Deconstructing the Myth: A Comprehensive Look at Taste Bud Distribution on the Tongue
Related Articles: Deconstructing the Myth: A Comprehensive Look at Taste Bud Distribution on the Tongue
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deconstructing the Myth: A Comprehensive Look at Taste Bud Distribution on the Tongue. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deconstructing the Myth: A Comprehensive Look at Taste Bud Distribution on the Tongue

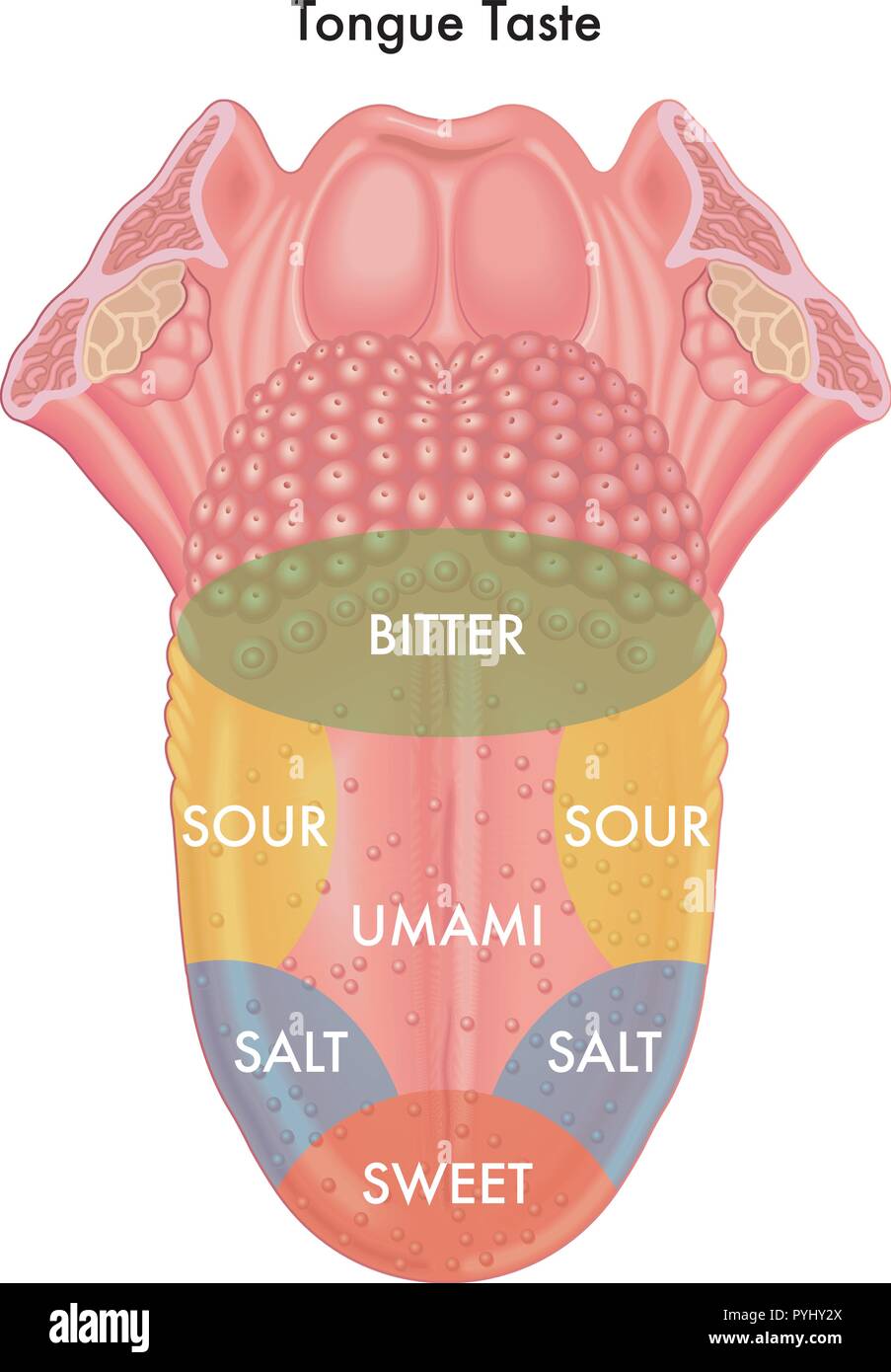
The concept of the "tongue map," illustrating distinct areas on the tongue responsible for specific tastes, has been ingrained in popular consciousness for decades. This image, often depicted in textbooks and educational materials, suggests that the tip of the tongue perceives sweetness, the sides detect saltiness, the back registers bitterness, and the middle experiences sourness. However, this widely accepted notion is a simplification of a more complex reality. While taste buds are indeed distributed across the tongue, they are not confined to specific zones dedicated to particular tastes.
This article delves into the intricacies of taste bud distribution on the tongue, debunking the myth of the tongue map and exploring the true nature of taste perception.
Beyond the Tongue Map: A Deeper Dive into Taste Bud Distribution
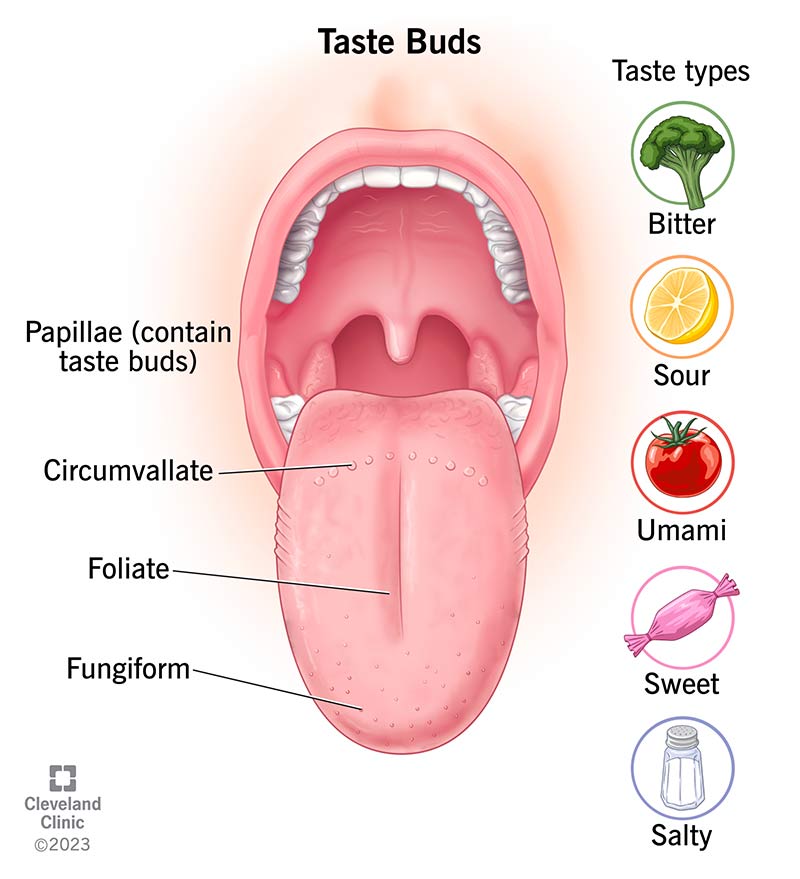
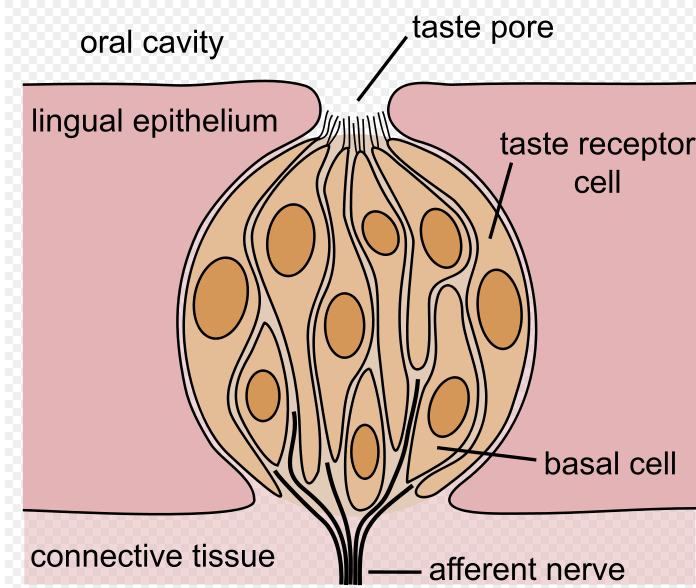
The human tongue is a complex organ, covered in tiny bumps called papillae. These papillae house taste buds, the sensory receptors responsible for detecting taste. Contrary to the tongue map, taste buds are not confined to specific regions. They are found on all areas of the tongue, albeit in varying densities.
Types of Papillae and Their Role in Taste Perception
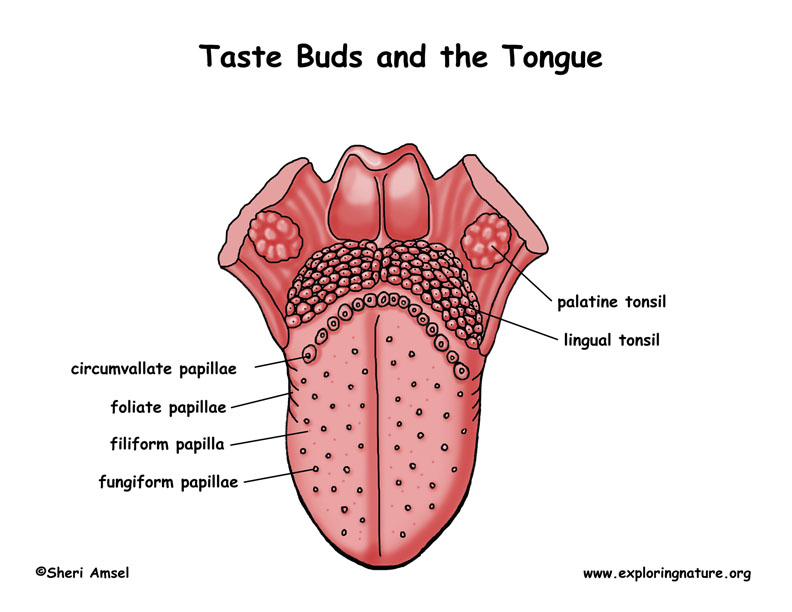
The tongue houses four primary types of papillae:
-
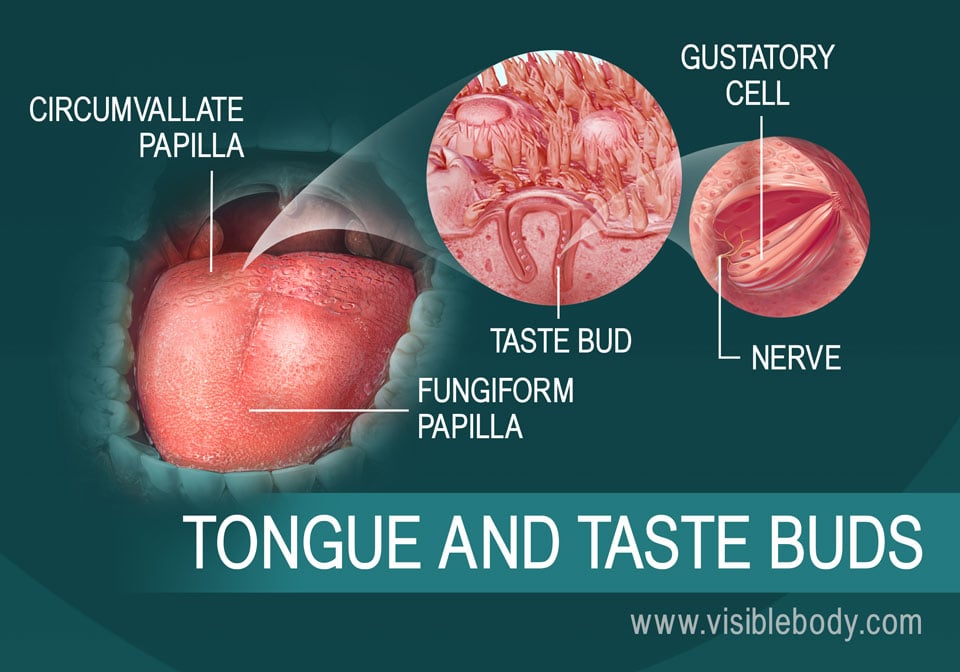
Circumvallate papillae: These large, dome-shaped structures are located at the back of the tongue, forming a V-shaped pattern. They contain the highest concentration of taste buds, contributing significantly to the overall taste experience.
-
Foliate papillae: These vertical folds are located on the sides of the tongue, particularly towards the back. They contain a smaller number of taste buds compared to circumvallate papillae and are primarily responsible for detecting bitterness.
-
Fungiform papillae: These mushroom-shaped structures are scattered across the tongue, particularly towards the tip and edges. They are less numerous than circumvallate papillae but still contribute to taste perception.
-
Filiform papillae: These cone-shaped structures are the most numerous on the tongue, covering its surface. However, they do not contain taste buds and primarily function in tactile sensation, aiding in food manipulation and texture perception.
Taste Perception: A Collaborative Effort
The perception of taste is not a solitary process confined to specific tongue regions. Instead, it is a complex interplay of various factors, including:
-
Taste bud distribution: While taste buds are present on all areas of the tongue, their density varies. The back of the tongue, with its high concentration of circumvallate papillae, is particularly sensitive to bitter tastes.
-
Neural pathways: Taste information is transmitted to the brain through specific neural pathways, which are further influenced by olfactory signals and other sensory inputs.
-
Individual variability: Taste perception can vary significantly from person to person due to genetic factors, age, and environmental influences.
The Importance of the Tongue Map Myth
While the tongue map is an inaccurate depiction of taste perception, it has played a significant role in shaping our understanding of taste. It has served as a simplified framework for teaching basic taste concepts and introducing children to the world of flavors. Additionally, it has contributed to the development of various culinary techniques, encouraging chefs to experiment with flavor combinations and manipulate taste perception through food presentation and preparation.
FAQs about Taste Bud Distribution on the Tongue
Q: If the tongue map is incorrect, how do we perceive different tastes?
A: Taste perception is a complex process involving multiple factors, including taste bud distribution, neural pathways, and individual variability. While taste buds are present on all areas of the tongue, their density varies, and different areas may be more sensitive to specific tastes.
Q: What are the implications of the tongue map myth for food science and culinary arts?
A: The tongue map myth has influenced culinary techniques and food presentation, but it is important to understand that taste perception is more complex than a simple map suggests. Chefs should focus on creating balanced flavors and appealing textures to enhance the overall dining experience.
Q: Can taste bud distribution change over time?
A: Taste bud distribution can change over time due to factors such as age, smoking, and certain medical conditions. However, the fundamental principle remains the same: taste buds are present on all areas of the tongue, albeit in varying densities.
Tips for Enhancing Taste Perception
-
Pay attention to texture: Texture plays a crucial role in taste perception. Experiment with different food textures to enhance your culinary experience.
-
Combine flavors: Explore different flavor combinations to create balanced and harmonious taste profiles.
-
Use aromatic ingredients: Utilize herbs, spices, and other aromatic ingredients to enhance the flavor of your dishes.
-
Practice mindful eating: Focus on the sensory experience of food, paying attention to taste, texture, and aroma.
Conclusion: A Holistic Perspective on Taste
The tongue map myth, despite its inaccuracies, has served as a stepping stone in our understanding of taste perception. However, it is essential to move beyond this simplified representation and embrace a more holistic perspective. Taste perception is a complex process involving multiple factors, including taste bud distribution, neural pathways, and individual variability. By recognizing the intricate nature of taste, we can appreciate the nuances of flavors and cultivate a deeper understanding of the culinary world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deconstructing the Myth: A Comprehensive Look at Taste Bud Distribution on the Tongue. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!