Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Water Hardness Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Water Hardness Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Water Hardness Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Water Hardness Maps
Water hardness, a measure of dissolved calcium and magnesium content, plays a significant role in various aspects of our lives, from household chores to industrial processes. While invisible to the naked eye, its presence or absence significantly impacts water quality and the efficiency of water-based activities. To visualize and understand the distribution of water hardness across geographic regions, water hardness maps have emerged as indispensable tools.
The Essence of Water Hardness Maps
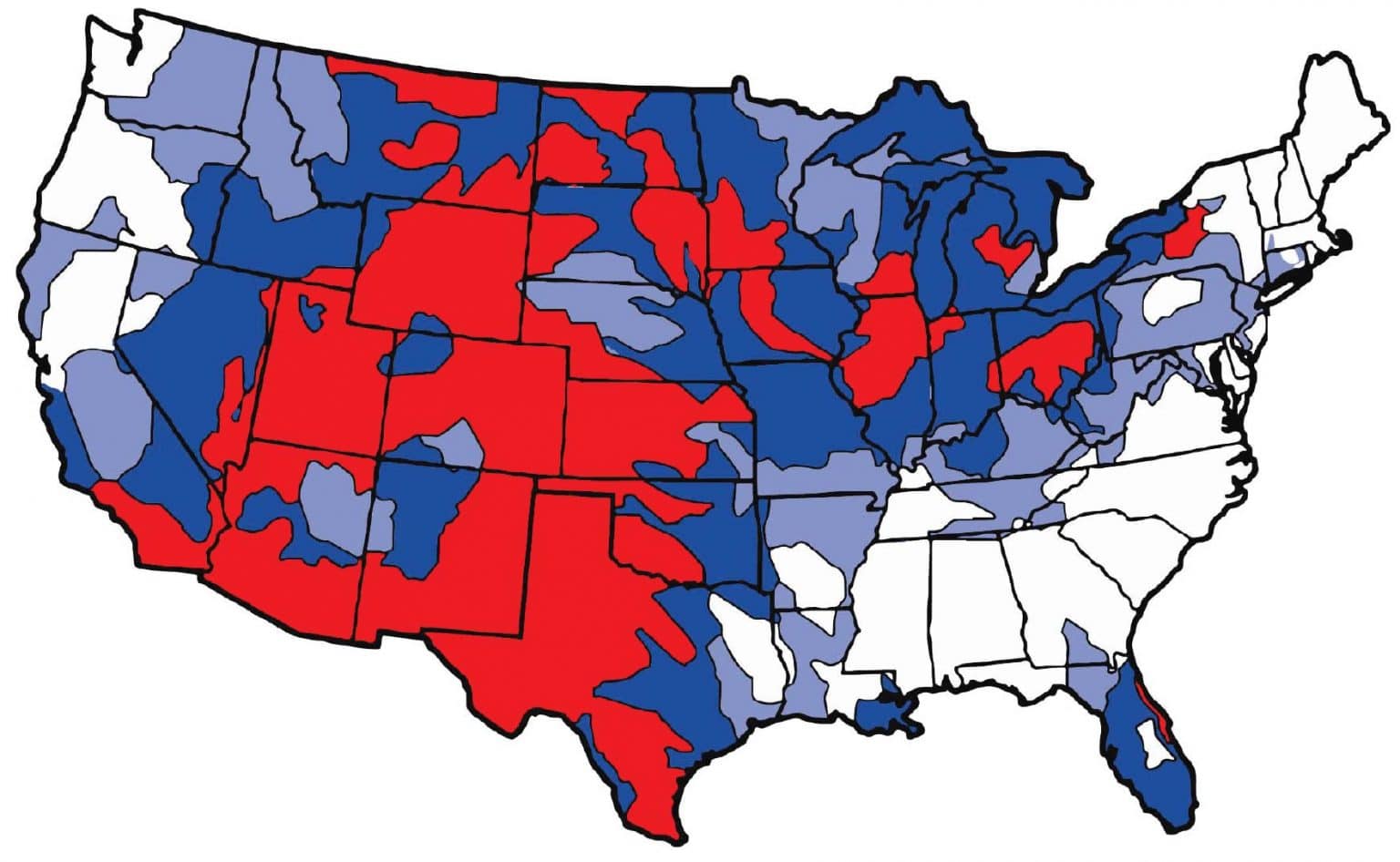
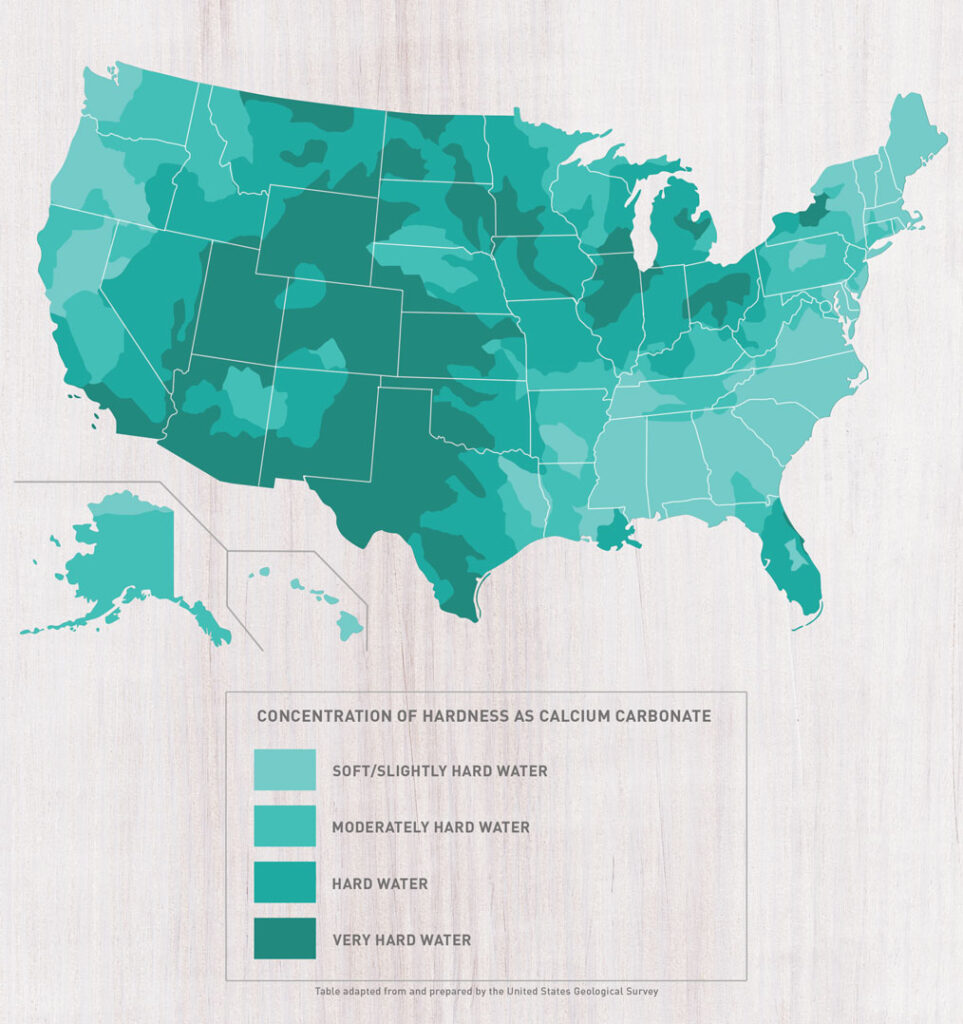
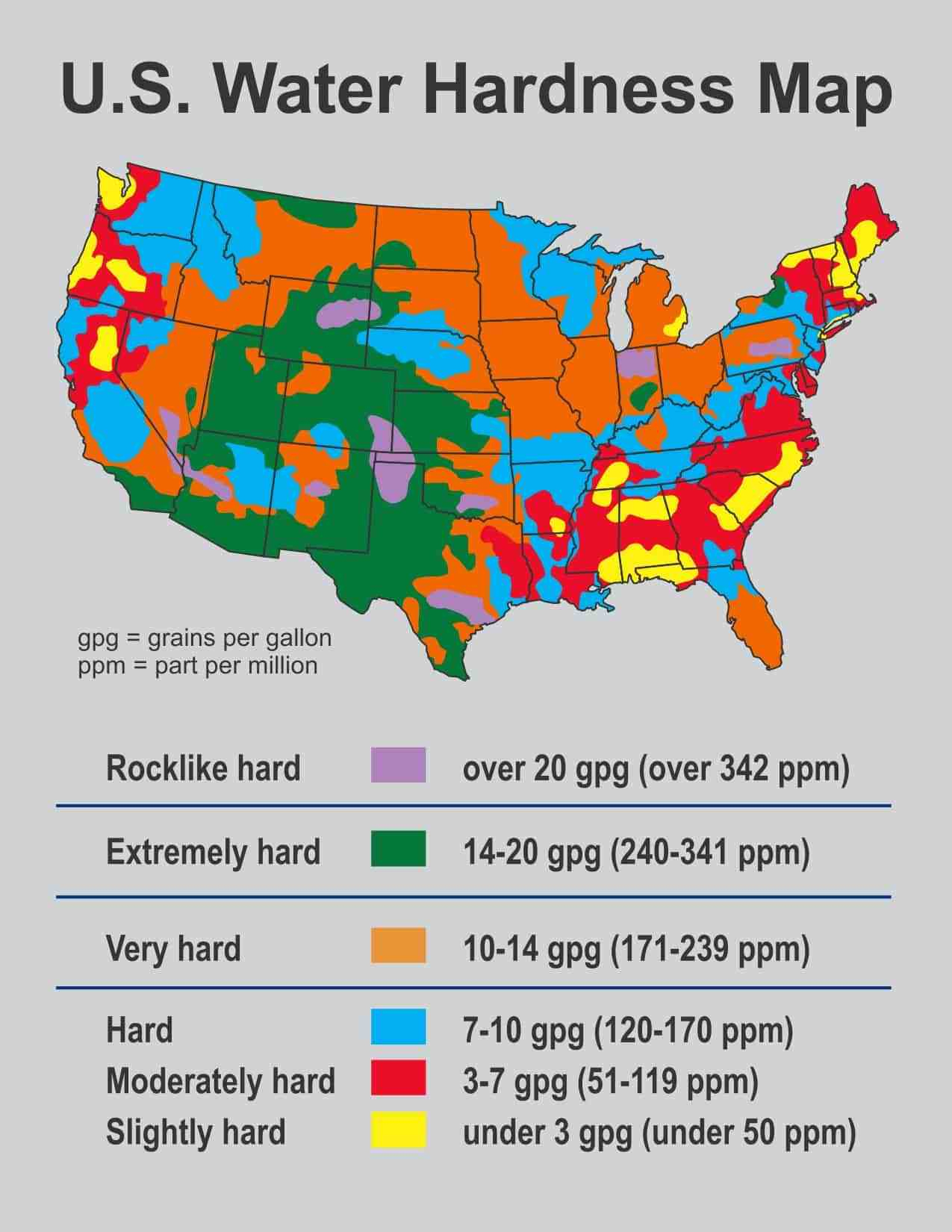
A water hardness map is a visual representation of the spatial distribution of water hardness levels in a particular area. It typically utilizes color gradients or symbols to depict varying levels of hardness, allowing for a clear and intuitive understanding of the water quality landscape. These maps can encompass various scales, from local regions to entire countries or continents, providing valuable insights into water quality trends and potential issues.
Construction and Data Sources
Water hardness maps rely on extensive data collection and analysis. The primary sources of information include:
- Water sampling and analysis: Samples are collected from various sources, such as rivers, lakes, groundwater wells, and public water supply systems. These samples undergo laboratory analysis to determine the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions.
- Geological surveys: Understanding the underlying geology of an area is crucial, as the presence of specific minerals and rock formations can influence water hardness. Geological surveys provide insights into the potential for mineral dissolution and the subsequent contribution to water hardness.
- Historical data: Existing water hardness data from previous studies and monitoring programs can be integrated to provide a comprehensive picture of long-term trends and variations.
Interpreting the Map: Unveiling Water Hardness Patterns
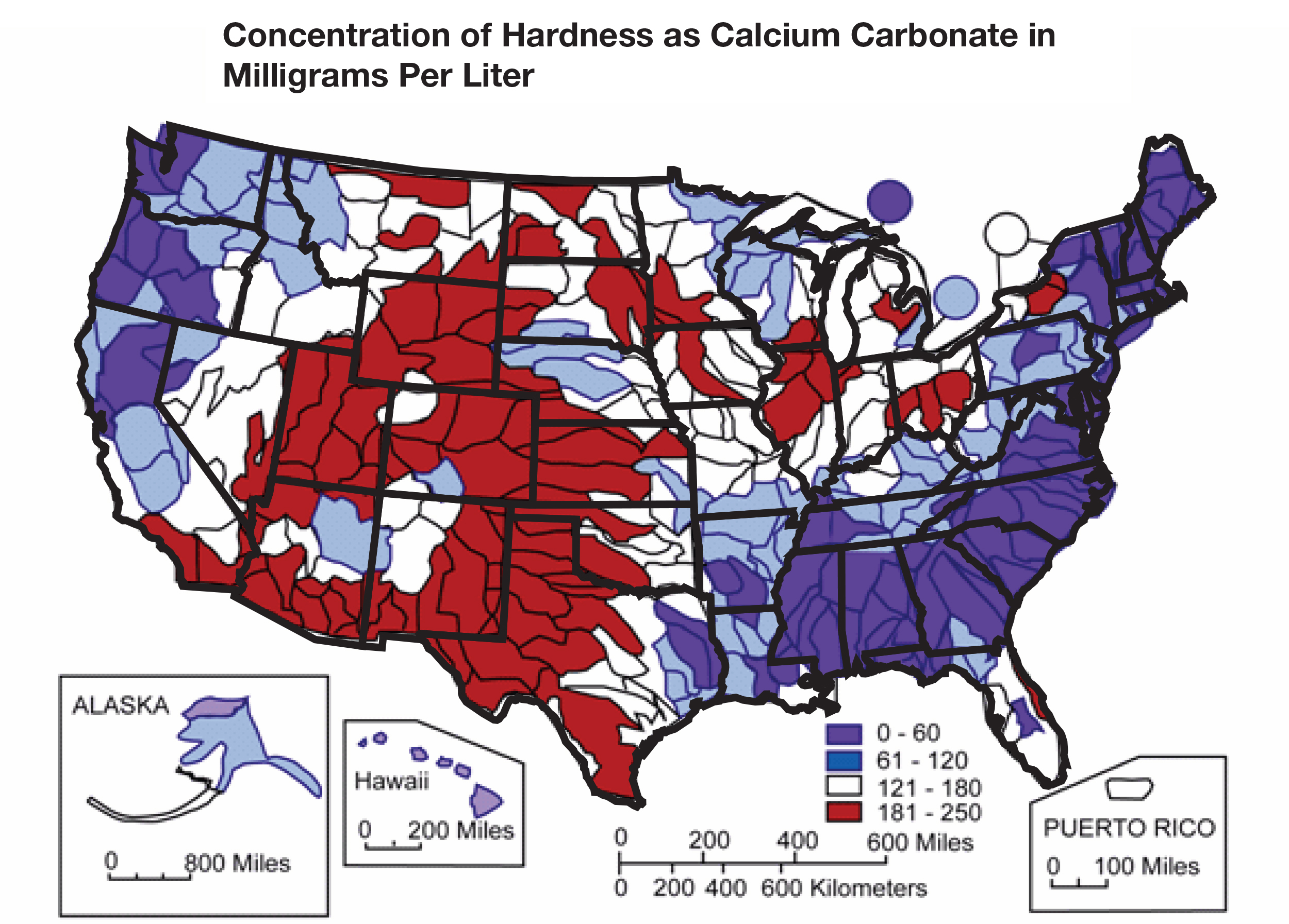
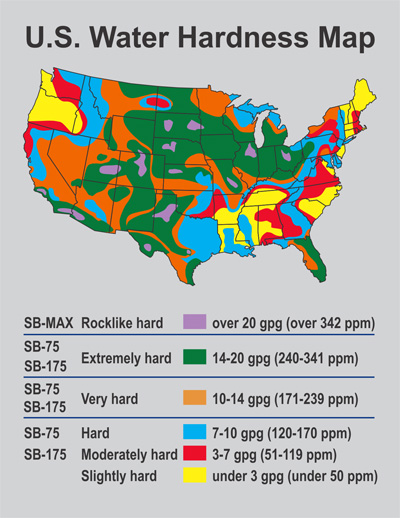
Water hardness maps offer a visual representation of water quality variations across different regions. The color gradients or symbols typically correspond to specific hardness classifications, such as:
- Soft water: Low mineral content, typically below 60 ppm (parts per million) of calcium carbonate.
- Moderately hard water: Moderate mineral content, ranging from 60 to 120 ppm.
- Hard water: High mineral content, exceeding 120 ppm.
- Very hard water: Extremely high mineral content, often above 180 ppm.
These classifications help identify areas with different water hardness levels, allowing for targeted interventions and management strategies.
Importance and Benefits of Water Hardness Maps
Water hardness maps are crucial for various stakeholders, including:
- Public health authorities: Understanding water hardness levels allows for the identification of areas prone to health risks associated with hard water, such as kidney stones, cardiovascular disease, and skin problems.
- Water treatment facilities: Maps provide valuable information for optimizing water treatment processes. Hard water requires additional treatment steps to reduce mineral content and prevent scaling and corrosion in pipes.
- Industries: Industries relying on water, such as manufacturing, agriculture, and power generation, can use water hardness maps to optimize their processes and minimize the impact of hard water on equipment and operations.
- Consumers: Individuals can utilize water hardness maps to understand the water quality in their area and make informed decisions about water softeners or other treatment options.
FAQs about Water Hardness Maps
1. What factors influence water hardness?
Water hardness is primarily influenced by the geological formations through which water flows. Rocks rich in calcium and magnesium, such as limestone and dolomite, readily dissolve and contribute to water hardness. Other factors include:
- Climate: Rainfall and temperature patterns can influence mineral dissolution and water hardness levels.
- Agricultural practices: Fertilizers and pesticides can contribute to increased mineral content in water.
- Industrial activities: Wastewater discharge from industrial processes can elevate water hardness levels.
2. What are the benefits of soft water?
Soft water offers several benefits, including:
- Improved skin and hair health: Reduced mineral content leads to softer and smoother skin and hair.
- Reduced soap consumption: Soft water requires less soap for effective cleaning, leading to cost savings.
- Reduced appliance damage: Soft water minimizes the formation of scale buildup in pipes and appliances, extending their lifespan.
- Enhanced cleaning efficiency: Soft water allows for better cleaning results, especially for laundry and dishwashing.
3. What are the drawbacks of hard water?
Hard water can have several drawbacks, including:
- Scale buildup: Calcium and magnesium minerals precipitate out of solution, forming a hard, white deposit called scale. This scale can clog pipes, reduce water flow, and damage appliances.
- Soap scum: Hard water reacts with soap to form a white, sticky residue, making it difficult to lather and clean effectively.
- Dry skin and hair: Hard water can strip natural oils from the skin and hair, leading to dryness, itchiness, and dullness.
- Increased energy consumption: Scale buildup in pipes reduces water flow, requiring more energy to heat water.
4. How can I soften hard water?
There are several methods for softening hard water, including:
- Water softeners: These devices use ion exchange resin to remove calcium and magnesium ions from water.
- Reverse osmosis: This method forces water through a semi-permeable membrane, removing minerals and impurities.
- Boiling: Boiling water can temporarily reduce hardness by precipitating out some calcium and magnesium.
Tips for Using Water Hardness Maps
- Consult with local water authorities: Contact your local water company or environmental agency for specific water hardness data and recommendations for your area.
- Consider water softening options: If your area has hard water, investigate the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of water softening systems.
- Use water-saving devices: Reduce water consumption to minimize the impact of hard water on appliances and plumbing.
- Be mindful of water usage: Avoid excessive water usage to reduce the risk of scale buildup and other problems associated with hard water.
Conclusion
Water hardness maps provide a valuable tool for understanding and managing water quality. By visualizing the spatial distribution of water hardness, these maps enable stakeholders to identify areas with potential problems, develop targeted solutions, and optimize water usage for various purposes. Whether it’s ensuring public health, protecting infrastructure, or improving household water quality, water hardness maps play a crucial role in promoting sustainable water management practices and ensuring the efficient use of this precious resource.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Water Hardness Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
