Jamaica’s Geographical Positioning: A Caribbean Jewel
Related Articles: Jamaica’s Geographical Positioning: A Caribbean Jewel
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Jamaica’s Geographical Positioning: A Caribbean Jewel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Jamaica’s Geographical Positioning: A Caribbean Jewel

Jamaica, a vibrant island nation in the Caribbean Sea, holds a strategic location that has shaped its history, culture, and economy. Understanding its geographical positioning is crucial for comprehending its unique characteristics and global significance.
Island Geography:
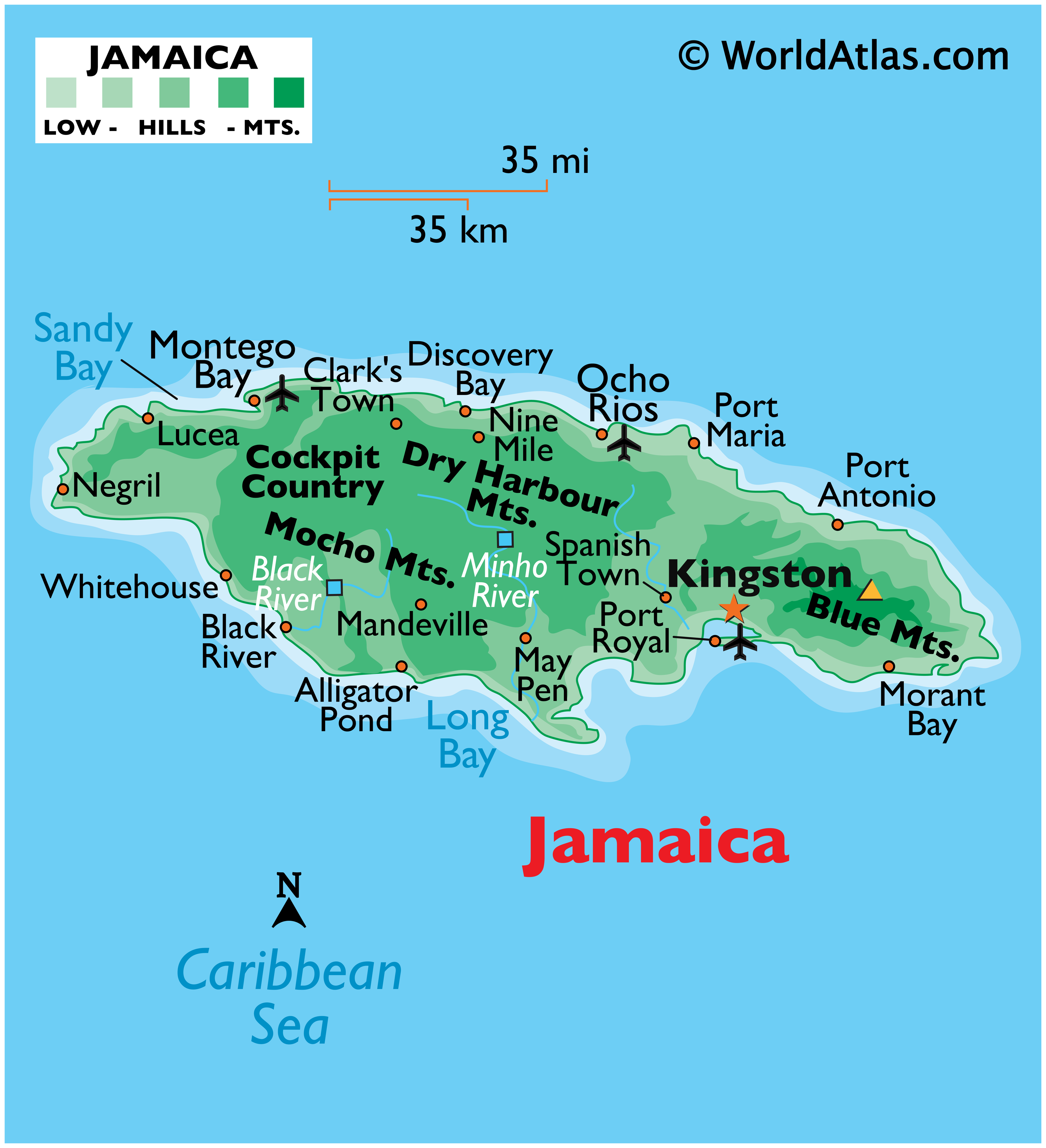
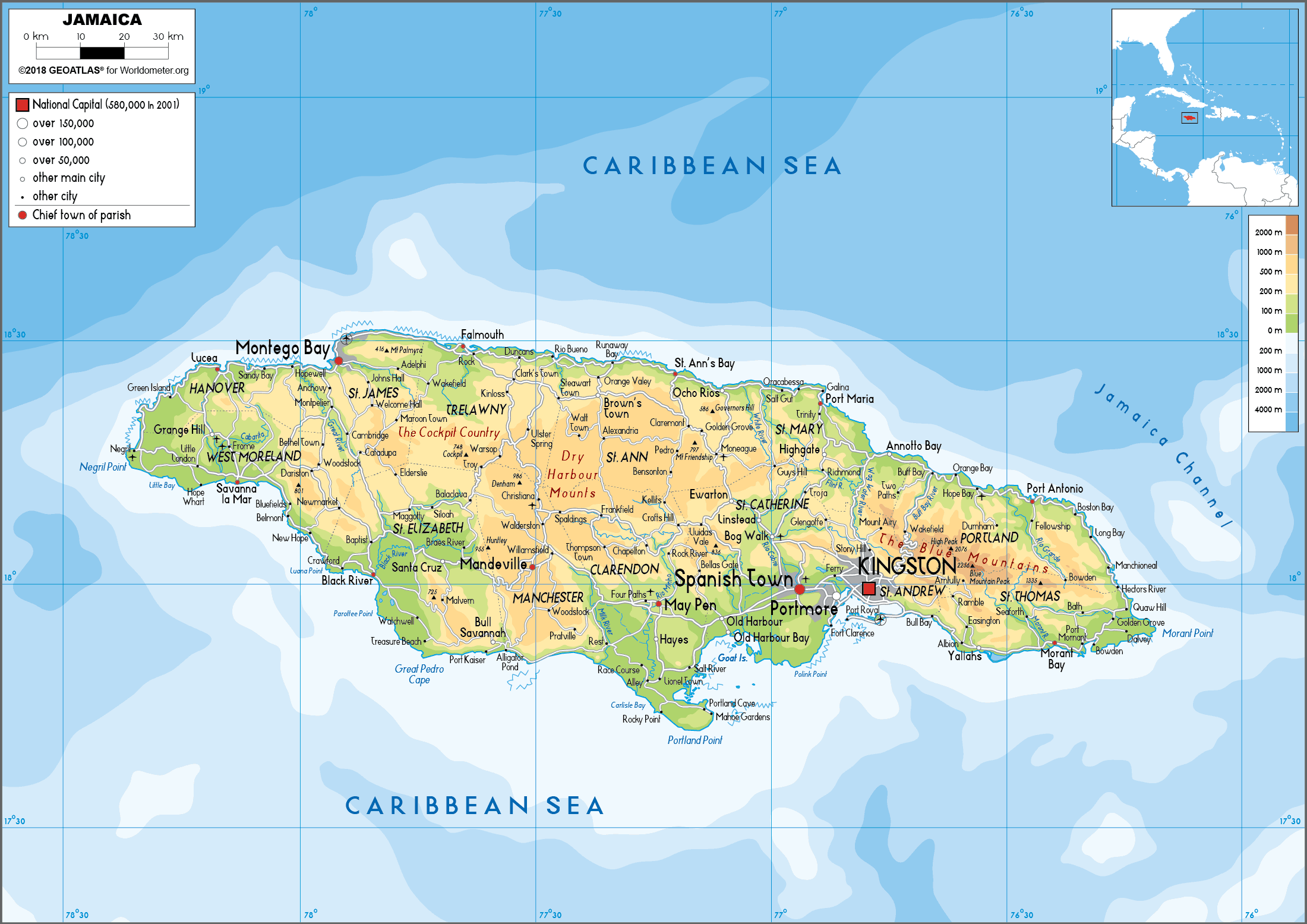
Jamaica is situated in the northern Caribbean Sea, approximately 90 miles south of Cuba and 100 miles west of Haiti. It is the third-largest island in the Greater Antilles, with a total area of 10,991 square kilometers. Its geographic coordinates are 18.1096° N, 77.2975° W.
The island’s topography is diverse, ranging from lush mountain ranges to fertile plains and pristine beaches. The Blue Mountains, Jamaica’s highest peak, reach an elevation of 2,256 meters, offering stunning views and unique biodiversity. The island’s coastline is characterized by numerous bays, inlets, and cays, providing ample opportunities for tourism and marine activities.
Strategic Location:
Jamaica’s location at the crossroads of the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea has made it a significant maritime hub throughout history. Its proximity to major shipping routes and its deep-water harbors have attracted traders and explorers for centuries. This strategic positioning has also influenced its cultural diversity, as various groups have interacted and settled on the island over time.
Climate and Weather:
Jamaica enjoys a tropical climate with warm temperatures year-round. The island experiences a distinct wet season from May to November and a dry season from December to April. The average temperature ranges from 24°C to 30°C, with occasional variations depending on altitude and location.
The island’s climate is influenced by trade winds, which bring moisture from the Atlantic Ocean. These winds also play a crucial role in shaping the island’s vegetation and wildlife.
Natural Resources:
Jamaica is endowed with a rich array of natural resources, including fertile land, mineral deposits, and abundant marine life. The island’s soil is particularly suitable for agriculture, leading to the production of various crops, such as sugar cane, coffee, bananas, and citrus fruits.
The island also possesses significant mineral reserves, including bauxite, which is the primary source of aluminum. Jamaica is one of the world’s leading producers of bauxite, contributing significantly to its economy.
Economic Significance:
Jamaica’s strategic location, natural resources, and cultural heritage have played a pivotal role in its economic development. The island’s economy is largely driven by tourism, agriculture, and mining.
Tourism is a major contributor to Jamaica’s GDP, with the island attracting millions of visitors annually. The island’s pristine beaches, vibrant culture, and diverse attractions make it a popular destination for travelers from around the world.
Agriculture remains an important sector, providing employment and contributing to food security. The island’s fertile land allows for the production of various crops, both for domestic consumption and export.
Mining, particularly bauxite extraction, is another key industry in Jamaica. The island’s abundant bauxite deposits have made it a leading exporter of this mineral, contributing significantly to its foreign exchange earnings.
Cultural Significance:
Jamaica’s unique cultural heritage is a product of its historical interactions and geographical location. The island’s diverse population, composed of indigenous Arawak people, European colonists, African slaves, and other immigrants, has created a rich tapestry of traditions, music, and language.
Jamaica is renowned for its vibrant music scene, with genres like reggae, ska, and dancehall gaining global recognition. The island’s cuisine is equally diverse, blending indigenous ingredients with African, European, and Asian influences.
International Relations:
Jamaica’s strategic location has also influenced its international relations. The island is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the United Nations. It maintains strong diplomatic ties with numerous countries, particularly those in the Americas and Europe.
Jamaica’s location has also made it a hub for regional cooperation and diplomacy. The island has played a significant role in promoting peace and stability in the Caribbean region.
Environmental Importance:
Jamaica’s geographical positioning and its rich biodiversity make it an important ecological region. The island’s diverse ecosystems, including its coral reefs, mangrove forests, and rainforests, provide habitat for a wide range of species.
However, Jamaica’s environment faces various challenges, including climate change, deforestation, and pollution. The island is vulnerable to the effects of sea-level rise and extreme weather events.
Conclusion:
Jamaica’s geographical positioning, at the crossroads of the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, has shaped its history, culture, and economy. Its strategic location, natural resources, and vibrant culture have made it a significant player on the global stage. Understanding Jamaica’s geographical context is essential for appreciating its unique characteristics and its contributions to the world.
FAQs about Jamaica’s Geographical Location:
Q1: What are the major geographical features of Jamaica?
A: Jamaica is characterized by its diverse topography, including lush mountain ranges, fertile plains, and pristine beaches. The Blue Mountains, its highest peak, reach an elevation of 2,256 meters. The island’s coastline is marked by numerous bays, inlets, and cays.
Q2: What is the climate like in Jamaica?
A: Jamaica enjoys a tropical climate with warm temperatures year-round. The island experiences a distinct wet season from May to November and a dry season from December to April. The average temperature ranges from 24°C to 30°C.
Q3: What are the main natural resources of Jamaica?
A: Jamaica possesses a rich array of natural resources, including fertile land, mineral deposits, and abundant marine life. Its soil is suitable for agriculture, and the island is a significant producer of bauxite, the primary source of aluminum.
Q4: How has Jamaica’s location influenced its economic development?
A: Jamaica’s strategic location has made it a maritime hub, attracting traders and explorers. Its natural resources and cultural heritage have contributed to its economy, with tourism, agriculture, and mining playing key roles.
Q5: What is the cultural significance of Jamaica’s geographical location?
A: Jamaica’s location at the crossroads of the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea has facilitated interactions between various cultures, resulting in its diverse population and rich cultural heritage.
Q6: How does Jamaica’s location impact its international relations?
A: Jamaica’s strategic location has made it a hub for regional cooperation and diplomacy. The island maintains strong diplomatic ties with numerous countries and plays a significant role in promoting peace and stability in the Caribbean.
Q7: What are the environmental challenges facing Jamaica?
A: Jamaica’s environment faces challenges like climate change, deforestation, and pollution. The island is vulnerable to the effects of sea-level rise and extreme weather events.
Tips for Exploring Jamaica’s Geographical Location:
1. Visit the Blue Mountains: Explore Jamaica’s highest peak and witness breathtaking views of the island’s diverse landscape.
2. Discover the island’s coastline: Explore Jamaica’s numerous bays, inlets, and cays, enjoying pristine beaches and marine activities.
3. Learn about the island’s history: Visit historical sites and museums to understand Jamaica’s rich past and its cultural heritage.
4. Experience Jamaican culture: Immerse yourself in the island’s vibrant music scene, taste its diverse cuisine, and witness its traditions.
5. Explore the island’s natural resources: Visit agricultural farms, bauxite mines, and marine reserves to understand Jamaica’s economic and environmental significance.
6. Engage in eco-tourism: Participate in sustainable tourism activities that support the preservation of Jamaica’s unique ecosystems.
7. Learn about the island’s environmental challenges: Be aware of the threats facing Jamaica’s environment and support efforts to protect its natural resources.
Conclusion:
Jamaica’s geographical positioning, at the heart of the Caribbean Sea, has played a crucial role in shaping its identity. Its strategic location, diverse landscape, and vibrant culture have made it a captivating island nation with a rich history and a promising future. Understanding Jamaica’s geographical context provides valuable insights into its unique characteristics and its contributions to the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Jamaica’s Geographical Positioning: A Caribbean Jewel. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!