity and Continuity: Tribal maps are integral to the preservation of indigenous identity. They provide a tangible link to the past, connecting present generations to their ancestors and their ancestral lands. They serve as visual reminders of cultural traditions, languages, and spiritual practices that have been passed down through generations.
3. Land Rights and Resource Management: Tribal maps are crucial in asserting and protecting indigenous land rights. They provide evidence of historical land claims, demonstrating the long-standing relationship between indigenous communities and their territories. This information is essential for negotiating treaties, accessing resources, and ensuring the sustainable management of land and resources.
4. Environmental Stewardship and Conservation: Tribal maps often incorporate traditional ecological knowledge, reflecting an understanding of the natural world that has been developed over centuries. This knowledge is essential for understanding and managing ecosystems, conserving biodiversity, and ensuring the long-term health of the environment.
5. Education and Awareness: Tribal maps play a vital role in educating the public about indigenous cultures and histories. They challenge Eurocentric perspectives on geography and history, offering alternative narratives that acknowledge the diverse and rich cultural heritage of indigenous peoples.
The Diverse Forms of Tribal Maps
Tribal maps are not confined to a single format. They can be expressed in various ways, reflecting the diverse cultural traditions and practices of indigenous communities. Some common forms include:
1. Traditional Maps: These are often created using materials found in nature, such as bark, animal hides, sand, or clay. They may be drawn, woven, or carved, and they often incorporate symbols and patterns that hold deep cultural significance.
2. Digital Maps: Modern technologies have enabled indigenous communities to create digital maps that combine traditional knowledge with modern cartographic techniques. These maps can incorporate data on language, cultural sites, traditional ecological knowledge, and other important information.
3. Story Maps: These maps integrate narratives, oral histories, and cultural traditions into the geographic representation. They weave together stories, songs, and legends, offering a multi-dimensional understanding of the land and its significance.
4. Interactive Maps: These maps utilize technology to create immersive experiences that allow users to explore different aspects of indigenous culture, history, and land use. They may include audio, video, and other interactive elements that enhance the learning experience.
Understanding the Power of Tribal Maps
The power of tribal maps lies in their ability to connect people, places, and histories in a meaningful way. They are not simply static representations of geographic space; they are living documents that reflect the dynamic relationship between indigenous communities and their lands. They embody a deep understanding of the natural world, the interconnectedness of all living things, and the importance of cultural continuity.
Frequently Asked Questions about Tribal Maps
1. What are the differences between traditional and digital tribal maps?
Traditional tribal maps are often created using natural materials and reflect the artistic and cultural traditions of specific communities. Digital maps, on the other hand, utilize modern technology to create interactive and data-rich representations.
2. How are tribal maps used in land rights advocacy?
Tribal maps provide evidence of historical land claims, demonstrating the long-standing relationship between indigenous communities and their territories. This information is crucial for negotiating treaties, accessing resources, and asserting land rights.
3. How can tribal maps contribute to environmental conservation?
Tribal maps often incorporate traditional ecological knowledge, which can be vital for understanding and managing ecosystems, conserving biodiversity, and ensuring the long-term health of the environment.
4. What are the challenges faced in creating and preserving tribal maps?
Challenges include the loss of traditional knowledge due to colonization and assimilation, the lack of resources for mapping projects, and the need to balance traditional practices with modern technologies.
5. How can individuals support the creation and use of tribal maps?
Individuals can support the creation and use of tribal maps by engaging with indigenous communities, learning about their histories and cultures, and advocating for the recognition of indigenous land rights.
Tips for Using Tribal Maps Effectively
1. Approach with Respect: Recognize the cultural significance of tribal maps and treat them with the respect they deserve.
2. Seek Guidance: Consult with indigenous communities and experts on the proper interpretation and use of tribal maps.
3. Acknowledge the Historical Context: Understand the historical and cultural context in which tribal maps were created and the stories they tell.
4. Embrace Diversity: Recognize that tribal maps vary significantly across cultures and regions, reflecting the diversity of indigenous communities.
5. Promote Accessibility: Advocate for the accessibility of tribal maps to a wider audience, promoting education and awareness about indigenous cultures and histories.
Conclusion
Tribal maps are more than just geographical representations; they are powerful tools for preserving cultural identity, asserting land rights, and promoting environmental stewardship. They offer a profound glimpse into the rich tapestry of indigenous cultures, histories, and relationships with the land. By understanding the significance of tribal maps and supporting their creation and use, we can contribute to the recognition, respect, and preservation of indigenous knowledge and traditions.
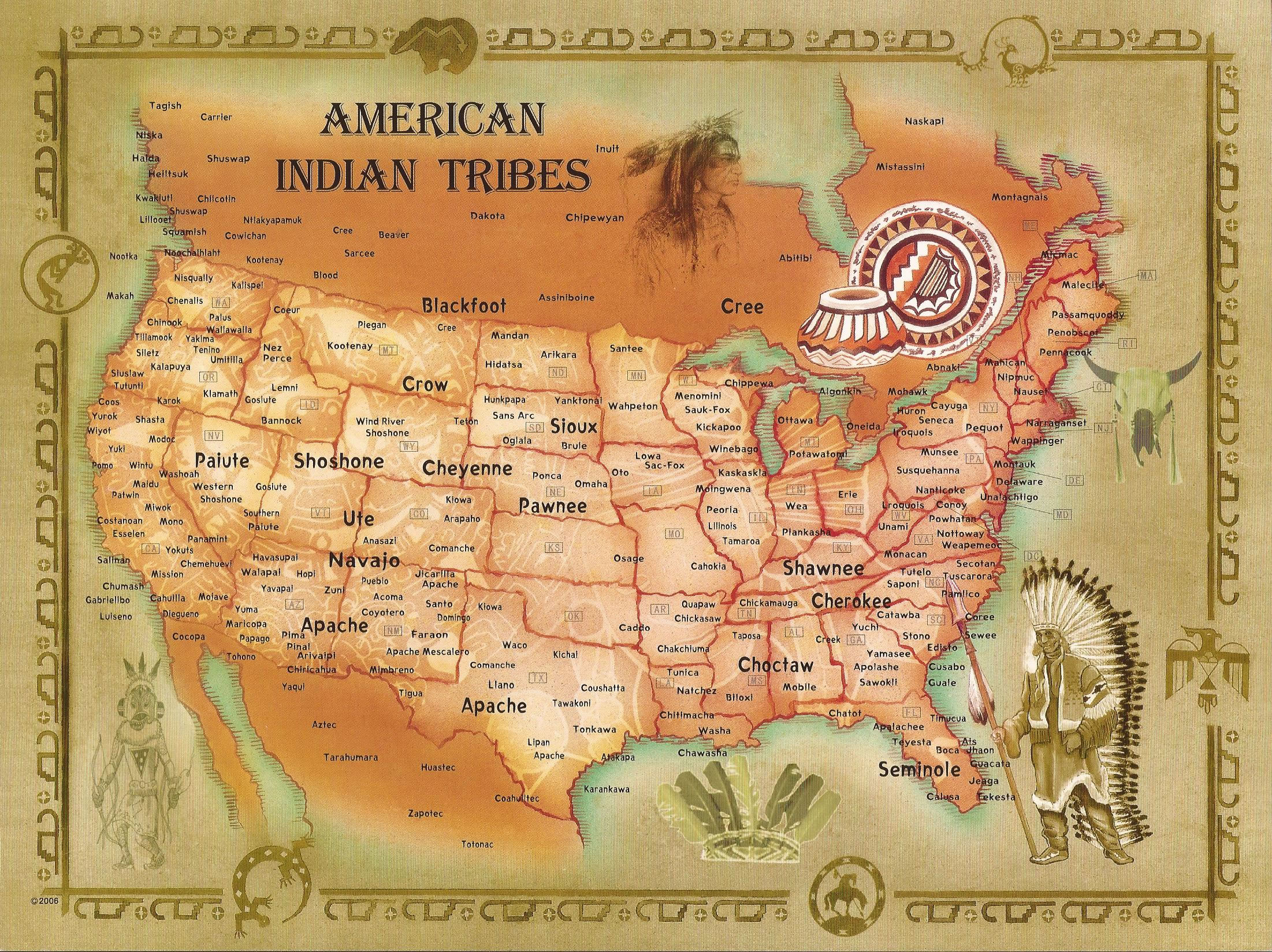





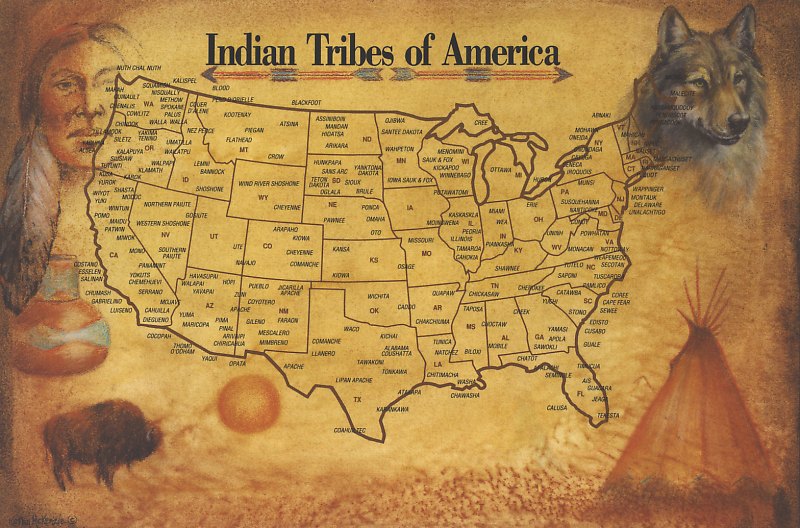

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Identity: An Exploration of Tribal Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!