Mapping the Landscape of Poverty in the United States: A Visual Guide to Understanding Economic Disparities
Related Articles: Mapping the Landscape of Poverty in the United States: A Visual Guide to Understanding Economic Disparities
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Landscape of Poverty in the United States: A Visual Guide to Understanding Economic Disparities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Landscape of Poverty in the United States: A Visual Guide to Understanding Economic Disparities
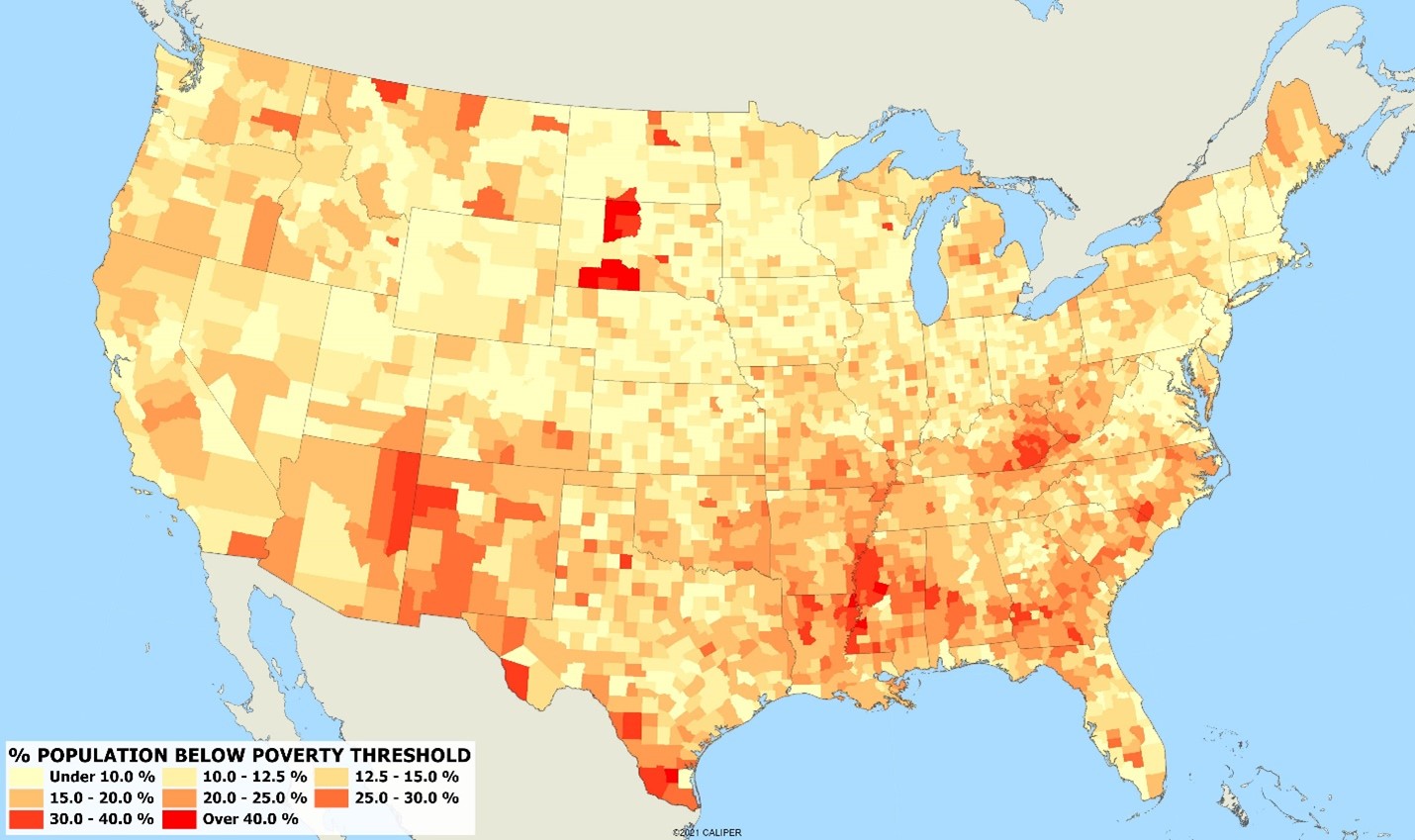
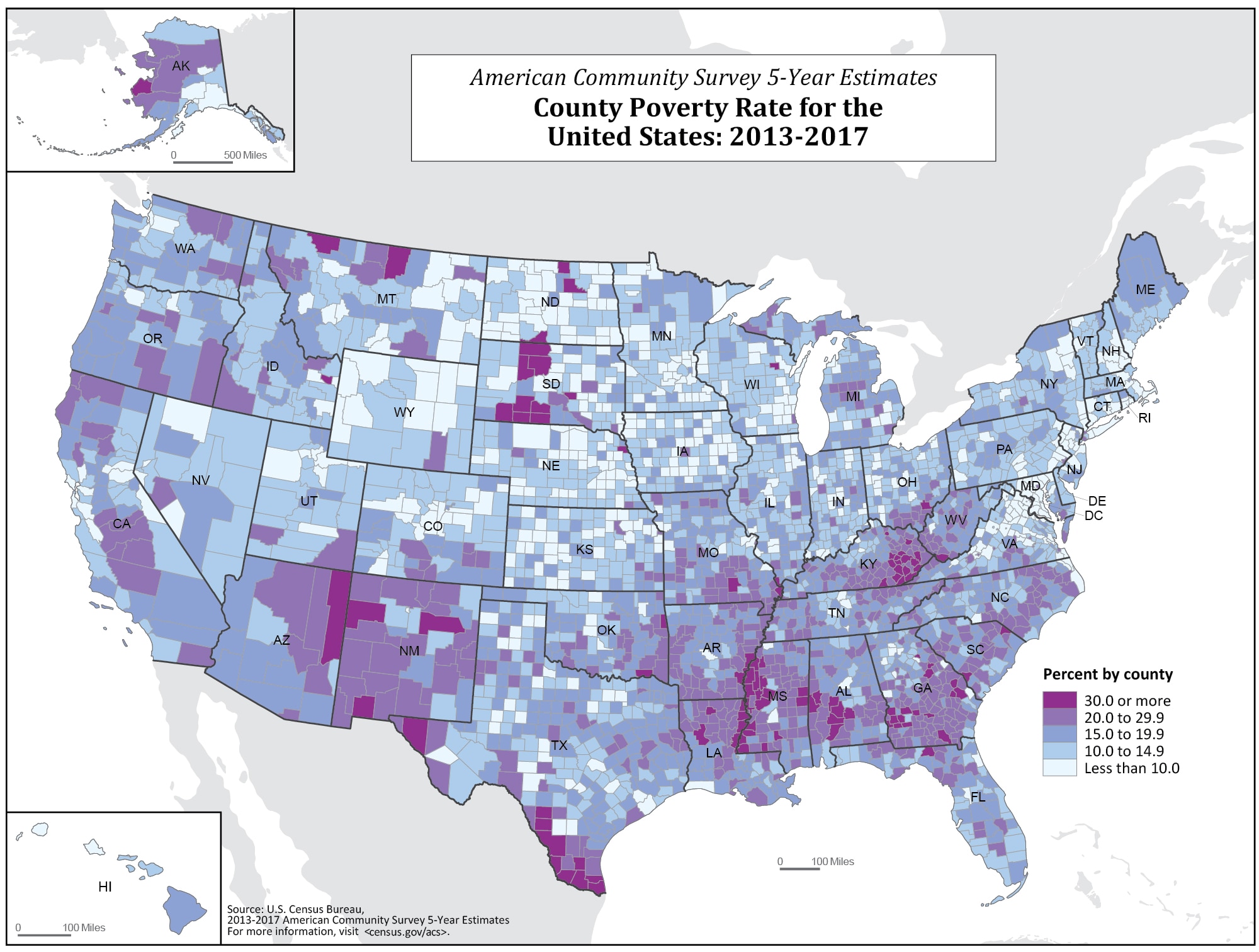
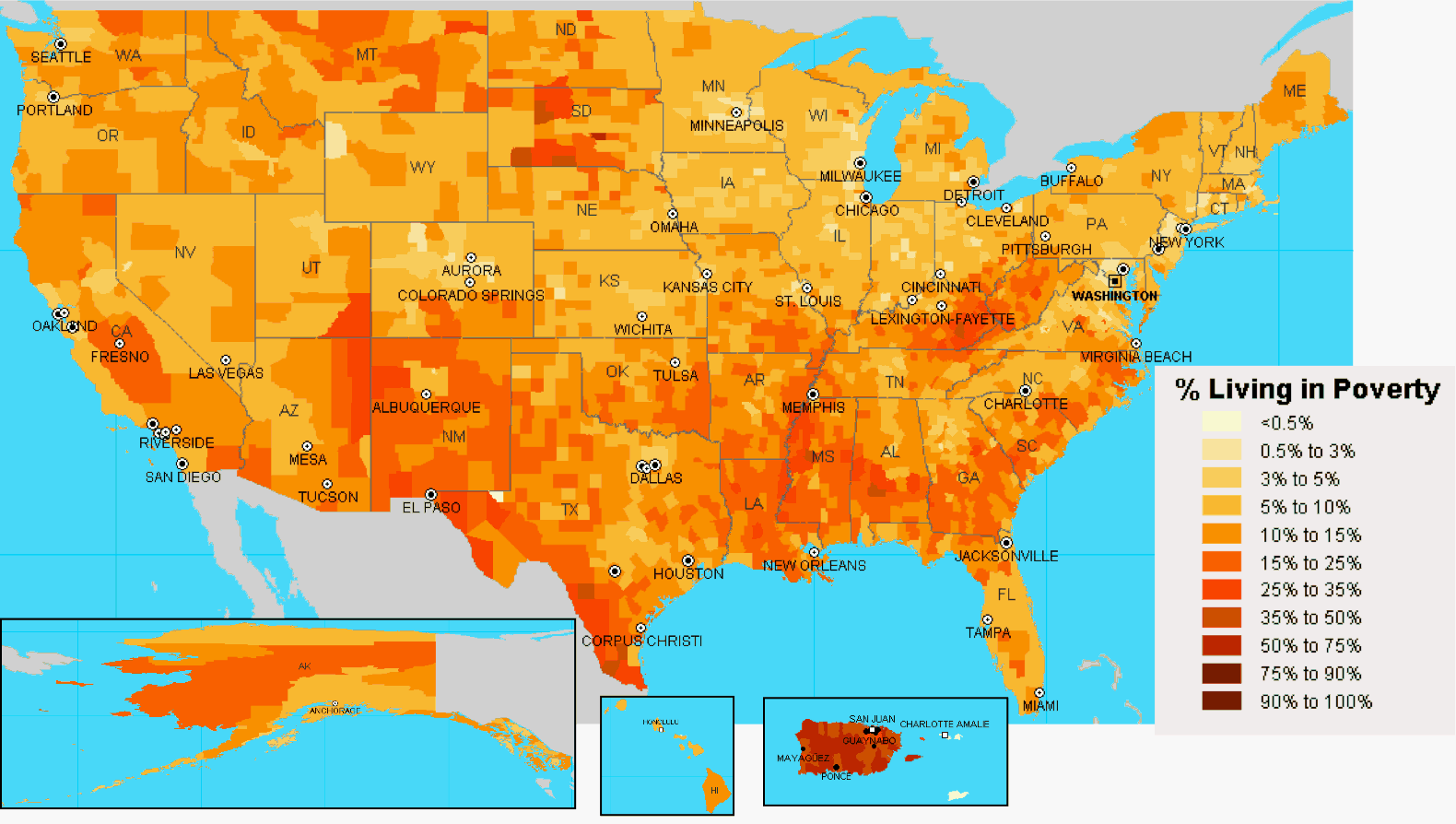
The United States, a nation often lauded for its economic prowess and opportunities, also grapples with significant levels of poverty. Understanding the geographical distribution of poverty is crucial for developing effective policies and interventions to address this complex issue. The Poverty US Map, a visual representation of poverty rates across the country, provides a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing these disparities.
Understanding the Data and Methodology
The Poverty US Map typically relies on data collected by the U.S. Census Bureau, which conducts the American Community Survey (ACS). The ACS gathers information on a wide range of social and economic characteristics, including income, housing, and employment. Based on this data, the Census Bureau calculates the poverty rate for different geographical units, such as counties, states, and metropolitan areas. The poverty threshold, which defines the income level below which individuals or families are considered poor, is determined by the federal government and adjusted annually for inflation and family size.
Visualizing the Landscape: Patterns and Trends
The Poverty US Map reveals a complex and often stark reality. Certain regions consistently exhibit higher poverty rates than others, reflecting a deeply rooted interplay of factors such as economic opportunities, access to education and healthcare, and historical patterns of segregation and discrimination.
Key Observations:
- Rural vs. Urban Divide: Poverty rates tend to be higher in rural areas compared to urban centers. This disparity can be attributed to factors like limited employment opportunities, lower wages in agricultural industries, and fewer social services.
- Southern Concentration: The Southern states generally have higher poverty rates than other regions. This can be attributed to a combination of factors, including a history of racial segregation and discrimination, lower educational attainment, and a reliance on industries with lower wages.
- Regional Clusters: Specific geographic clusters within states often exhibit higher poverty rates, highlighting the concentration of poverty within certain communities. These clusters may be associated with factors such as lack of infrastructure, limited access to transportation, and concentrated populations of marginalized groups.
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Poverty rates are significantly higher among Black, Hispanic, and Native American populations compared to white populations. These disparities are rooted in historical and ongoing systemic inequalities, including discrimination in housing, education, and employment.
Beyond the Map: The Importance of Context and Nuance
While the Poverty US Map offers a valuable overview of poverty distribution, it’s essential to recognize that it represents a snapshot in time and cannot fully capture the complexities of poverty. The map should be used in conjunction with other data sources and qualitative research to gain a comprehensive understanding of the lived experiences of individuals and families living in poverty.
Analyzing the Causes and Consequences of Poverty
The Poverty US Map serves as a starting point for exploring the underlying causes and consequences of poverty. Several factors contribute to poverty, including:
- Lack of Economic Opportunity: Limited job opportunities, low wages, and underemployment are significant contributors to poverty.
- Educational Disparities: Unequal access to quality education, limited educational attainment, and skills gaps exacerbate poverty.
- Healthcare Access and Costs: Lack of affordable healthcare, high medical expenses, and health disparities contribute to poverty and limit economic mobility.
- Housing Affordability: Rising housing costs, limited affordable housing options, and unstable housing situations contribute to poverty and financial instability.
- Social and Systemic Barriers: Discrimination based on race, ethnicity, gender, and other factors can limit opportunities and perpetuate poverty.
The Consequences of Poverty:
Poverty has profound consequences for individuals, families, and communities, including:
- Health Disparities: Higher rates of chronic diseases, mental health issues, and reduced life expectancy.
- Educational Attainment: Lower educational attainment and increased school dropout rates.
- Limited Economic Mobility: Reduced opportunities for advancement, lower income potential, and intergenerational poverty.
- Social Exclusion: Limited access to social services, social networks, and civic engagement.
- Increased Crime Rates: Higher crime rates in areas with high poverty concentrations.
Addressing Poverty: A Multifaceted Approach
Addressing poverty requires a multifaceted approach that tackles both the root causes and the consequences of poverty. Key strategies include:
- Economic Development: Creating jobs, increasing wages, and promoting entrepreneurship.
- Education Reform: Investing in early childhood education, improving K-12 education, and expanding access to higher education.
- Healthcare Access and Affordability: Expanding access to affordable healthcare, reducing medical debt, and addressing health disparities.
- Housing Affordability: Increasing the supply of affordable housing, providing rental assistance, and protecting tenants’ rights.
- Social Safety Nets: Strengthening social safety nets, such as SNAP (food stamps), TANF (Temporary Assistance for Needy Families), and Medicaid.
- Anti-discrimination Policies: Addressing systemic discrimination and promoting equal opportunities for all.
FAQs about the Poverty US Map
Q: What is the most accurate way to use the Poverty US Map?
A: The Poverty US Map is a visual representation of poverty rates, but it is crucial to use it in conjunction with other data sources and qualitative research. Consider factors like population density, economic diversity, and historical context when interpreting the map.
Q: What are the limitations of the Poverty US Map?
A: The Poverty US Map relies on data collected through surveys, which may not accurately capture the full extent of poverty. It also doesn’t account for the lived experiences of individuals and families living in poverty.
Q: How can the Poverty US Map be used for policy development?
A: The Poverty US Map can help policymakers identify areas with high poverty rates and target resources and interventions to address specific needs. It can also inform the development of policies aimed at promoting economic opportunity and reducing inequality.
Q: Is the Poverty US Map a static representation of poverty?
A: Poverty rates fluctuate over time due to economic cycles, policy changes, and other factors. The Poverty US Map should be viewed as a snapshot in time, and it is essential to track changes in poverty rates over time.
Tips for Using the Poverty US Map Effectively
- Consider the scale of the map: The Poverty US Map can be presented at different scales, from national to local levels. Choose the scale that best suits your analysis.
- Compare data over time: Analyze changes in poverty rates over time to identify trends and patterns.
- Integrate with other data sources: Combine the Poverty US Map with other data sources, such as unemployment rates, educational attainment, and health indicators, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Engage with communities: Connect with local organizations and community leaders to understand the lived experiences of poverty and inform policy development.
Conclusion
The Poverty US Map is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing poverty in the United States. By understanding the geographical distribution of poverty, we can develop more effective policies and interventions to address this complex issue. However, it is essential to recognize the limitations of the map and to use it in conjunction with other data sources and qualitative research to gain a comprehensive understanding of the lived experiences of individuals and families living in poverty. By working together, we can build a more equitable and just society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
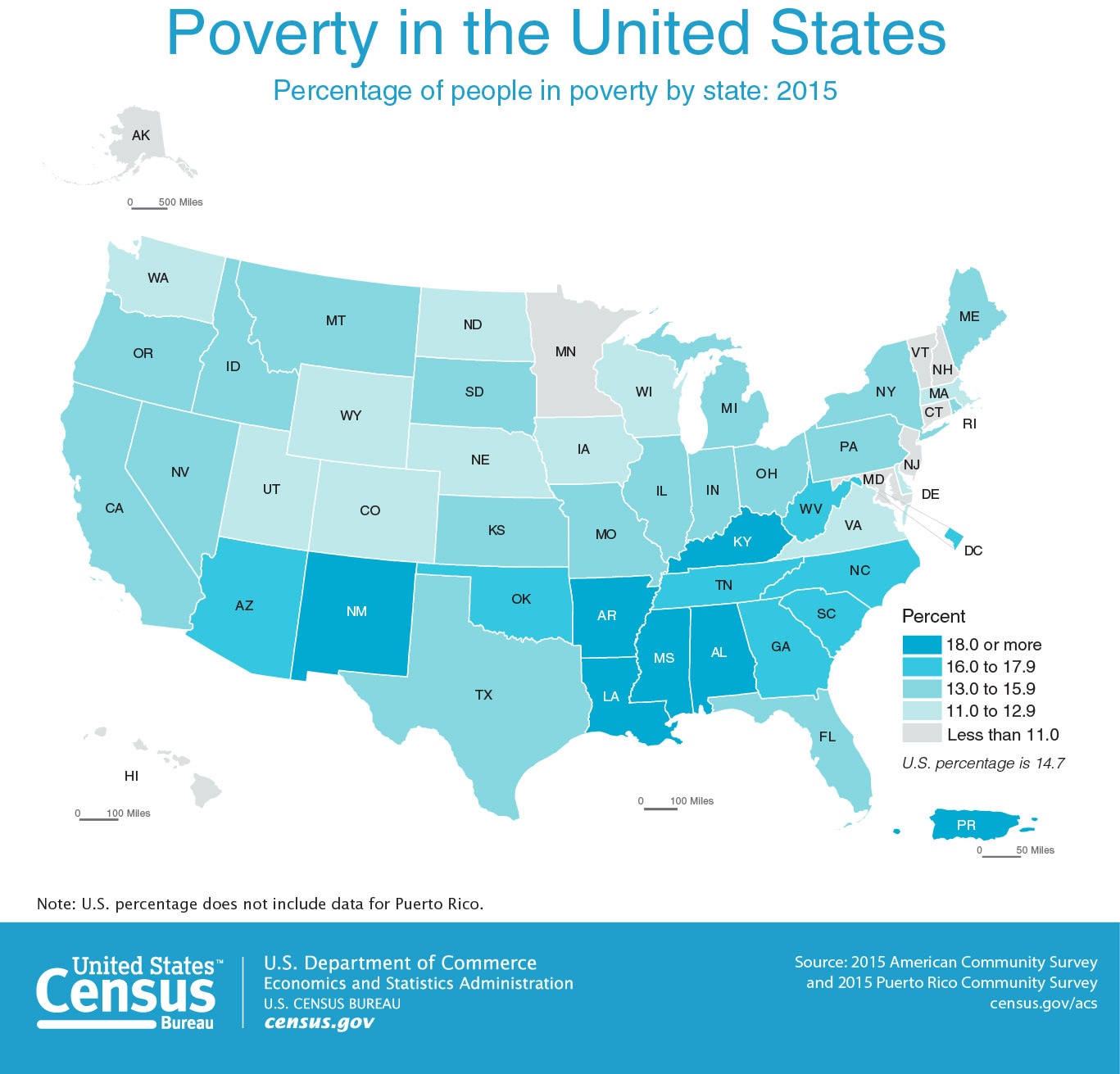

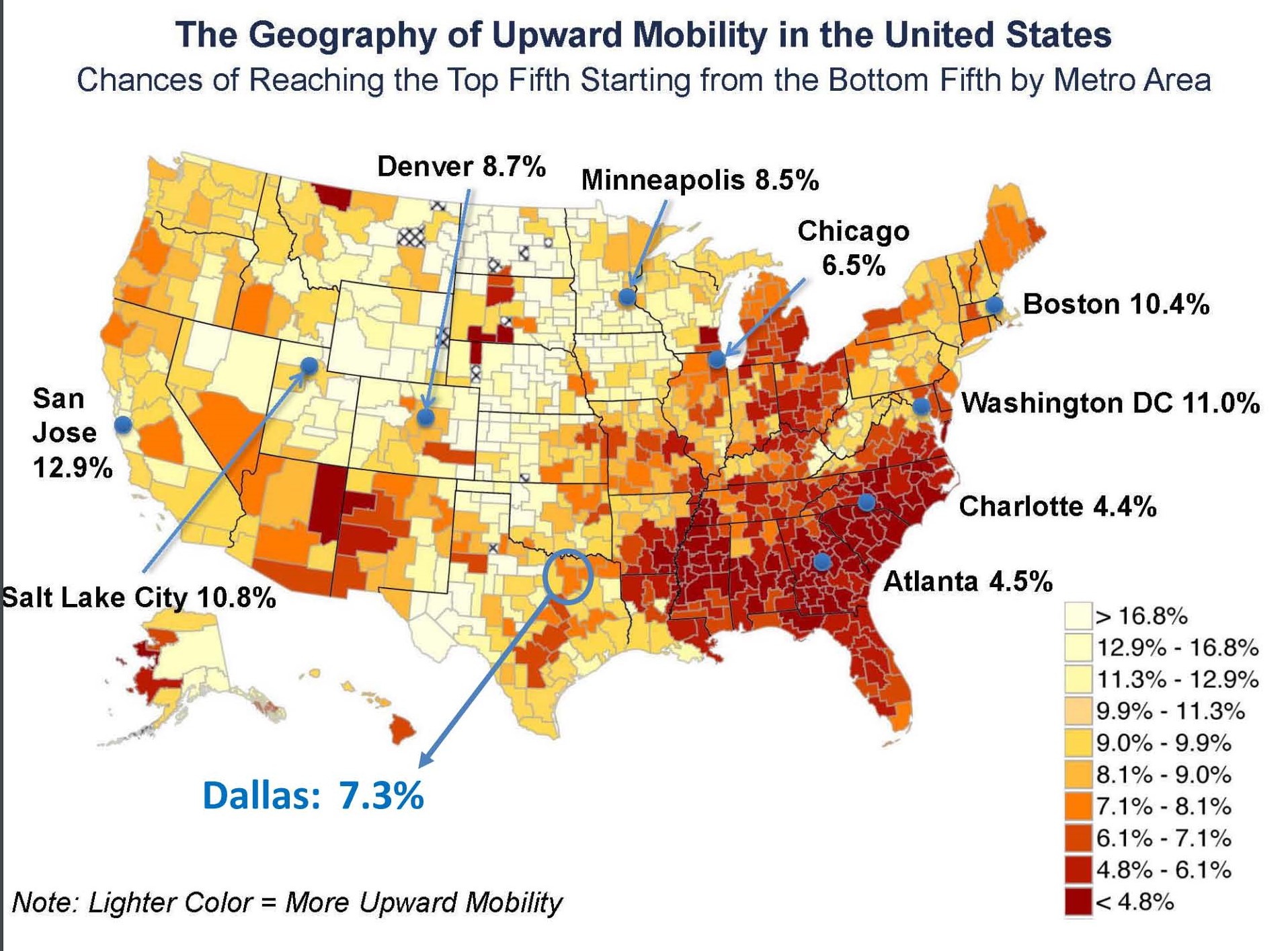
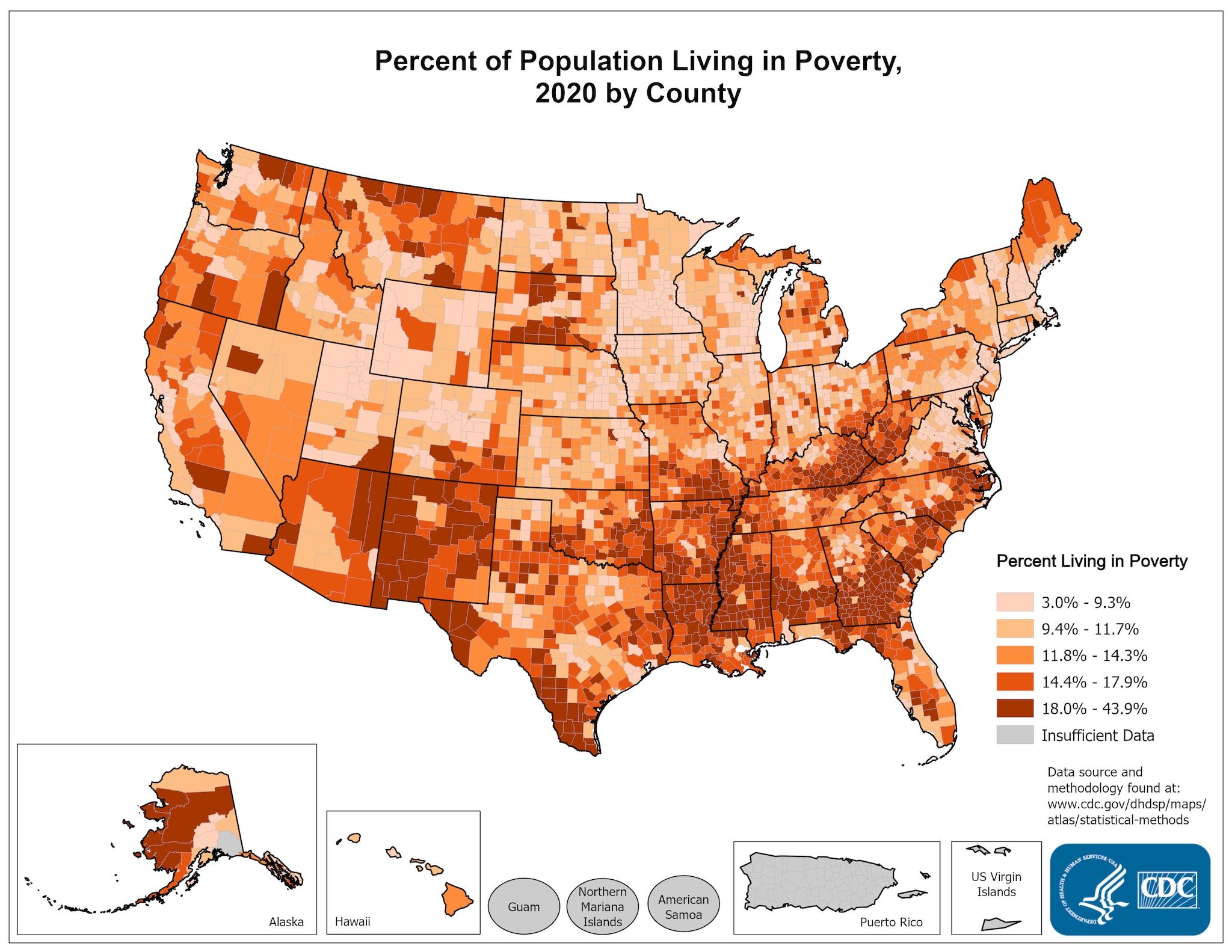


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Landscape of Poverty in the United States: A Visual Guide to Understanding Economic Disparities. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!