Greenbelts: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development
Related Articles: Greenbelts: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Greenbelts: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Greenbelts: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development

Greenbelts, often referred to as green spaces, are designated areas of land that are protected from urban development. They serve as a critical buffer between urban areas and the surrounding countryside, offering a multitude of ecological, social, and economic benefits. This article delves into the concept of greenbelts, exploring their significance in contemporary urban planning, highlighting their multifaceted advantages, and addressing common questions surrounding their implementation and maintenance.
Understanding Greenbelts: A Multifaceted Approach
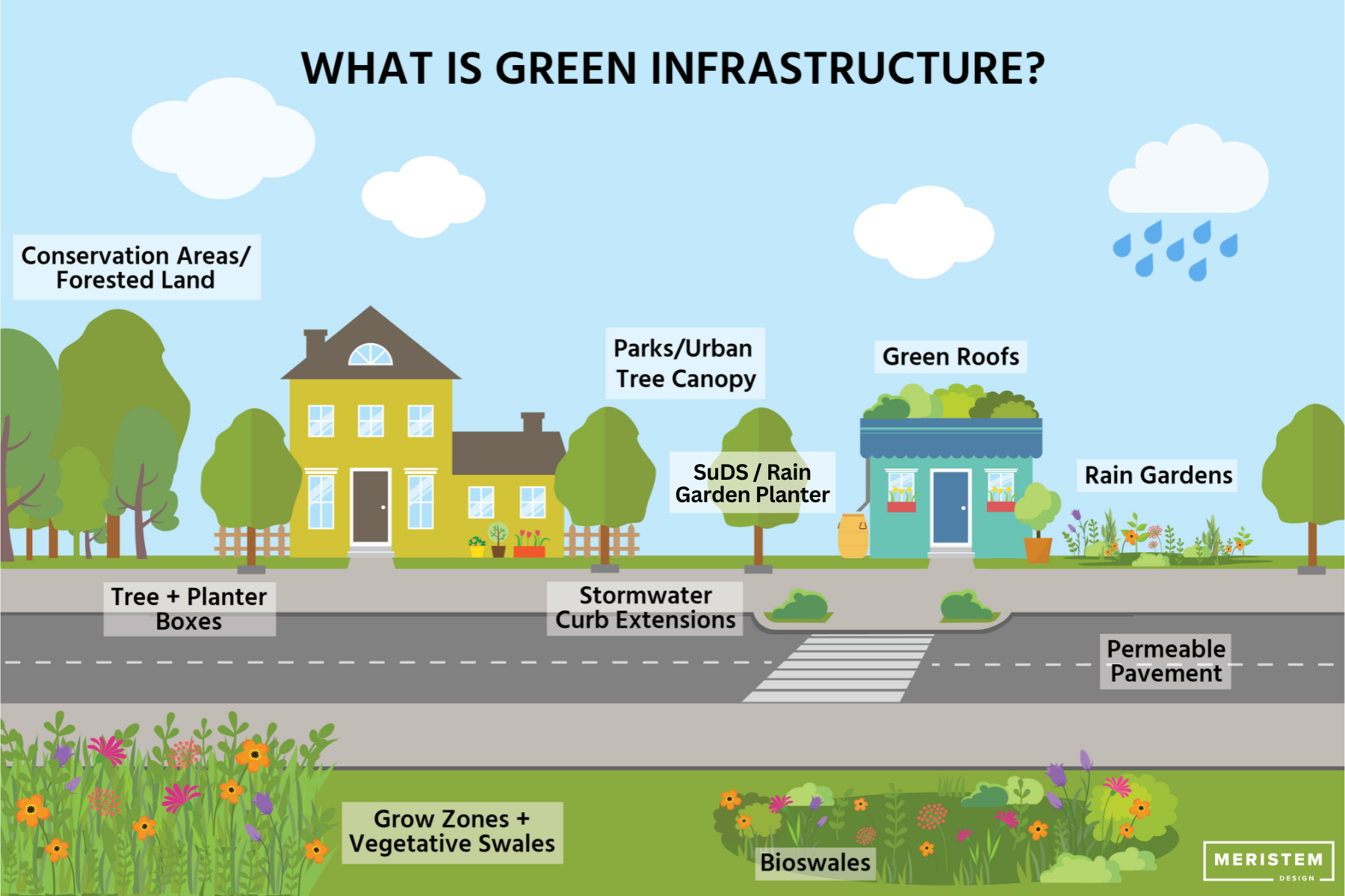
Greenbelts encompass a diverse range of landscapes, including forests, woodlands, meadows, parks, and agricultural land. These areas are typically characterized by their natural beauty, biodiversity, and recreational potential. The primary objective of greenbelt policies is to preserve these valuable natural resources while controlling urban sprawl and promoting sustainable development.
The Importance of Greenbelts: A Web of Benefits
Greenbelts play a crucial role in fostering healthy and resilient urban environments. Their benefits are multifaceted and interconnected, contributing to a holistic approach to urban planning:
1. Ecological Preservation and Biodiversity Conservation:
Greenbelts act as vital ecological corridors, connecting fragmented natural habitats and facilitating the movement of wildlife. They provide refuge for a wide range of plant and animal species, safeguarding biodiversity and promoting ecosystem services. This includes pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration, crucial for mitigating climate change.
2. Air and Water Quality Improvement:
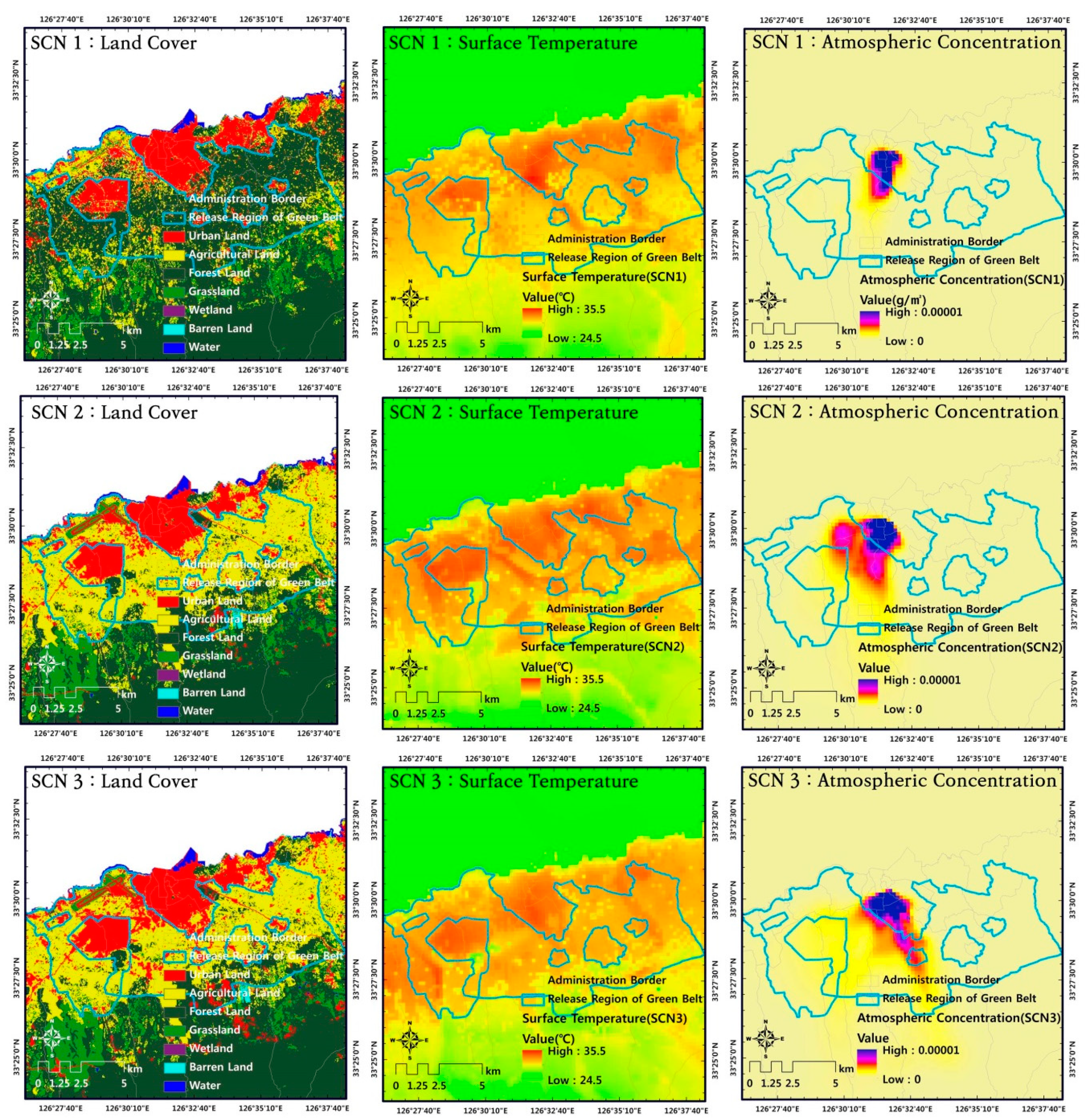
Greenbelts act as natural filters, absorbing pollutants from the air and water. Trees and vegetation within greenbelts help reduce air pollution, improve air quality, and mitigate the urban heat island effect. They also contribute to water purification by filtering runoff and preventing soil erosion, ensuring cleaner water sources for urban communities.
3. Recreation and Leisure:
Greenbelts offer valuable recreational opportunities for urban residents. They provide spaces for hiking, biking, picnicking, and other outdoor activities, promoting physical and mental well-being. This access to nature is particularly important for urban dwellers, who may have limited access to green spaces in their immediate surroundings.
4. Flood Prevention and Mitigation:
Greenbelts act as natural sponges, absorbing excess rainwater and reducing the risk of flooding. They help regulate water flow, preventing rapid runoff and erosion, and minimizing damage to urban infrastructure.
5. Economic Benefits:
Greenbelts contribute to the economic vitality of urban areas. They enhance property values, attract tourism, and create jobs in sectors like agriculture, forestry, and recreation. They also support local economies by providing fresh produce and other agricultural products.
6. Public Health and Wellbeing:
Greenbelts promote physical and mental health by providing opportunities for exercise, relaxation, and stress reduction. They also contribute to a sense of community by providing spaces for social interaction and fostering a connection with nature.
7. Sustainable Urban Development:
Greenbelts are essential for managing urban sprawl and promoting sustainable development. They act as a barrier to uncontrolled expansion, preventing the loss of valuable agricultural land and natural habitats. They also encourage more compact and efficient urban development, reducing reliance on cars and promoting sustainable transportation options.
Addressing Common Questions: A Clear Perspective
1. How are greenbelts established and managed?
Greenbelt policies are typically implemented through legislation and planning regulations. These measures may include land acquisition, zoning restrictions, and development controls. The management of greenbelts often involves collaboration between government agencies, local communities, and non-profit organizations.
2. What are the challenges associated with greenbelt management?
Challenges to greenbelt management include:
- Pressure from development: Urban sprawl and increasing demand for land can put pressure on greenbelt boundaries.
- Funding constraints: Maintaining greenbelts requires significant financial resources for land acquisition, infrastructure development, and ongoing management.
- Public perception: Some communities may perceive greenbelts as restrictive or limiting economic opportunities.
3. How can greenbelts be made more accessible and inclusive?
Greenbelts should be designed with accessibility in mind, providing pathways and amenities for people with disabilities. They should also be located within close proximity to urban communities, ensuring that all residents have equal access to their benefits.
4. What are the future trends in greenbelt planning?
Future trends in greenbelt planning include:
- Integration with urban infrastructure: Greenbelts are increasingly being integrated with urban infrastructure, such as transportation corridors and water management systems.
- Emphasis on ecological restoration: Efforts are being made to restore degraded greenbelt areas and enhance their ecological value.
- Community engagement: Greenbelt planning is increasingly involving community members in decision-making processes, ensuring that their needs and priorities are considered.
Tips for Successful Greenbelt Implementation:
- Strong political commitment: Greenbelt policies require strong political commitment to ensure their long-term sustainability.
- Comprehensive planning: Greenbelt plans should be comprehensive and address a range of issues, including land acquisition, infrastructure development, and community engagement.
- Effective management: Greenbelts require effective management to ensure their ecological integrity and recreational value.
- Public education and outreach: Public education and outreach are essential for building support for greenbelt policies and promoting their benefits.
Conclusion: A Vision for Sustainable Urban Futures
Greenbelts are a cornerstone of sustainable urban development, offering a multitude of ecological, social, and economic benefits. By preserving natural landscapes, mitigating environmental challenges, and enhancing urban livability, greenbelts contribute to the creation of healthier, more resilient, and equitable urban environments. As cities continue to grow and evolve, the importance of greenbelts as vital urban frameworks will only increase. By embracing a holistic approach to greenbelt planning and management, we can ensure that these valuable natural assets continue to play a crucial role in shaping sustainable urban futures.


/466951919-58bf02c15f9b58af5caa70a6.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Greenbelts: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!